Abstract
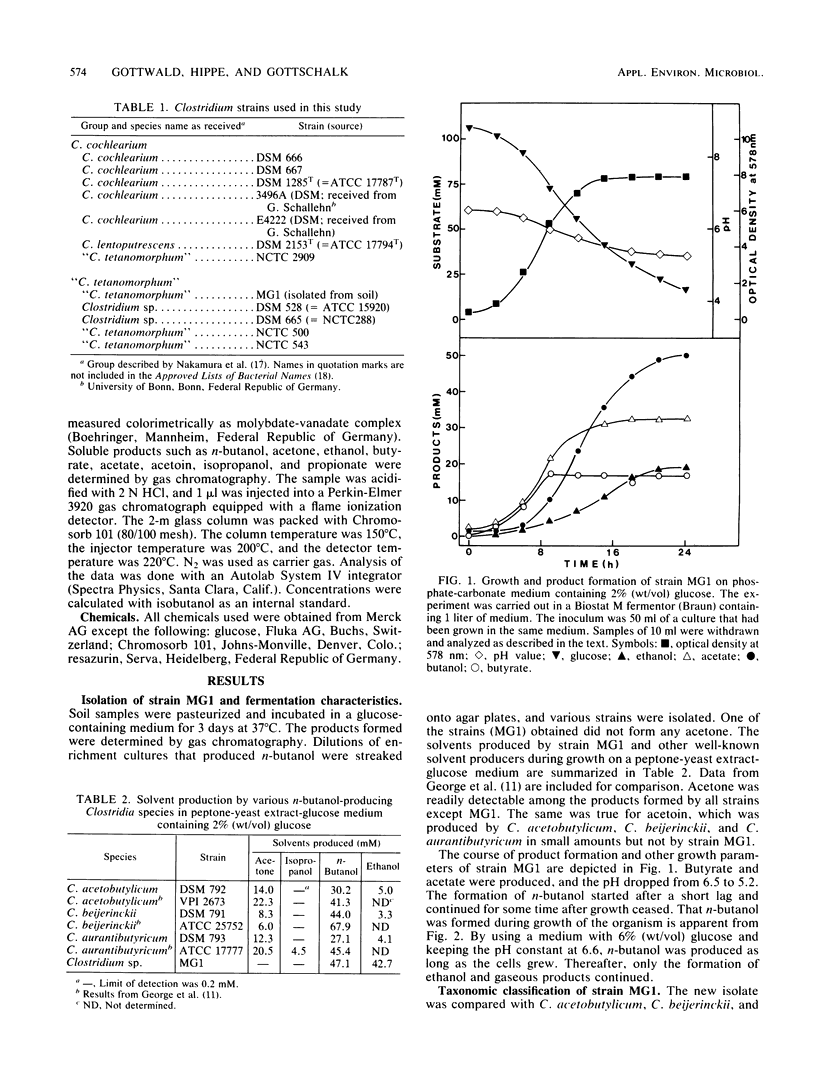
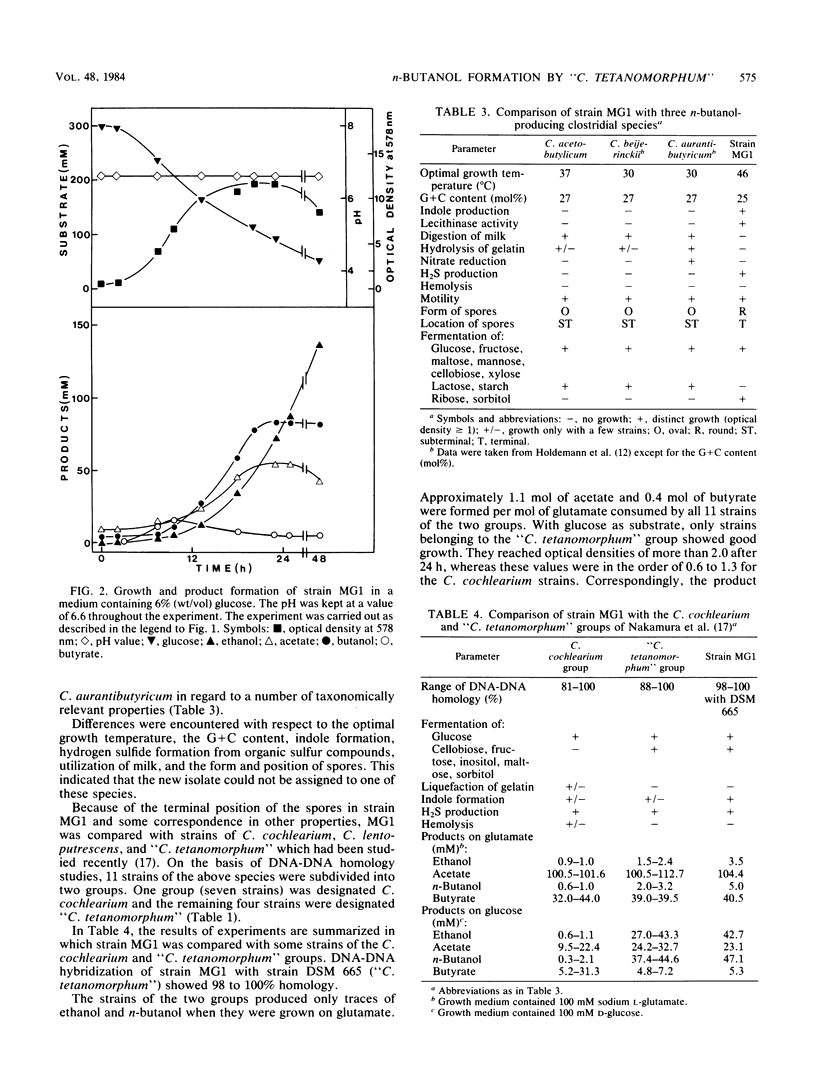
A clostridial strain has been isolated that produced n-butanol, ethanol, butyrate, and acetate as major fermentation products from glucose but no acetone. At a pH of 6.6, n-butanol was formed by this microorganism only during growth. On the basis of its physiological characteristics and DNA-DNA homology data, the strain was assigned to the “Clostridium tetanomorphum” group (S. Nakamura, I. Okado, T. Abe, and S. Nishida, J. Gen. Microbiol. 113:29-35, 1979). All members of this group were shown to produce n-butanol from glucose as the major fermentation product, whereas C. cochlearium produced it in only minor amounts.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R., Stephenson M. Studies on the acetone-butyl alcohol fermentation: Nutritional and other factors involved in the preparation of active suspensions of Cl. acetobutylicum (Weizmann). Biochem J. 1941 Dec;35(12):1320–1331. doi: 10.1042/bj0351320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J. Reexamination of the association between melting point, buoyant density, and chemical base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):738–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.738-754.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Chen J. S. Acidic Conditions Are Not Obligatory for Onset of Butanol Formation by Clostridium beijerinckii (Synonym, C. butylicum). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):321–327. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.321-327.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Johnson J. L., Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Chen J. S. Acetone, Isopropanol, and Butanol Production by Clostridium beijerinckii (syn. Clostridium butylicum) and Clostridium aurantibutyricum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1160–1163. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1160-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., van der Westhuizen A., Long S., Allcock E. R., Reid S. J., Woods D. R. Solvent Production and Morphological Changes in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1434–1439. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1434-1439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Okado I., Abe T., Nishida S. Taxonomy of Clostridium tetani and related species. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jul;113(1):29–35. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Tamai K., Nishida S. [Taxonomic studies on Clostridium tetanomorphum. 1]. Igaku To Seibutsugaku. 1967 Sep 10;75(3):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2143–2152. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


