Abstract
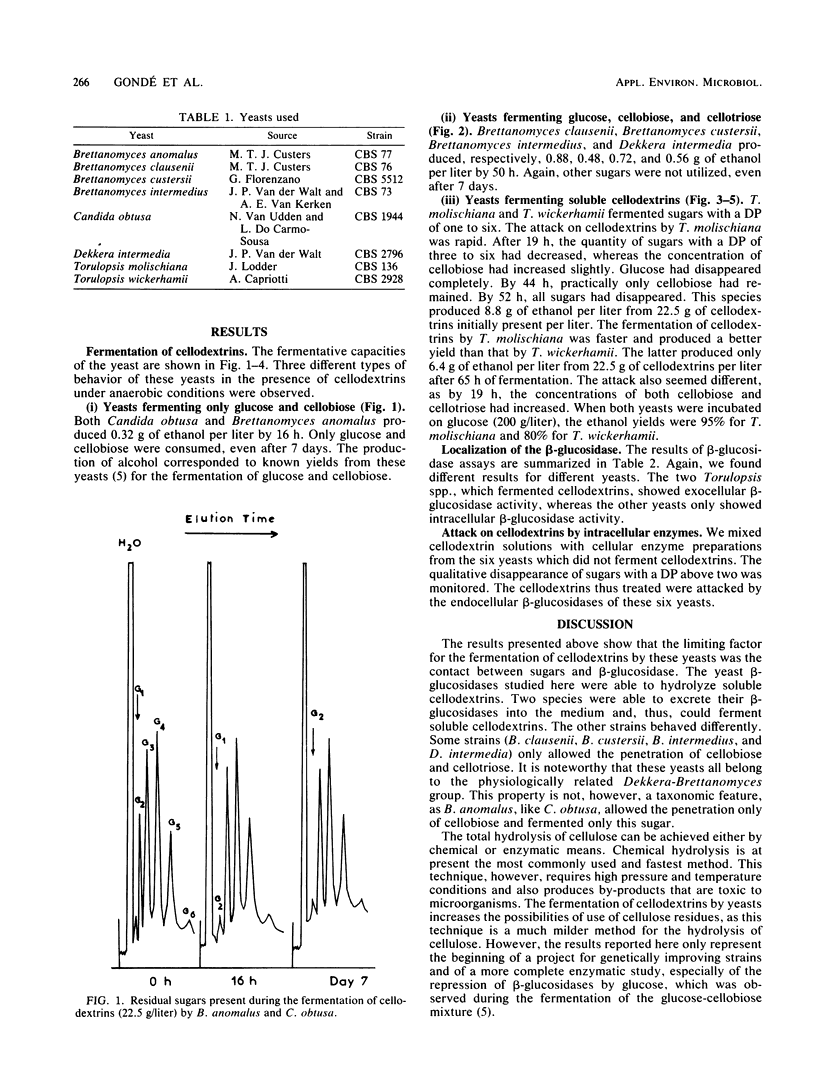
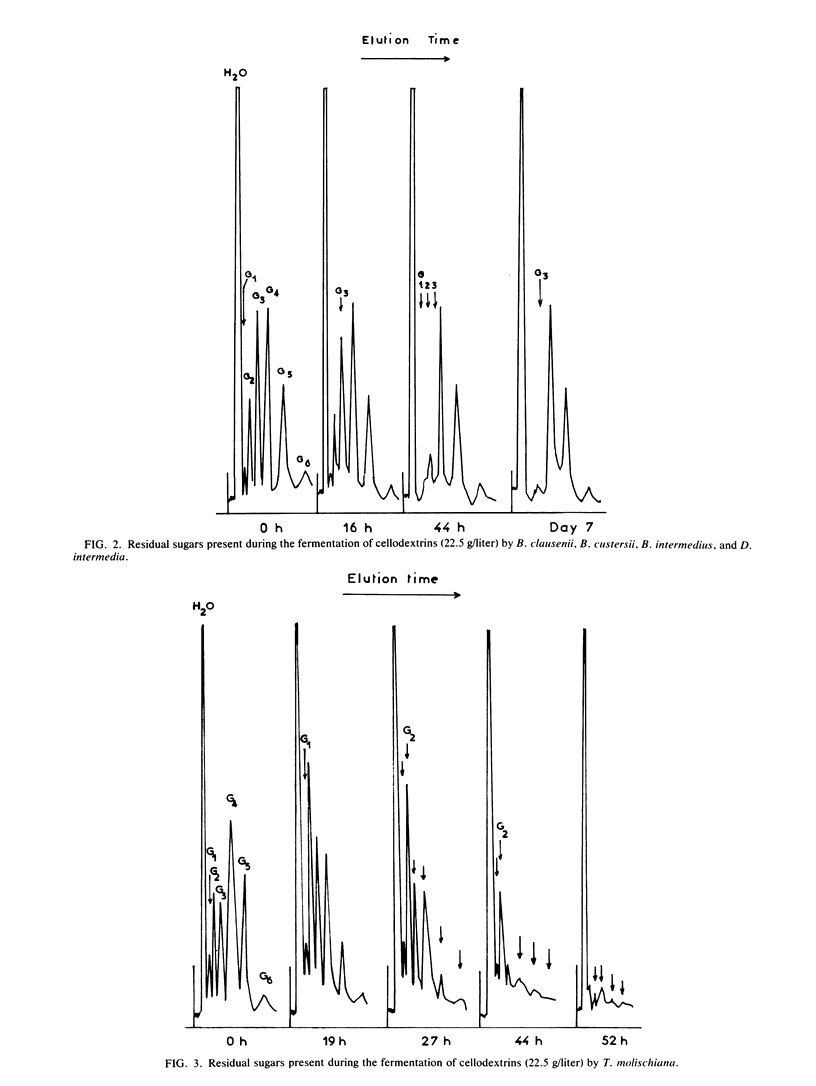
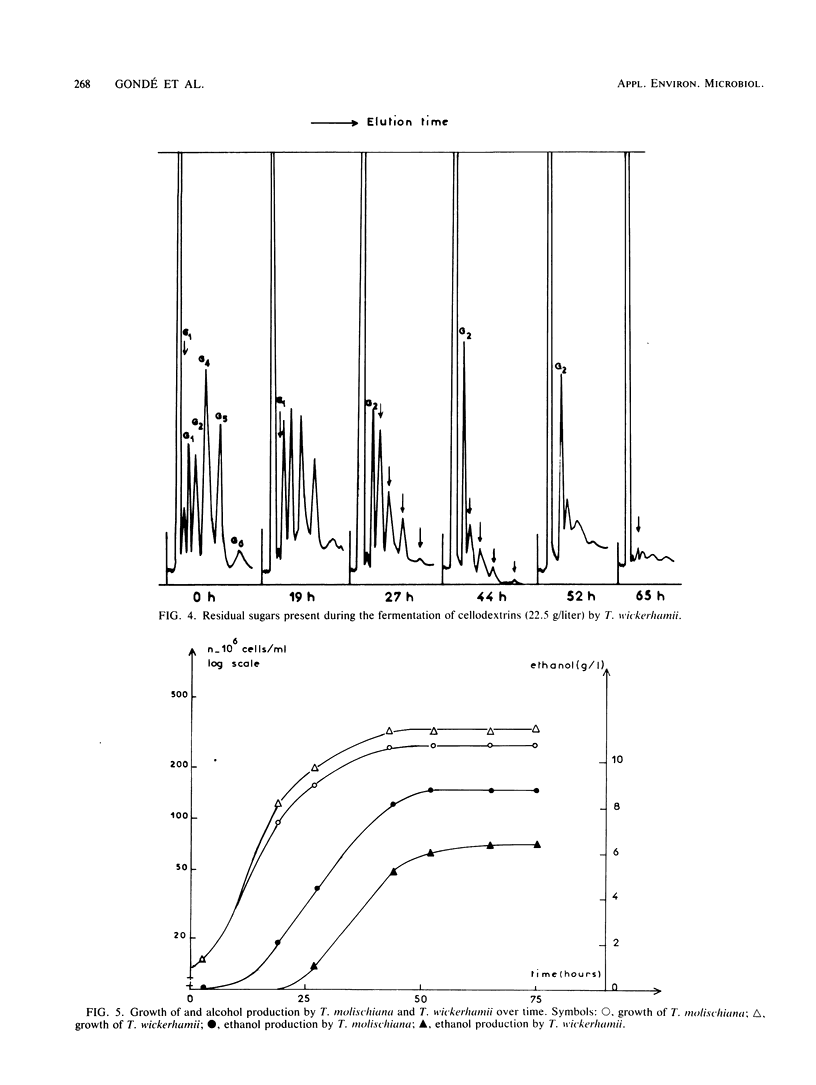
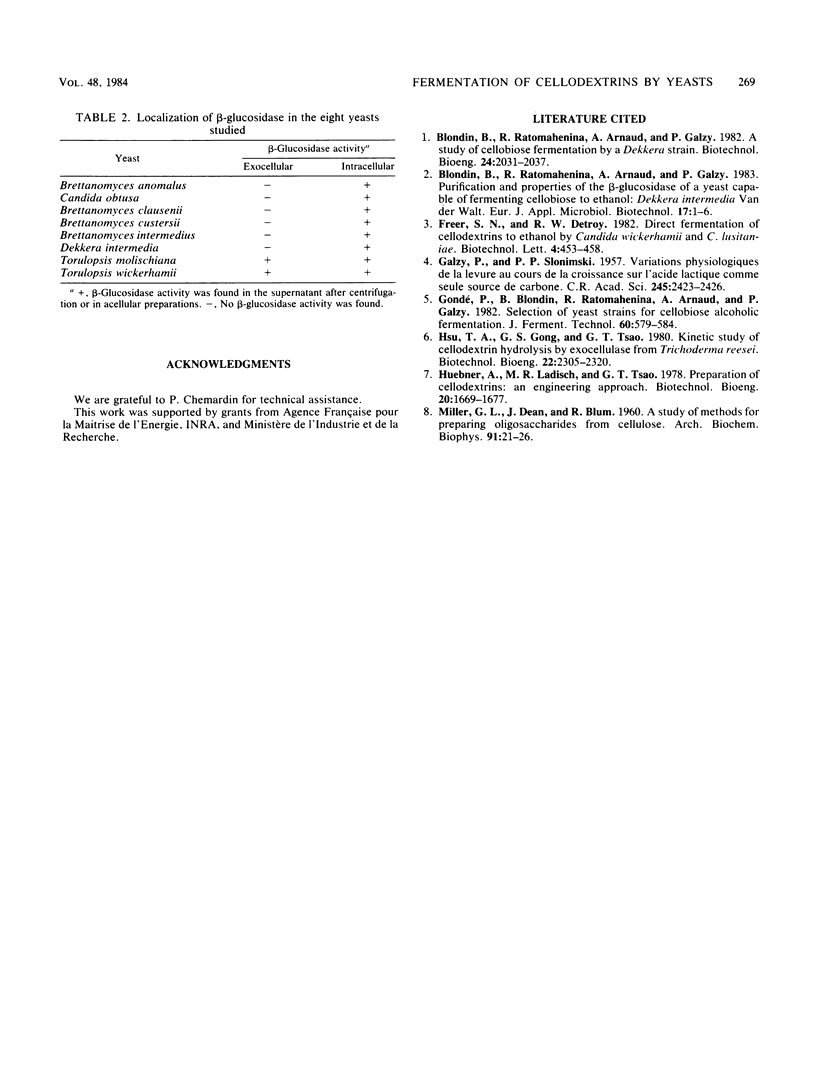
The fermentation of cellodextrins by eight yeast species capable of fermenting cellobiose was monitored. Only two of these species, Torulopsis molischiana and T. wickerhamii, were able to ferment β-glucosides with a degree of polymerization between one and six. These two species showed exocellular β-glucosidase activity. Four other species were able to ferment cellotriose, and the last two species only fermented cellobiose. These latter six species produced a β-glucosidase capable of attacking cellodextrins, but this enzyme was endocellular.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GALZY P., SLONIMSKI P. P. Variations physiologiques de la levure au cours de la croissance sur l'acide lactique comme seule source de carbone. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Dec 16;245(25):2423–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


