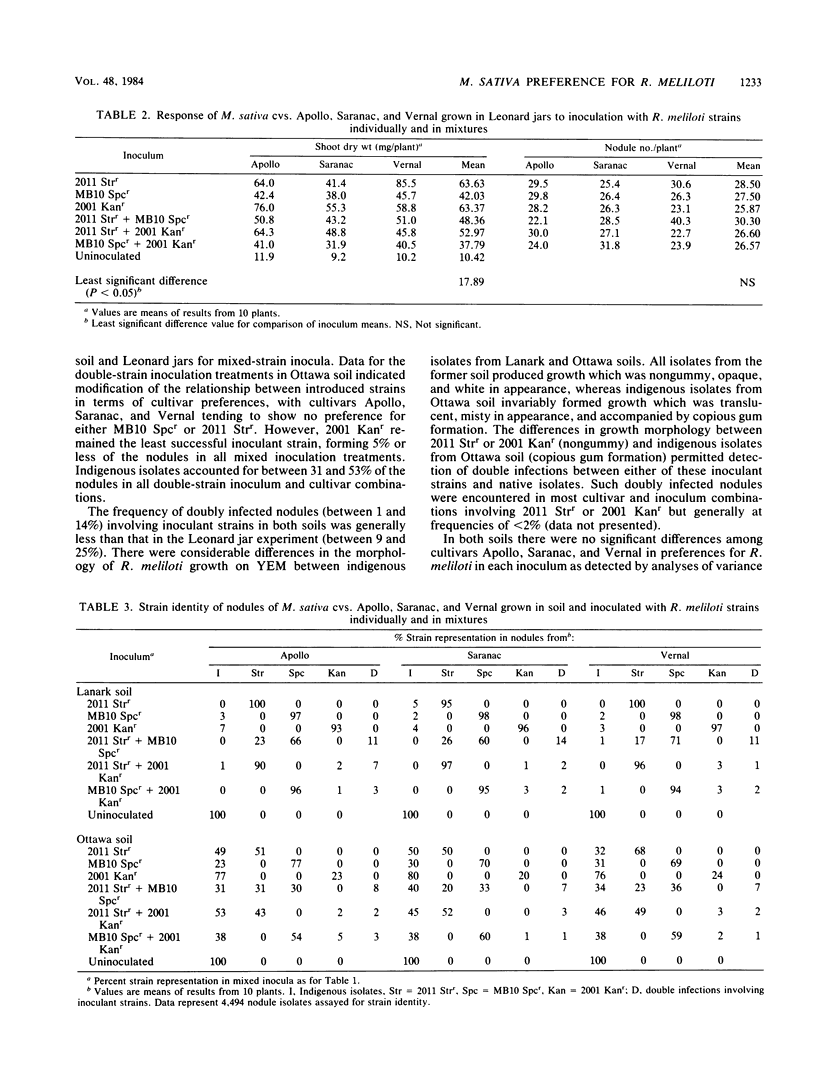
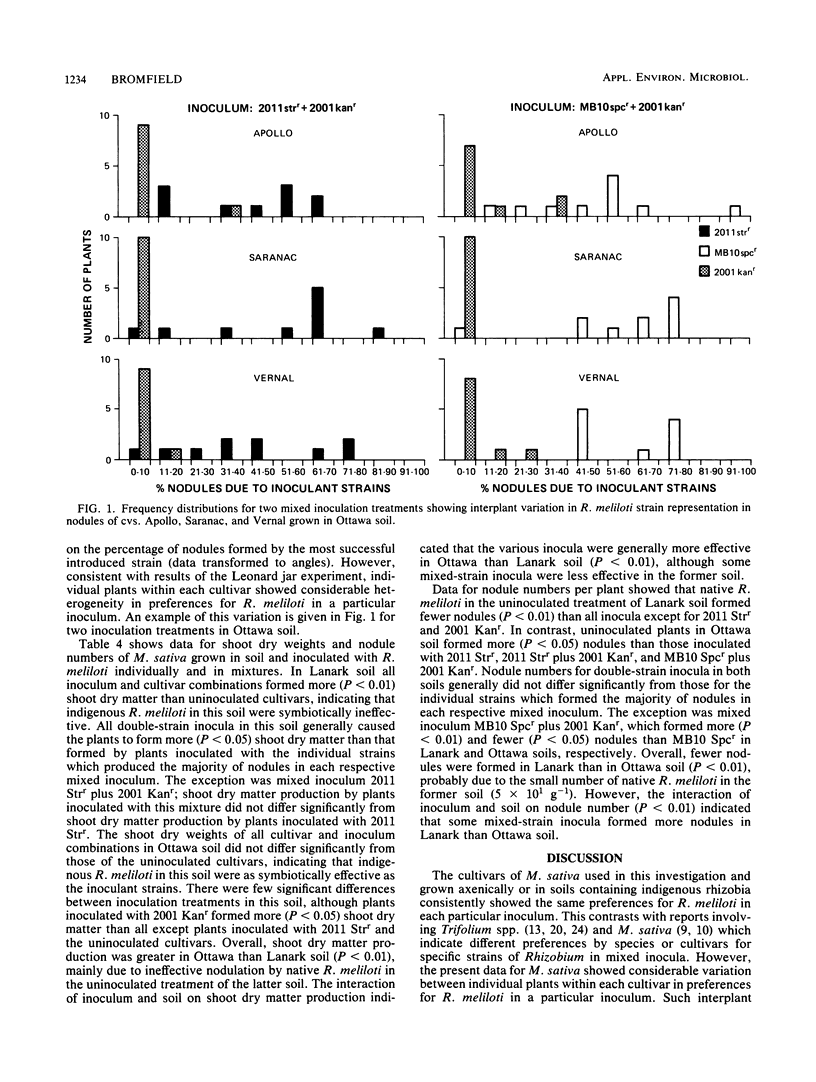
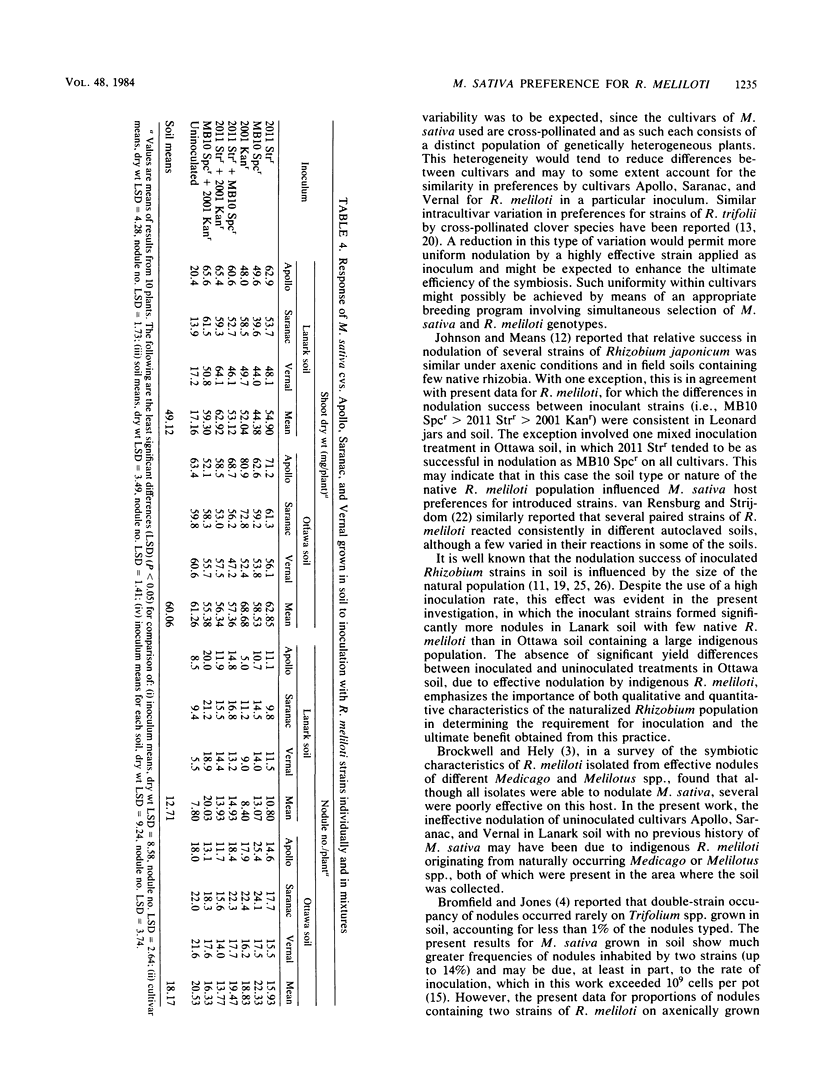
Abstract
Variation in nodulation preferences for Rhizobium strains within and between Medicago sativa cultivars was assessed in the greenhouse with plants grown in Leonard jars and two soils of diverse origin (Lanark and Ottawa), using inocula consisting of effective individual or paired strains of R. meliloti which could be recognized by high-concentration antibiotic resistance. The results indicated considerable variability in host preferences for R. meliloti among plants within cultivars but not between cultivars. The implications of this variation are discussed from the point of view of possible improvement of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. With one exception, the differences in nodulation success between inoculant R. meliloti strains were consistent in Leonard jars and both soils. All introduced strains formed significantly more nodules in Renfrew soil containing few native rhizobia than in Ottawa soil with a large resident R. meliloti population. Plants grown in Lanark soil without inoculation were ineffectively nodulated by native rhizobia and yielded significantly less growth than those receiving inoculation. In contrast, the yield of inoculated plants in Ottawa soil did not significantly differ from those without inoculation due to effective nodulation by native R. meliloti. The data indicated synergistic effects on yield by certain paired strain inocula relative to the same strains inoculated individually in Lanark but not in Ottawa soil or Leonard jars.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Schwinghamer E. A., Dudman W. F. Evaluation of spectinomycin resistance as a marker for ecological studies with Rhizobium spp. J Appl Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;36(2):263–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1973.tb04101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINCENT J. M., WATERS L. M. The influence of the host on competition amongst clover root-nodule bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):357–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rensburg H. J., Strijdom B. W. Competitive Abilities of Rhizobium meliloti Strains Considered to Have Potential as Inoculants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):98–106. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.98-106.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


