Abstract
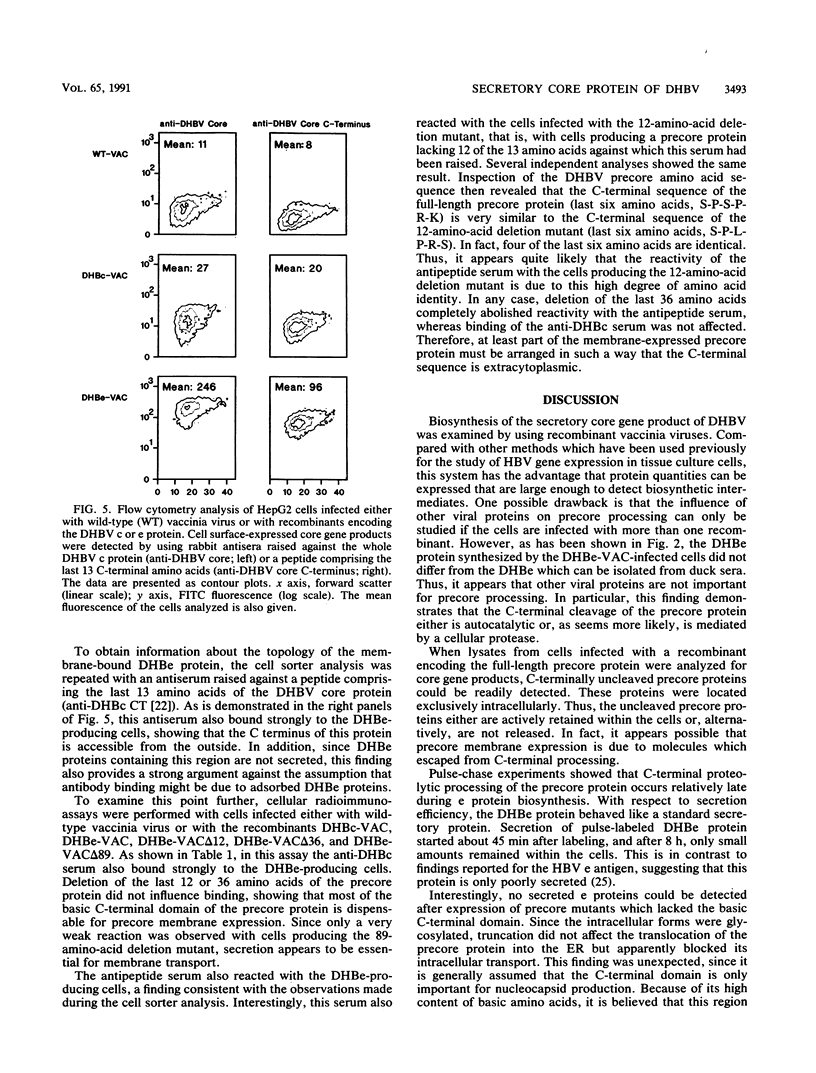
The biosynthesis of the secretory core gene product of the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBe protein) was examined. Recombinant vaccinia viruses were constructed encoding either the full-length or C-terminally truncated forms of the DHBe precursor protein (precore protein) and used to express these proteins in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Western immunoblot analysis of core gene products isolated from cells producing the full-length precore protein revealed the presence of DHBe precursor proteins containing the strongly basic C-terminal sequence which is lacking in the mature DHBe protein. These proteins were not secreted, suggesting that C-terminal proteolytic processing of the precore protein represents an obligatory step for DHBe biosynthesis. Pulse-chase experiments showed that this cleavage reaction occurs late during DHBe synthesis. Interestingly, when mutated precore proteins were expressed which lacked the basic C-terminal domain, proteins were produced which were glycosylated but not secreted. This shows that the transient presence of this region is essential for intracellular transport of the precore protein. Cell sorter analyses revealed that production of a cell surface-expressed variant of the secretory core protein is a feature conserved between the duck and the human hepatitis B viruses. Surprisingly, the C terminus of the membrane-expressed DHBe protein was accessible from the outside, showing that the topology of this interesting protein is more complicated than expected.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum F., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: primary structure requirements in the core protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3319–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3319-3330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruss V., Gerlich W. H. Formation of transmembraneous hepatitis B e-antigen by cotranslational in vitro processing of the viral precore protein. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Enders G., Sprengel R., Peters N., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Expression of the precore region of an avian hepatitis B virus is not required for viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3322–3325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3322-3325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia P. D., Ou J. H., Rutter W. J., Walter P. Targeting of the hepatitis B virus precore protein to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane: after signal peptide cleavage translocation can be aborted and the product released into the cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1093–1104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Jean O., Levrero M., Will H., Perricaudet M., Rossignol J. M. Expression mechanism of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) C gene and biosynthesis of HBe antigen. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker M., Galle P., Schaller H. Expression and replication of the hepatitis B virus genome under foreign promoter control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10117–10132. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Drillien R., Spehner D., Skory S., Schmitt D., Wiktor T., Koprowski H., Lecocq J. P. Expression of rabies virus glycoprotein from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):163–166. doi: 10.1038/312163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Espmark J. A. New specificities in Australia antigen positive sera distinct from the Le Bouvier determinants. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1017–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Jones J. E., Hughes J. L., Price J., Raney A. K., McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6599–6603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Galle P. R., Schaller H. Proteaselike sequence in hepatitis B virus core antigen is not required for e antigen generation and may not be part of an aspartic acid-type protease. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2598–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2598-2604.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus gene function: the precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Heat shock and the sorting of luminal ER proteins. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3171–3176. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus core protein contains a highly phosphorylated C terminus that is essential for replication but not for RNA packaging. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2995–3000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2995-3000.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Kuhn C., Guhr B., Mattaliano R. J., Schaller H. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the duck hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2280–2285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2280-2285.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Radziwill G., Schaller H. Synthesis and encapsidation of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase do not require formation of core-polymerase fusion proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Salfeld J., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus pre-C region encodes a signal sequence which is essential for synthesis and secretion of processed core proteins but not for virus formation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3701-3709.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Schaller H. The secretory core protein of human hepatitis B virus is expressed on the cell surface. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5399–5404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5399-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., von Brunn A., Theilmann L. Antibodies in anti-HBe-positive patient sera bind to an HBe protein expressed on the cell surface of human hepatoma cells: implications for virus clearance. Hepatology. 1991 Jan;13(1):57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Machida A., Funatsu G., Nomura M., Usuda S., Aoyagi S., Tachibana K., Miyamoto H., Imai M., Nakamura T. Immunochemical structure of hepatitis B e antigen in the serum. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2903–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]