Abstract
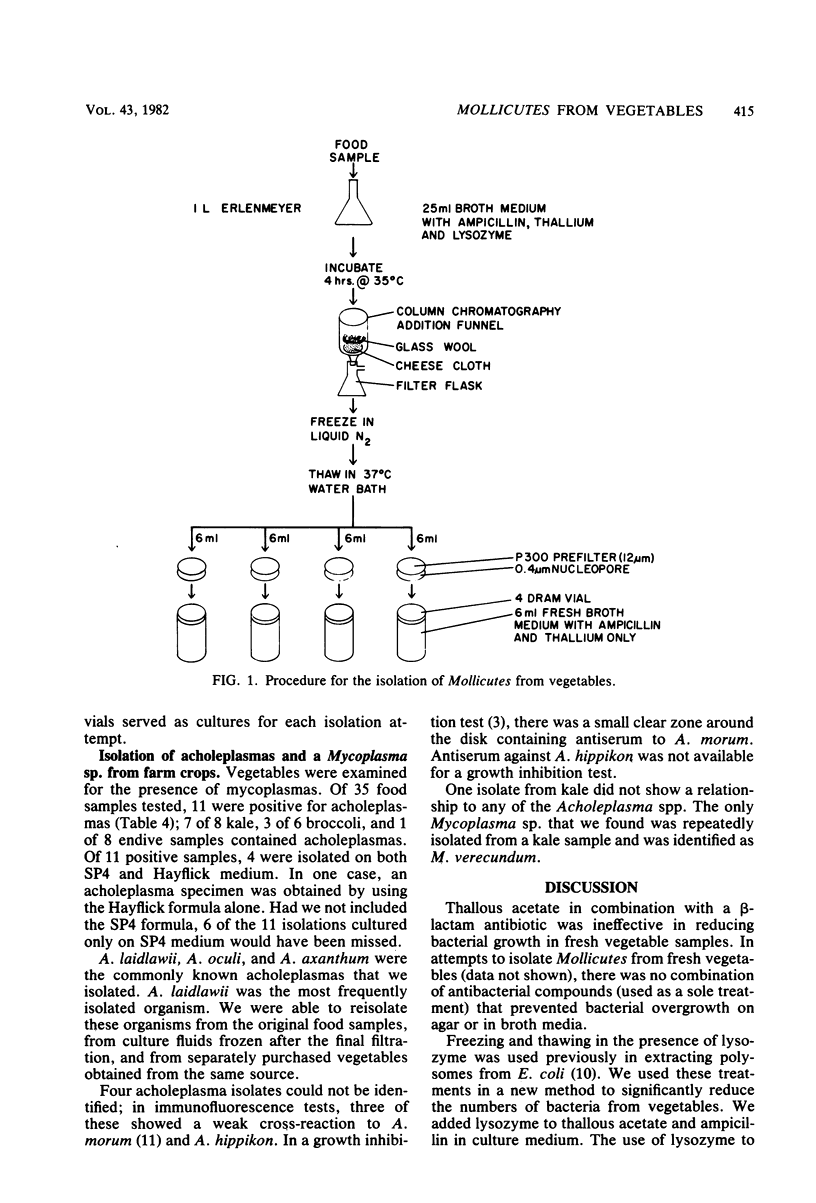
The isolation of Mollicutes from food has not been reported. To isolate Mollicutes in the presence of high levels of unwanted bacteria, we first incubated fresh vegetables in liquid culture media containing lysozyme, ampicillin, and thallous acetate. Culture fluids were than separated from the vegetable samples, subjected to one freeze-thaw cycle, and passed through a filter of 0.4-micron porosity. Filtered samples were cultured in SP4 medium and in a conventional medium containing horse serum. With this procedure 21 acholeplasma isolations representing three species were obtained from endive, broccoli, and kale. Of 35 food samples tested, 11 were positive for acholeplasmas; acholeplasmas isolated from 6 of these samples were recovered only in SP4 medium. In seven single vegetable samples, two or more Acholeplasma spp. were isolated. A. laidlawii was isolated from all three vegetables and A. axanthum was found in broccoli and kale. Four isolates were serologically identified as A. oculi. Mycoplasma verecundum was the only Mycoplasma species recovered. Several isolates could not be typed serologically, as they reacted with antisera to both A. morum and A. hippikon. these isolates may include new Acholeplasma spp.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice R. A., Robillard N. F., Carski T. R. Immunofluorescence identification of Mycoplasma on agar by use of incident illumination. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1205–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1205-1209.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundt E. A., Andrews B. E., Erno H., Kunze M., Black F. T. The sensitivity of mycoplasmatales to sodium-polyanethol-sulfonate and digitonin. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Oct;225(1):104–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Leach R. H., Howard C. J. Mycoplasma verecundum, a new species isolated from bovine eyes. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):475–484. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin E. P., Tierney J. T., Sullivan R., Peeler J. T. Collaborative study of the glass wool filtration method for the recovery of virus inoculated into ground beef. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1975 May;58(3):576–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A color test for the measurement of antibody to the non-acid-forming human Mycoplasma species. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jul;84(1):51–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron E. Z., Kohler R. E., Davis B. D. Polysomes extracted from Escherichia coli by freeze-thaw-lysozyme lysis. Science. 1966 Sep 2;153(3740):1119–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3740.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Rose D. L., Whitcomb R. F., Wenzel R. P. Enhanced isolation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from throat washings with a newly-modified culture medium. J Infect Dis. 1979 Apr;139(4):478–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.4.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. L., Whitcomb R. F. Plant mycoplasmas: a cultivable spiroplasma causes corn stunt disease. Science. 1975 Jun 6;188(4192):1018–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.188.4192.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


