Abstract
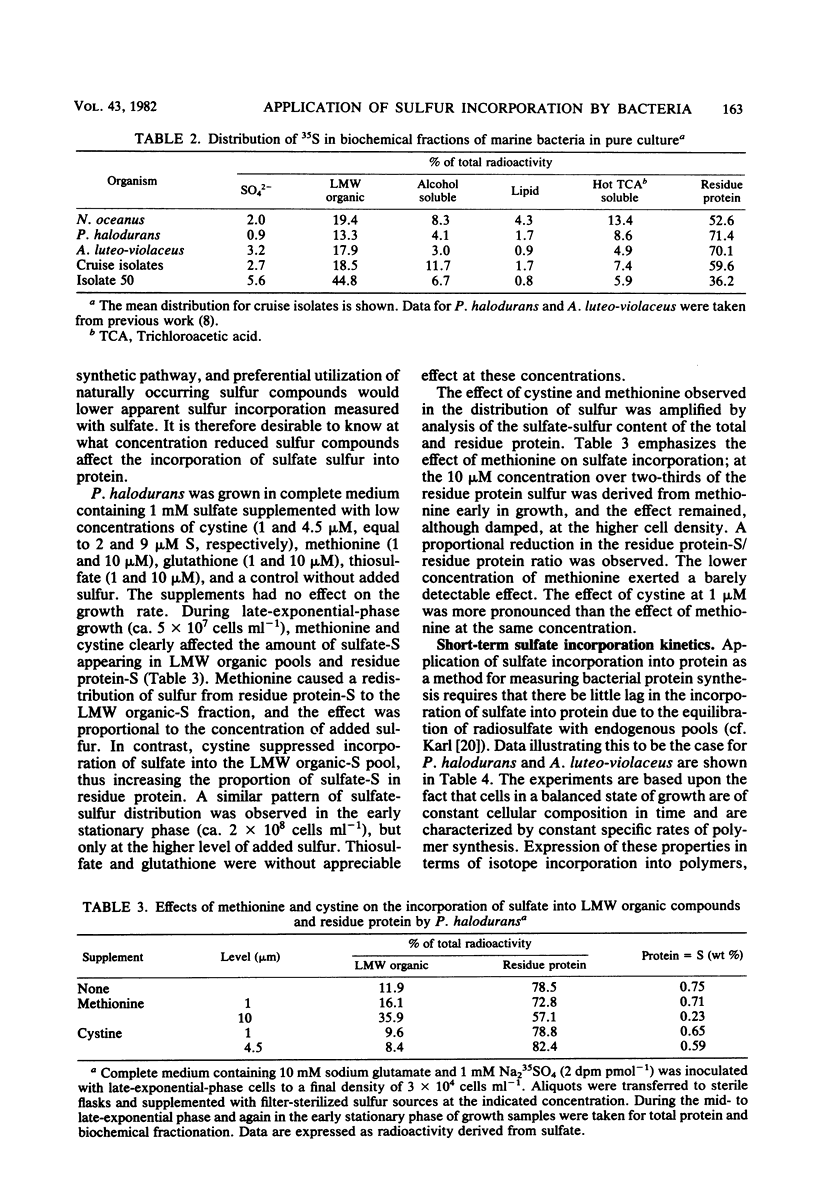
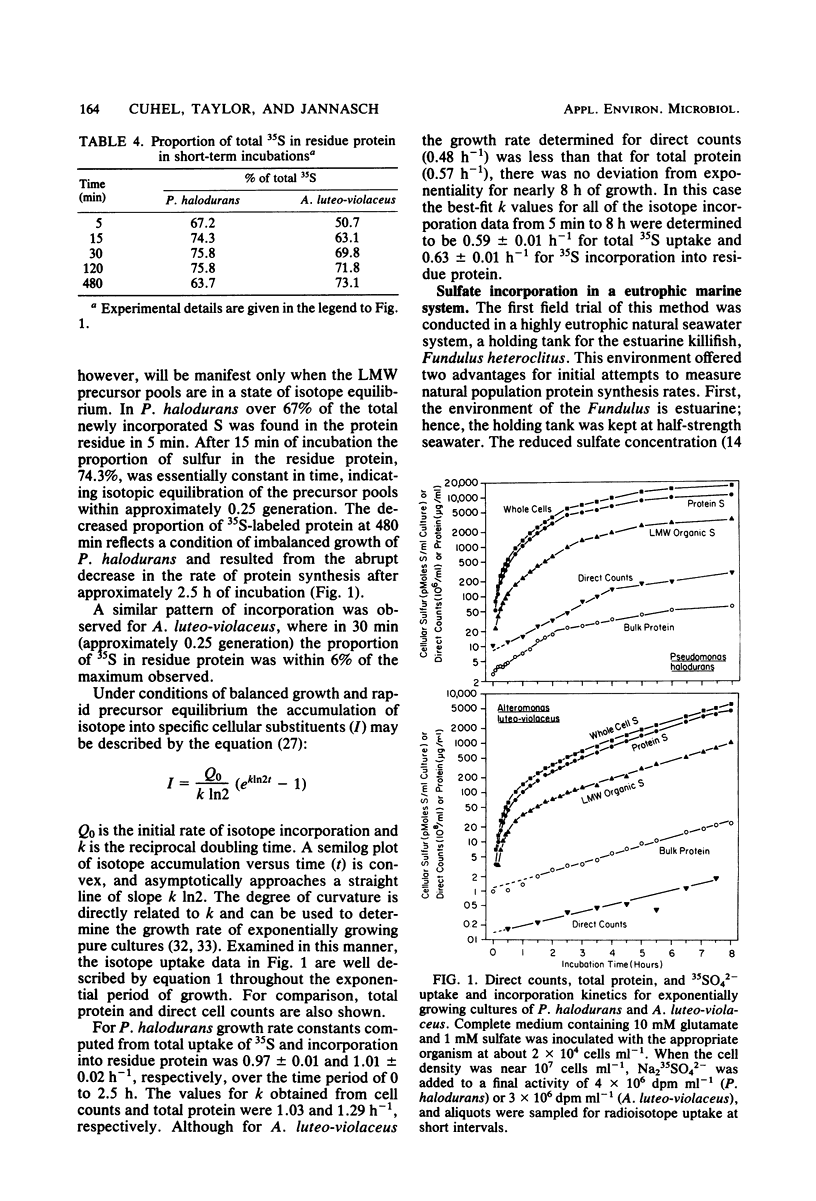
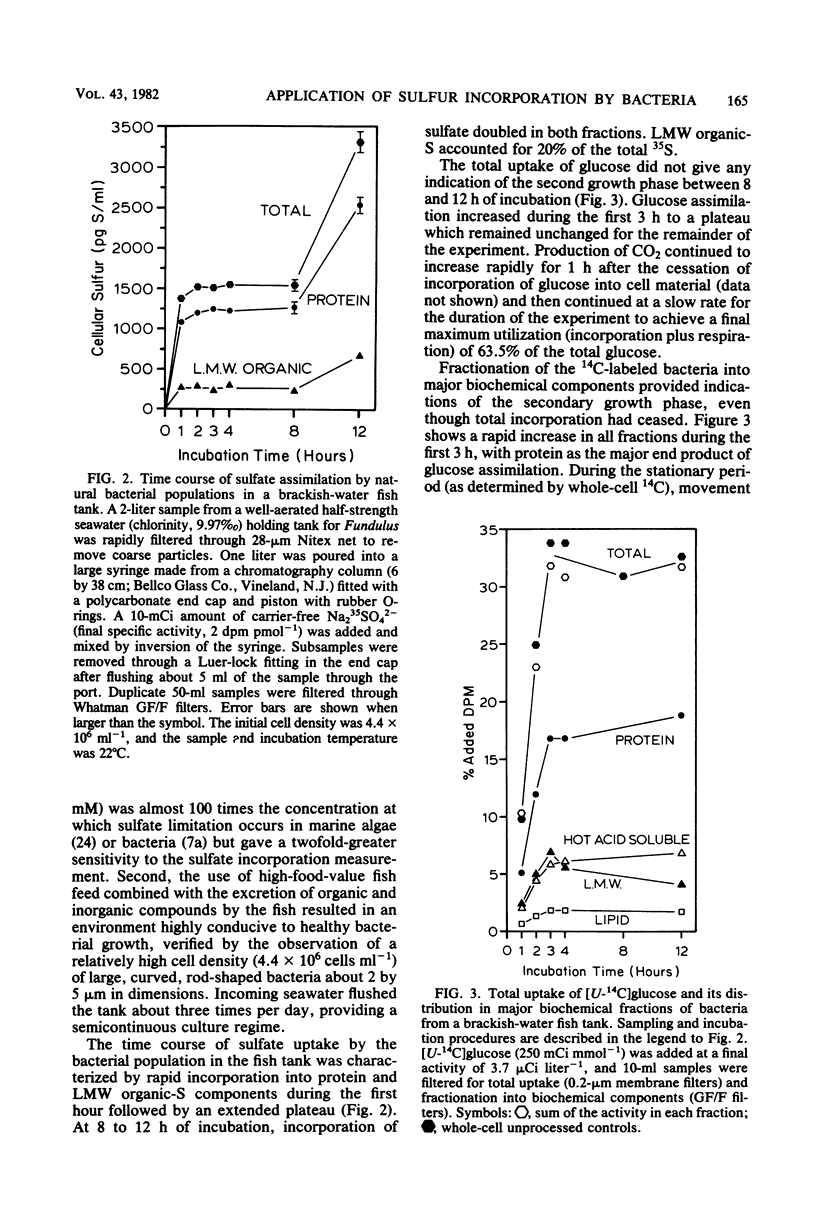
The sulfur content of residue protein was determined for pure cultures of Nitrosococcus oceanus, Desulfovibrio salexigens, 4 mixed populations of fermentative bacteria, 22 samples from mixed natural population enrichments, and 11 nutritionally and morphologically distinct isolates from enrichments of Sargasso Sea water. The average 1.09 ± 0.14% (by weight) S in protein for 13 pure cultures agrees with the 1.1% calculated from average protein composition. An operational value encompassing all mixed population and pure culture measurements has a coefficient of variation of only 15.1% (n = 41). Short-term [35S]sulfate incorporation kinetics by Pseudomonas halodurans and Alteromonas luteoviolaceus demonstrated a rapid appearance of 35S in the residue protein fraction which was well modelled by a simple exponential uptake equation. This indicates that little error in protein synthesis determination results from isotope dilution by endogenous pools of sulfur-containing compounds. Methionine effectively competed with sulfate for protein synthesis in P. halodurans at high concentrations (10 μM), but had much less influence at 1 μM. Cystine competed less effectively with sulfate, and glutathione did not detectably reduce sulfate-S incorporation into protein. [35S]sulfate incorporation was compared with [14C]glucose assimilation in a eutrophic brackish-water environment. Both tracers yielded similar results for the first 8 h of incubation, but a secondary growth phase was observed only with 35S. Redistribution of 14C from low-molecular-weight materials into residue protein indicated additional protein synthesis. [35S]sulfate incorporation into residue protein by marine bacteria can be used to quantitatively measure bacterial protein synthesis in unenriched mixed populations of marine bacteria.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apontoweil P., Berends W. Glutathione biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K 12. Properties of the enzymes and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 14;399(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuhel R. L., Taylor C. D., Jannasch H. W. Assimilatory Sulfur Metabolism in Marine Microorganisms: Sulfur Metabolism, Protein Synthesis, and Growth of Alteromonas luteo-violaceus and Pseudomonas halodurans During Perturbed Batch Growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):151–159. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.151-159.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuhel R. L., Taylor C. D., Jannasch H. W. Assimilatory sulfur metabolism in marine microorganisms: characteristics and regulation of sulfate transport in Pseudomonas halodurans and Alteromonas luteo-violaceus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):340–349. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.340-349.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J., Macnicol P. K. Sulfur-containing Compounds in Lemna perpusilla 6746 Grown at a Range of Sulfate Concentrations. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):629–635. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey R. C., Brown W. C., Adams W. B., Worsham M. B. Occurrence of glutathione in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1126–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1126-1129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Azam F. Bacterioplankton secondary production estimates for coastal waters of british columbia, antarctica, and california. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1085-1095.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Owens L. D., Mudd S. H. beta-Cystathionase In Vivo Inactivation by Rhizobitoxine and Role of the Enzyme in Methionine Biosynthesis in Corn Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1973 Mar;51(3):492–503. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.3.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist R. Evaluation of compositional nonrandomness in proteins. J Mol Evol. 1978 Oct 6;11(4):349–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01733842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. J. On counseling minority students in a university center. J Am Coll Health Assoc. 1974 Dec;23(2):146–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H., Holmquist R., Moise H. Amino acid composition of proteins: Selection against the genetic code. Science. 1975 Jul 4;189(4196):50–51. doi: 10.1126/science.237322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. Measurement of microbial activity and growth in the ocean by rates of stable ribonucleic Acid synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):850–860. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.850-860.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Becker M. A., Tomkins G. M. Purification and characterization of cysteine synthetase, a bifunctional protein complex, from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2428–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M. Regulation of L-cysteine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Effects of growth of varying sulfur sources and O-acetyl-L-serine on gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3474–3484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law A. T., Button D. K. Multiple-carbon-source-limited growth kinetics of a marine coryneform bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):115–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.115-123.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Abrams W. R., Schiff J. A. Reduction of adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate to cysteine in extracts from Chlorella and mutants blocked for sulfate reduction. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):423–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D. Growth of a bacterium under a high-pressure oxy-helium atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):42–49. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.42-49.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Jannasch H. W. Subsampling technique for measuring growth of bacterial cultures under high hydrostatic pressure. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):355–359. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.355-359.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


