Abstract
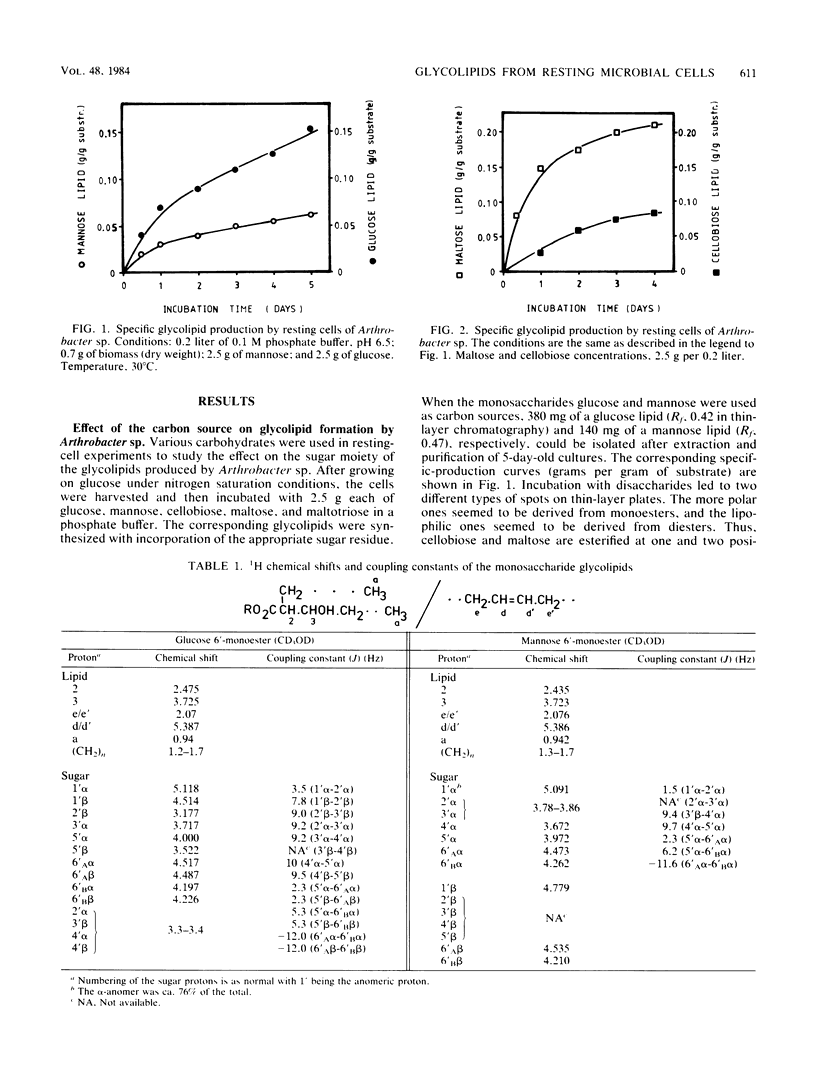
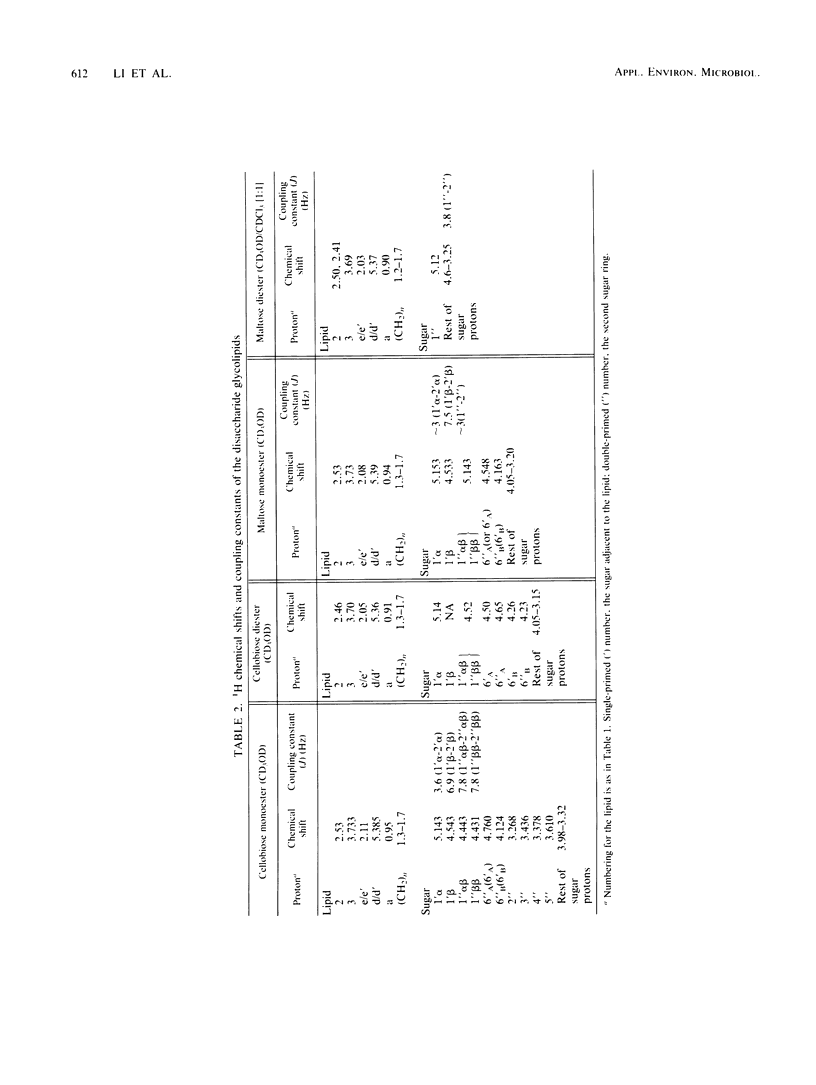
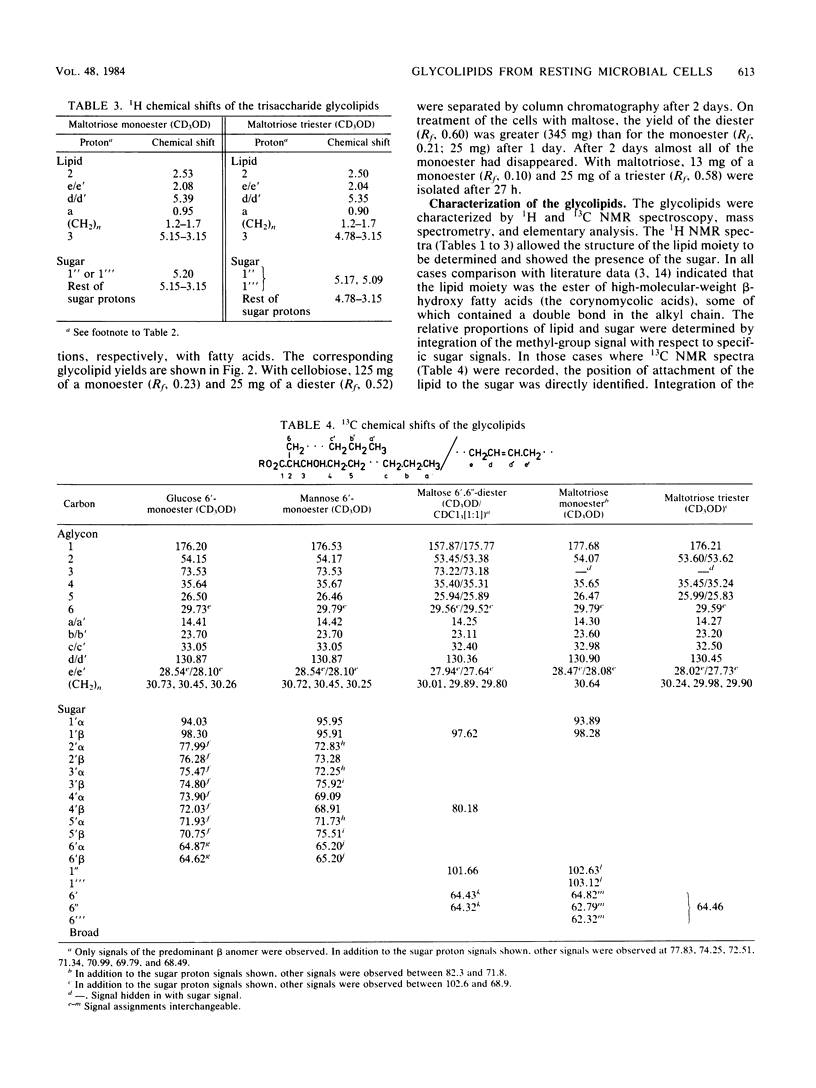
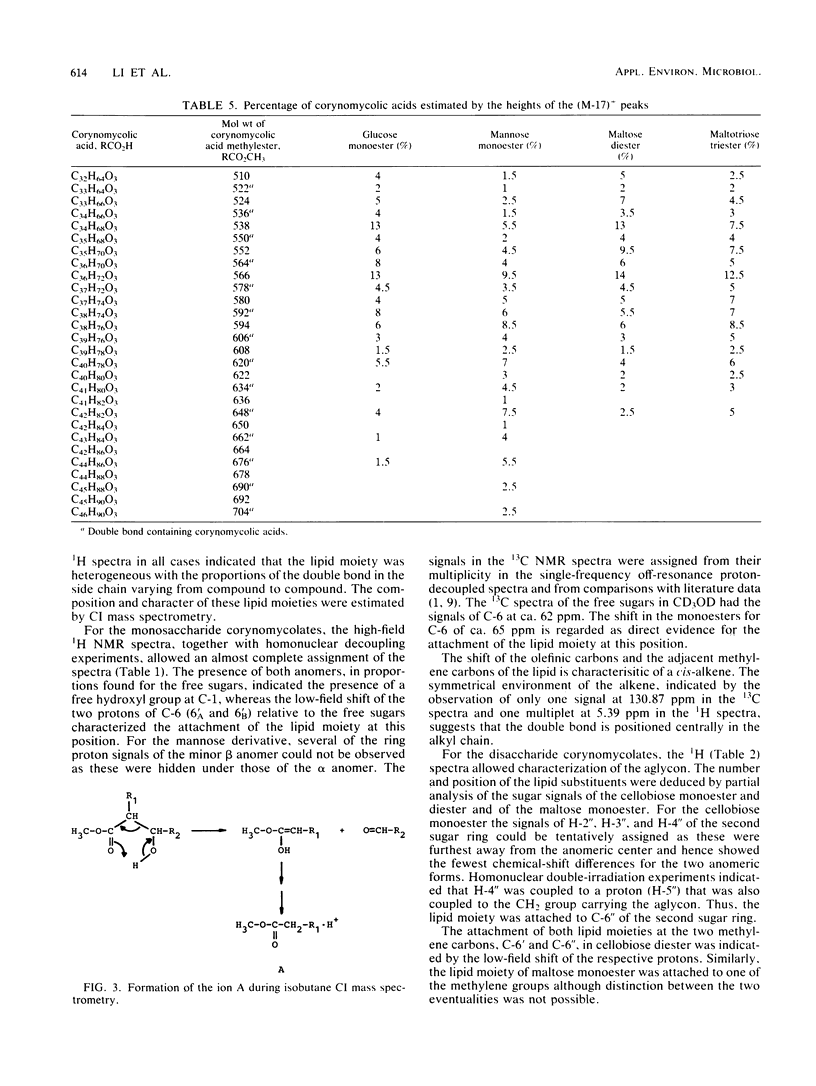
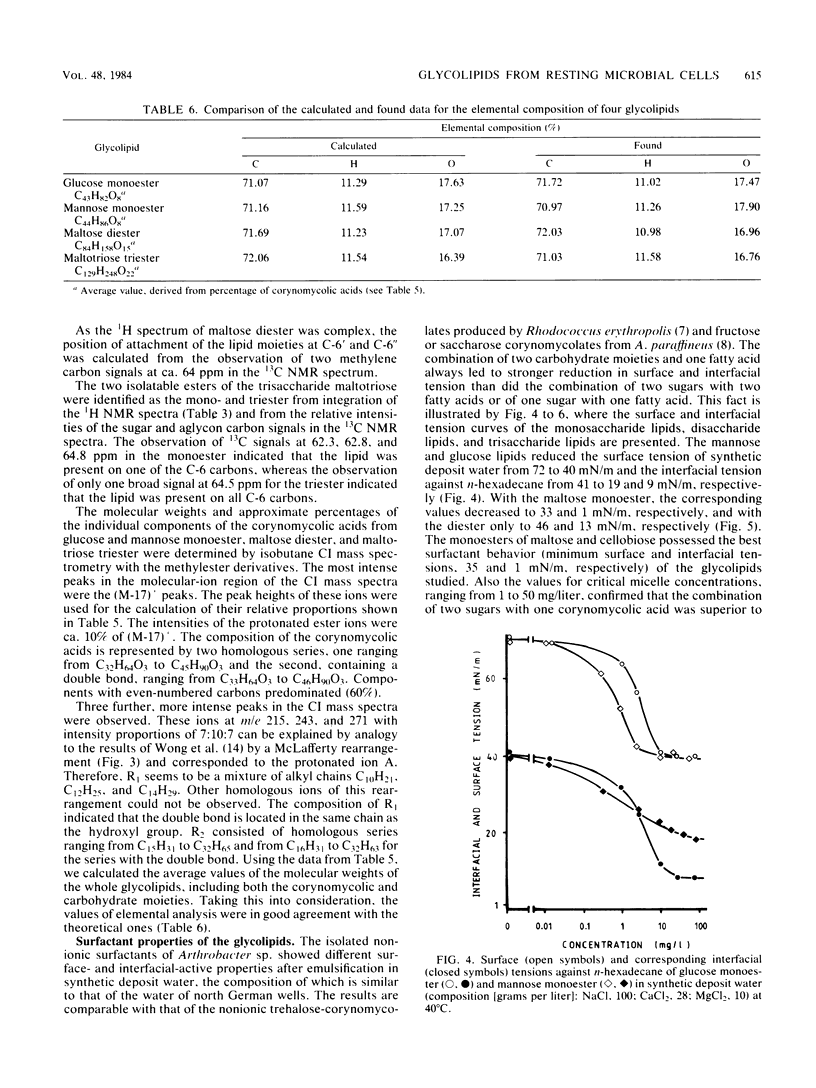
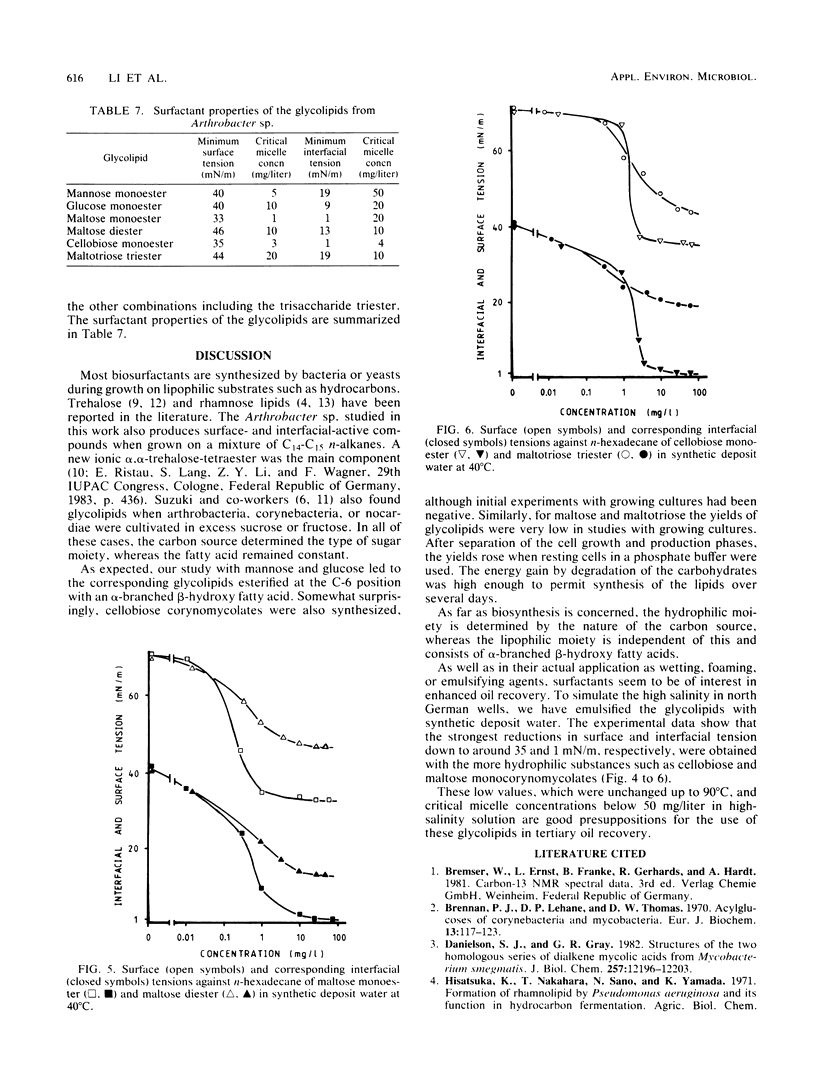
Resting cells of Arthrobacter sp. strain DSM2567 incubated in the presence of various mono-, di-, or trisaccharides biosynthesized different glycolipids. All eight glycolipids, containing the corresponding carbohydrate moiety and one, two, or three α-branched β-hydroxy fatty acids, were produced when mannose, glucose, cellobiose, maltose, and maltotriose were used as carbon sources in a simple phosphate buffer. The structures of the compounds were elucidated by means of 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and by chemical ionization mass spectroscopy. In high-salinity solution, the substances showed different surfactant properties. Cellobiose and maltose monocorynomycolates reduced the interfacial tension from 42 to 1 mN/m at critical micelle concentrations below 20 mg/liter.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brennan P. J., Lehane D. P., Thomas D. W. Acylglucoses of the corynebacteria and mycobacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):117–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson S. J., Gray G. R. Structures of the two homologous series of dialkene mycolic acids from Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12196–12203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer A., Bock H., Wagner F. Chemical and Physical Characterization of Interfacial-Active Lipids from Rhodococcus erythropolis Grown on n-Alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):864–870. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.864-870.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. Y., Steck P. A., Gray G. R. The major mycolic acids of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Characterization of their homologous series. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5734–5740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


