Abstract
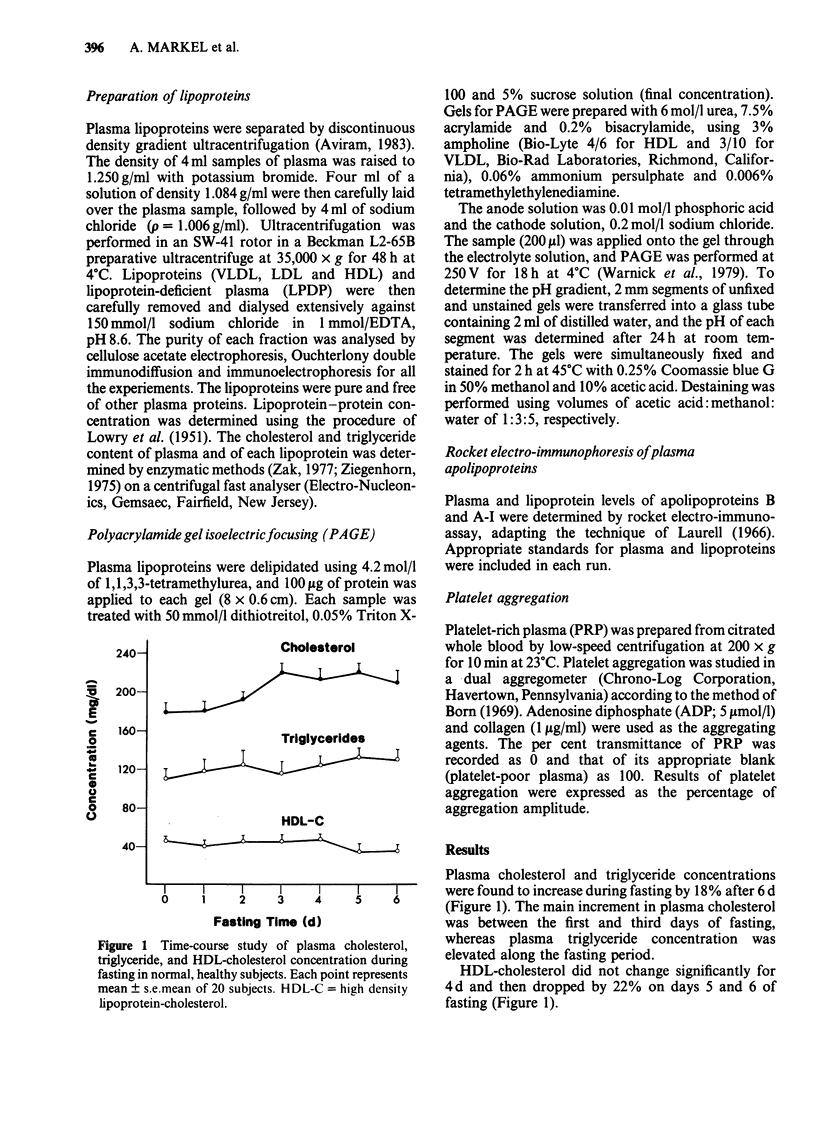
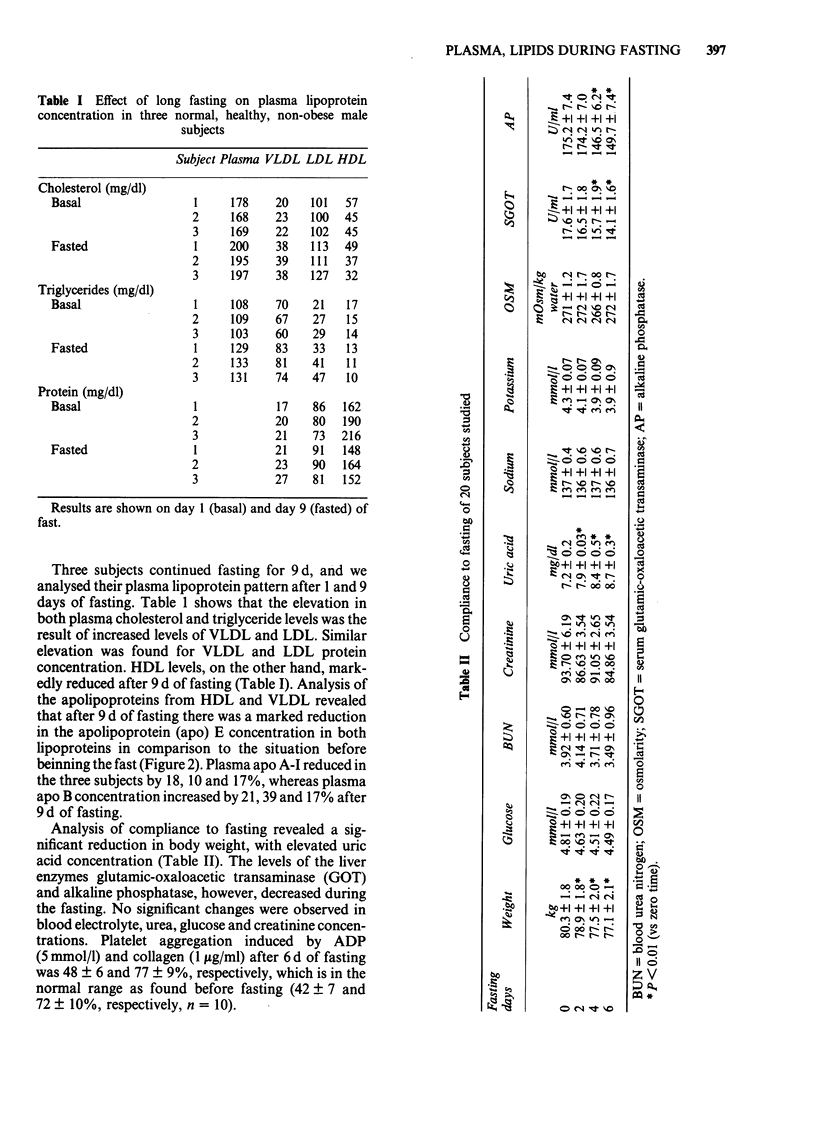
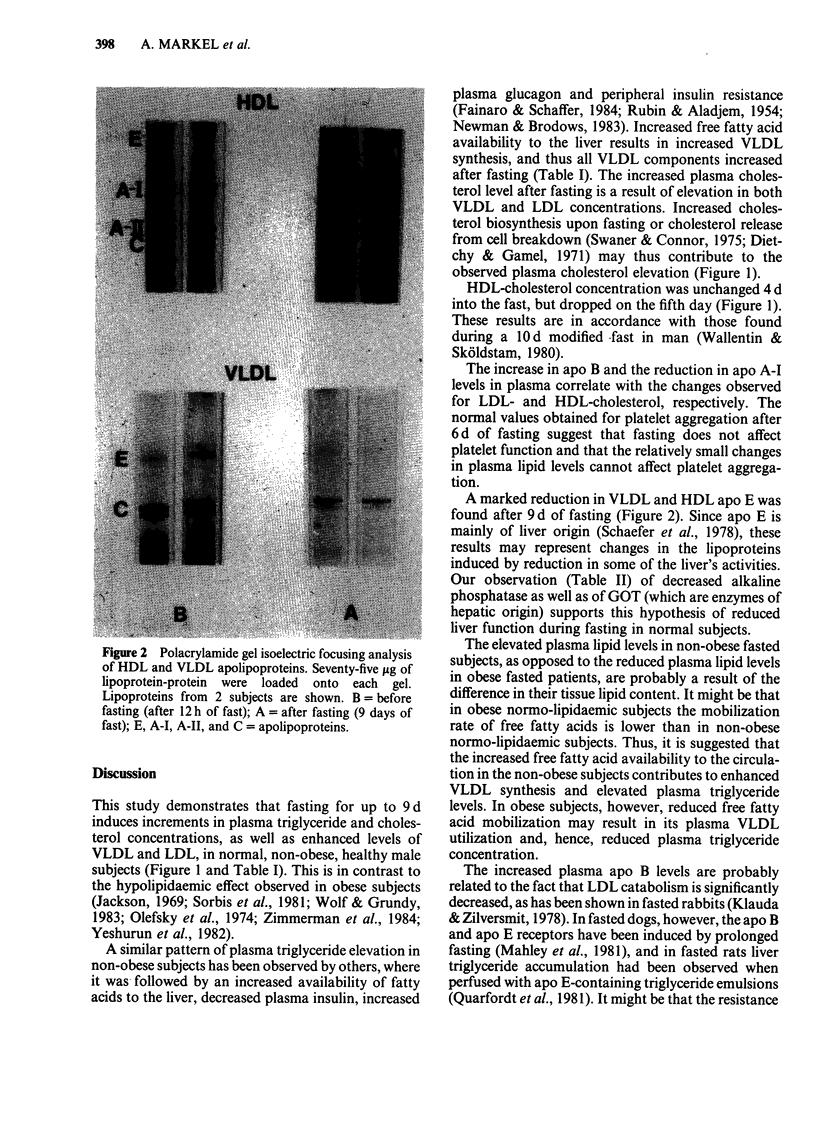
Plasma lipid and high density lipoprotein (HDL) levels were studied in 20 normal, healthy, non-obese males while fasting (150 kcal/d with free intake of water) for 6 d in a hunger strike. Plasma triglyceride and cholesterol levels were increased by 18% after 6 d of fasting. HDL-cholesterol concentration was not significantly changed for 4 d, but decreased by 22% after 6 d. Platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or collagen after 6 d of fasting was in the normal range. In 3 subjects fasted for 9 d, a complete plasma lipoprotein analysis was done. Very low and low density lipoprotein (VLDL and LDL) levels were elevated, whereas HDL was reduced after 9 d of fasting. On isoelectric focusing analysis, a marked reduction in apolipoprotein (apo) E concentration in both VLDL and HDL was noted. Liver function tests showed a reduction in hepatic enzyme activity; and since apo E is of hepatic origin also, we suggest that long fasting inhibits liver function in normal subjects.
Full text
PDF


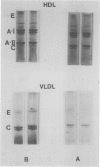
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviram M., Brook G. J. The effect of human plasma on platelet function in familial hypercholesterolemia. Thromb Res. 1982 Apr 15;26(2):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviram M., Brook J. G., Lees A. M., Lees R. S. Low density lipoprotein binding to human platelets: role of charge and of specific amino acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 16;99(1):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91746-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviram M., Brook J. G. Platelet interaction with high and low density lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Mar;46(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviram M., Brook J. G. The effect of blood constituents on platelet function: role of blood cells and plasma lipoproteins. Artery. 1983;11(4):297–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviram M. Plasma lipoprotein separation by discontinuous density gradient ultracentrifugation in hyperlipoproteinemic patients. Biochem Med. 1983 Aug;30(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(83)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook G., Winterstein G., Aviram M. Platelet function and lipoprotein levels after plasma-exchange in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jun;64(6):637–642. doi: 10.1042/cs0640637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell K. D., Stunkard A. J. Differential changes in plasma high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels in obese men and women during weight reduction. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Aug;141(9):1142–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consolazio C. F., Matoush L. O., Johnson H. L., Nelson R. A., Krzywicki H. J. Metabolic aspects of acute starvation in normal humans (10 days). Am J Clin Nutr. 1967 Jul;20(7):672–683. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/20.7.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Gamel W. G. Cholesterol synthesis in the intestine of man: regional differences and control mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):872–880. doi: 10.1172/JCI106559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. M. Effect of prolonged starvation on blood lipid levels of obese subjects. Metabolism. 1969 Jan;18(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klauda H. C., Zilversmit D. B. Influx of cholesterol into plasma in rabbits with fasting hyperbetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1974 Nov;15(6):593–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. H. Two independent lipoprotein receptors on hepatic membranes of dog, swine, and man. Apo-B,E and apo-E receptors. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1197–1206. doi: 10.1172/JCI110365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordasini R., Klose G., Greten H. Secondary type II hyperlipoproteinemia in patients with anorexia nervosa. Metabolism. 1978 Jan;27(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman W. P., Brodows R. G. Insulin action during acute starvation: evidence for selective insulin resistance in normal man. Metabolism. 1983 Jun;32(6):590–596. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Shelburne F. A., Meyers W., Jakoi L., Hanks J. Effect of apolipoproteins on the induction of hepatic steatosis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jan;80(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN L., ALADJEM F. Serum lipoprotein changes during fasting in man. Am J Physiol. 1954 Aug;178(2):263–266. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein apoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1978 Aug;19(6):667–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. W., Henry R. W., Buchanan K. D. Triglyceride metabolism in acute starvation: the role of secretin and glucagon. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar 31;6(2):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streja D. A., Boyko E., Rabkin S. W. Changes in plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration after weight reduction in grossly obese subjects. Br Med J. 1980 Sep 20;281(6243):770–772. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6243.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaner J. C., Connor W. E. Hypercholesterolemia of total starvation: its mechanism via tissue mobilization of cholesterol. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):365–369. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sörbris R., Petersson B. G., Nilsson-Ehle P. Effects of weight reduction on plasma lipoproteins and adipose tissue metabolism in obese subjects. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;11(6):491–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb02019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallentin L., Sköldstam L. Lipoproteins and cholesterol esterification rate in plasma during a 10-day modified fast in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Sep;33(9):1925–1931. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.9.1925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnick G. R., Albers J. J. A comprehensive evaluation of the heparin-manganese precipitation procedure for estimating high density lipoprotein cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):65–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnick G. R., Mayfield C., Albers J. J., Hazzard W. R. Gel isoelectric focusing method for specific diagnosis of familial hyperlipoproteinemia type 3. Clin Chem. 1979 Feb;25(2):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler J. G., Hutt V., Wenzel H., Klör H. U., Ditschuneit H. Lipids and lipoproteins during a very-low-calorie diet. Int J Obes. 1981;5(3):325–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. N., Grundy S. M. Influence of weight reduction on plasma lipoproteins in obese patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):160–169. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak B. Cholesterol methodologies: a review. Clin Chem. 1977 Jul;23(7):1201–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegenhorn J. Improved method for enzymatic determination of serum triglycerides. Clin Chem. 1975 Oct;21(11):1627–1629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]