Abstract
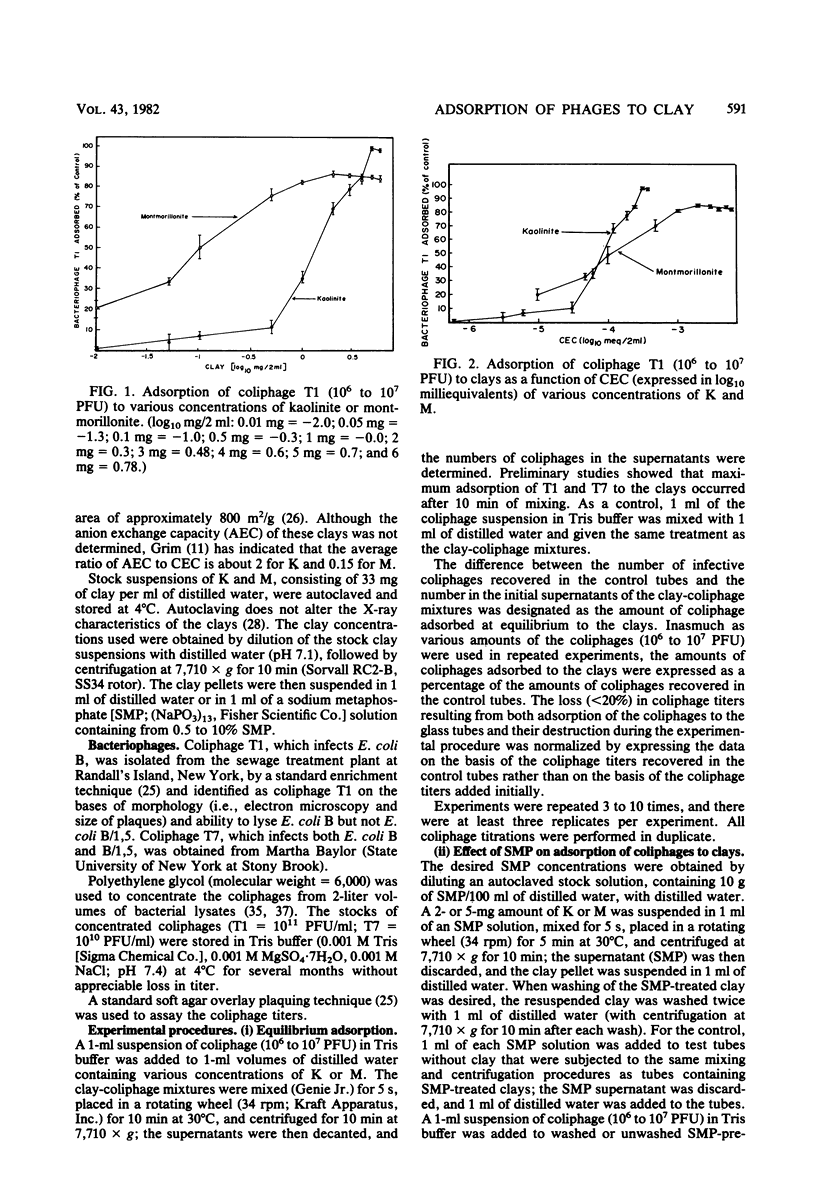
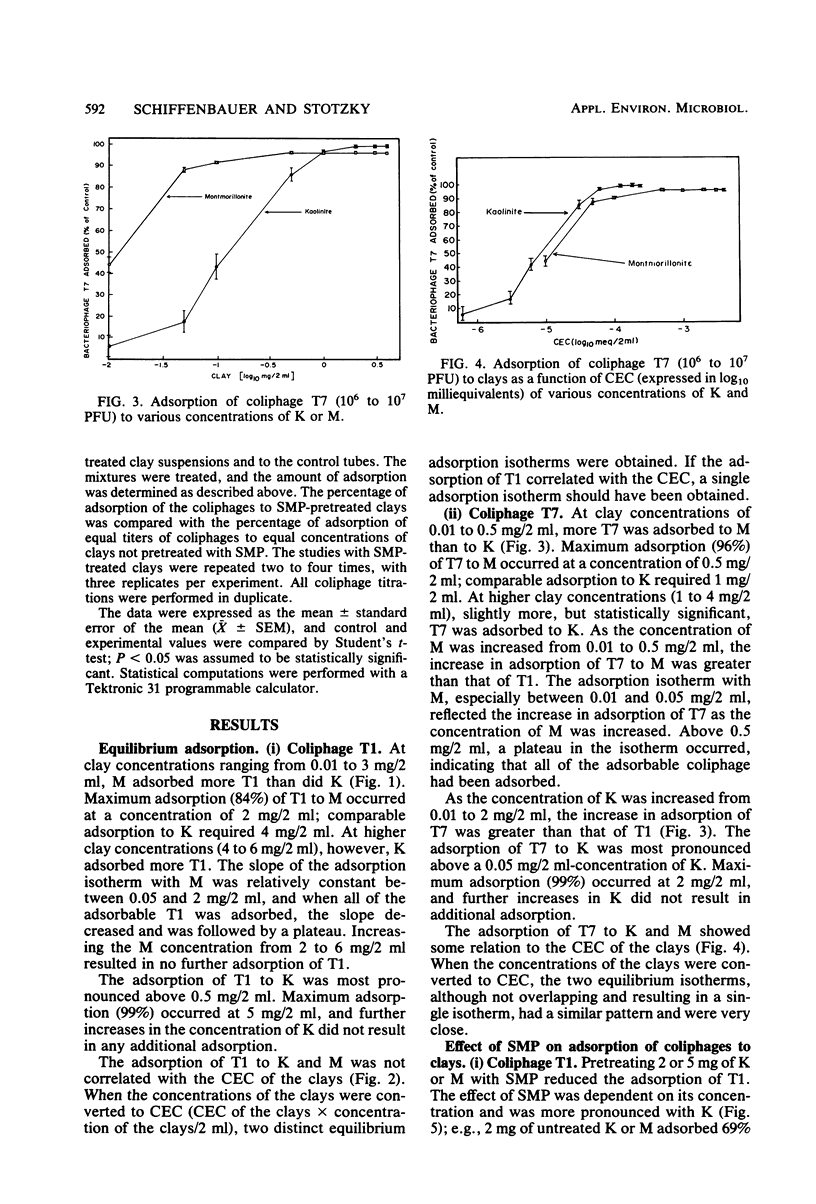
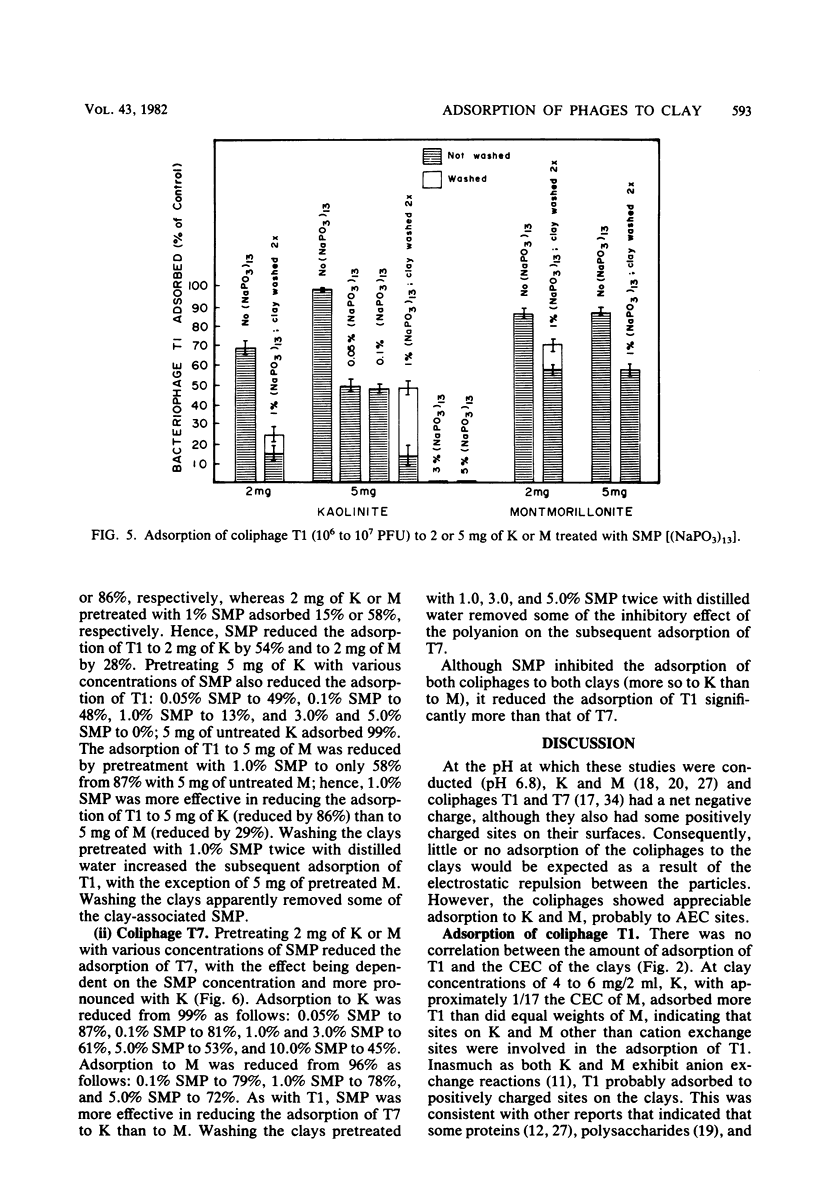
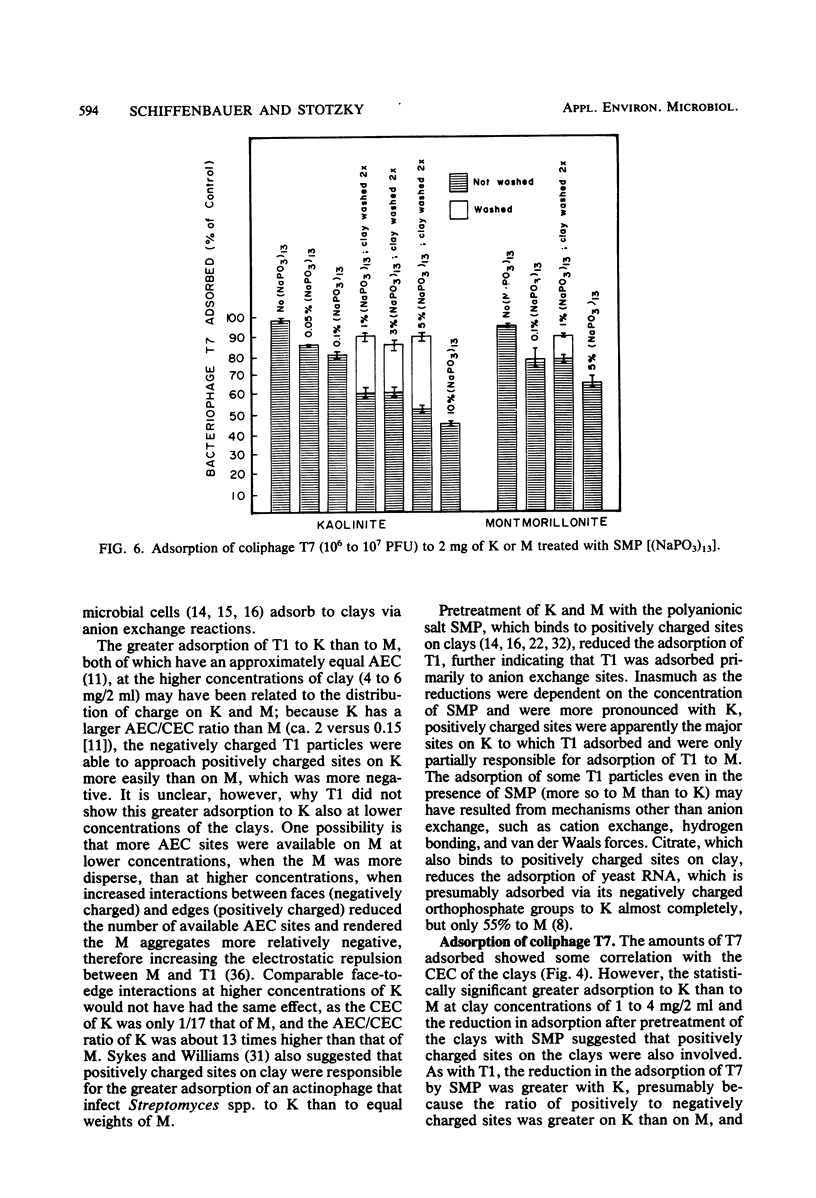
Coliphages T1 and T7 of Escherichia coli were absorbed by kaolinite (K) and montmorillonite (M). Maximum adsorption of T7 (96%) to M was greater than that of T1 (84%), but the adsorption of both coliphages to K was the same (99%). Positively charged sites (i.e., anion exchange sites) on the clays appeared to be primarily responsible for the adsorption of T1 to K but only partially responsible for the adsorption of T1 to M; equilibrium adsorption isotherms of T1 to K and M did not show a correlation between adsorption and the cation exchange capacity of the clays, and the reduction in adsorption caused by sodium metaphosphate (a polyanion that interacts with positively charged sites on clay) was more pronounced with K than with M. The equilibrium adsorption isotherms of T7 to K and M suggested a correlation between adsorption and the cation exchange capacity of the clays. However, studies with sodium metaphosphate indicated that T7 also adsorbed to positively charged sites on the clays, especially on K. Adsorption of the coliphages to positively charged sites was greater with K than with M, probably because the ratio of positively charged sites to negatively charged sites was greater on K than on M.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duboise S. M., Moore B. E., Sorber C. A., Sagik B. P. Viruses in soil systems. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1979 Nov;7(3):245–301. doi: 10.3109/10408417909082016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P. Comparative adsorption of human enteroviruses, simian rotavirus, and selected bacteriophages to soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):241–247. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.241-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal S. M., Zerda K. S., Gerba C. P. Concentration of coliphages from large volumes of water and wastewater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.85-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C. Interaction between colloidal montmorillonite and cells of Rhizobium species with different inogenic surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 1;156(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C. Orientation of clay particles sorbed on bacteria possessing different ionogenic surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):472–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUTNAM F. W. Molecular kinetic and electrophoretic properties of bacteriophages. Science. 1950 May 5;111(2888):481–488. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2888.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Glass J. S. Poliovirus concentration from tap water with electropositive adsorbent filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):201–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.201-210.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Jones B. L. Concentration of poliovirus from tap water using positively charged microporous filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):588–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.588-595.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. 3. Effect of particle size, cation exchange capacity, and surface area on bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Dec;12(6):1235–1246. doi: 10.1139/m66-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Rem L. T. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. I. Montmorillonite and kaolinite on bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):547–563. doi: 10.1139/m66-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vajda B. P. Concentration and purification of viruses and bacteriophages with polyethylene glycol. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1978;23(1):88–96. doi: 10.1007/BF02876605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


