Abstract
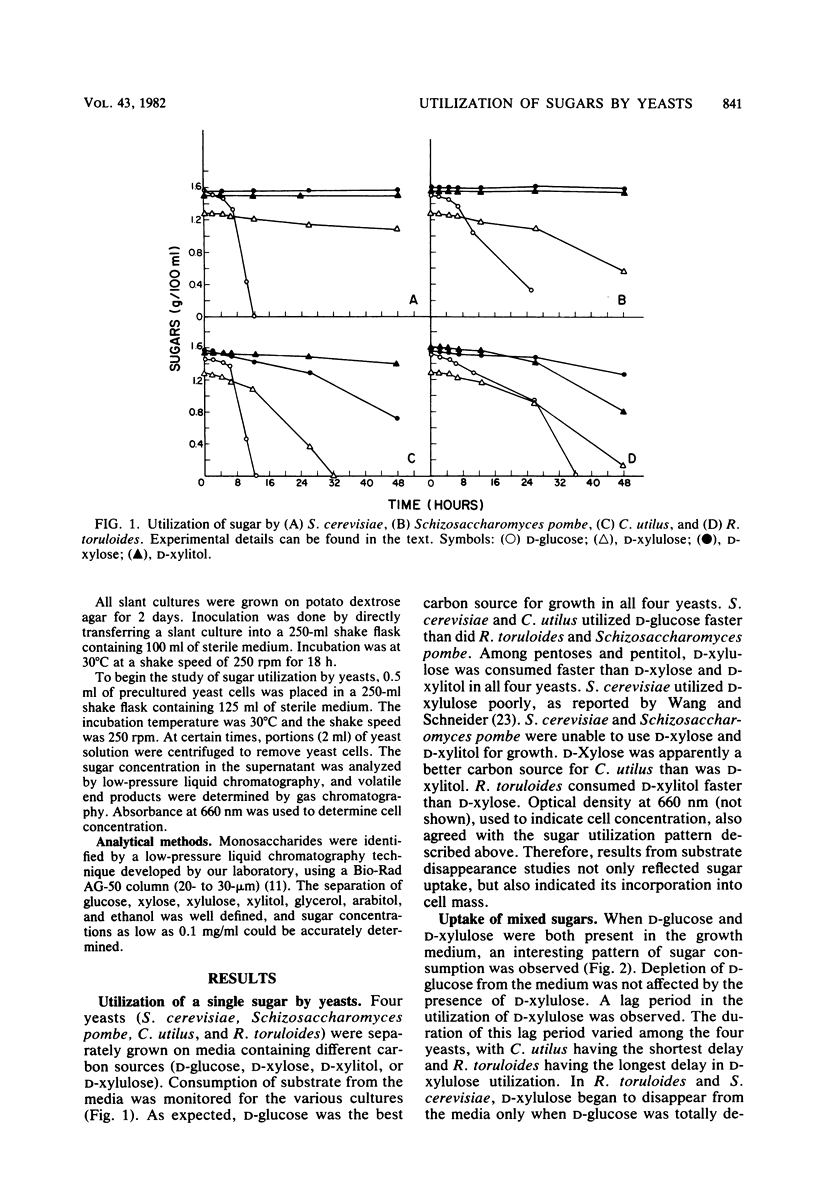
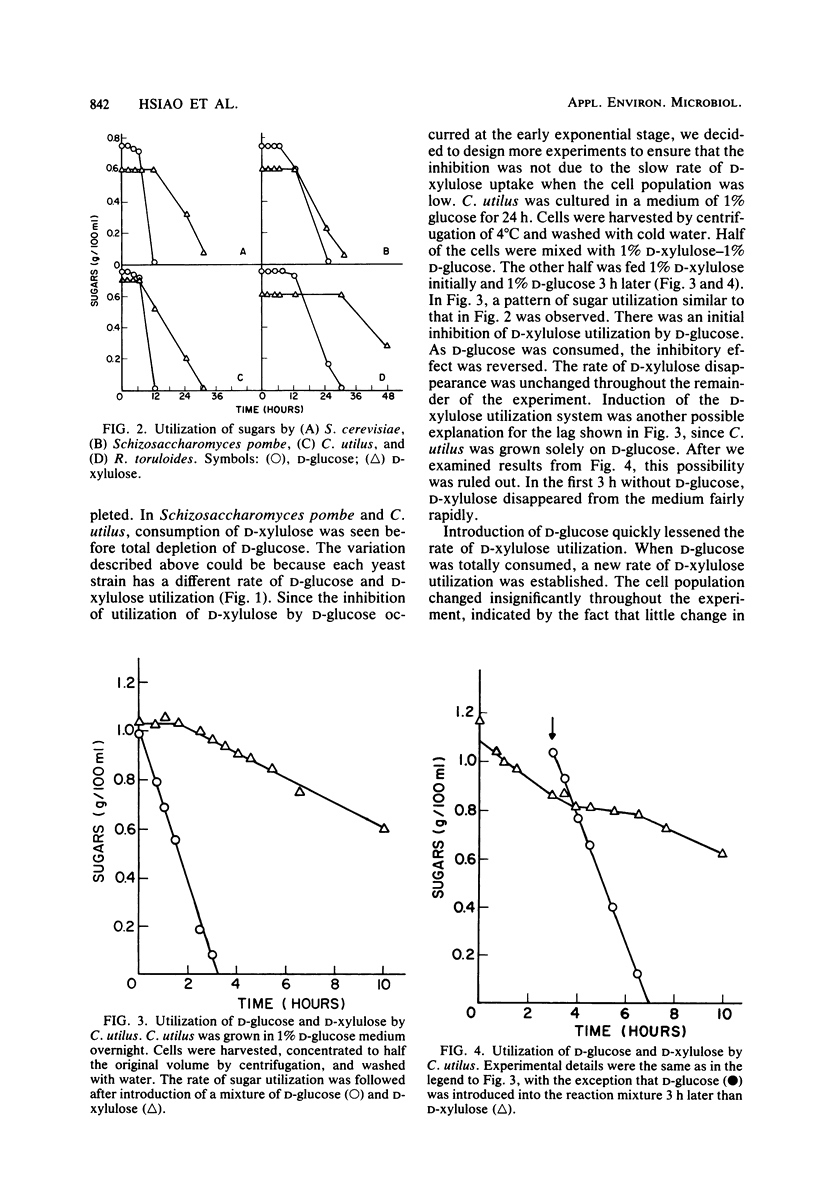
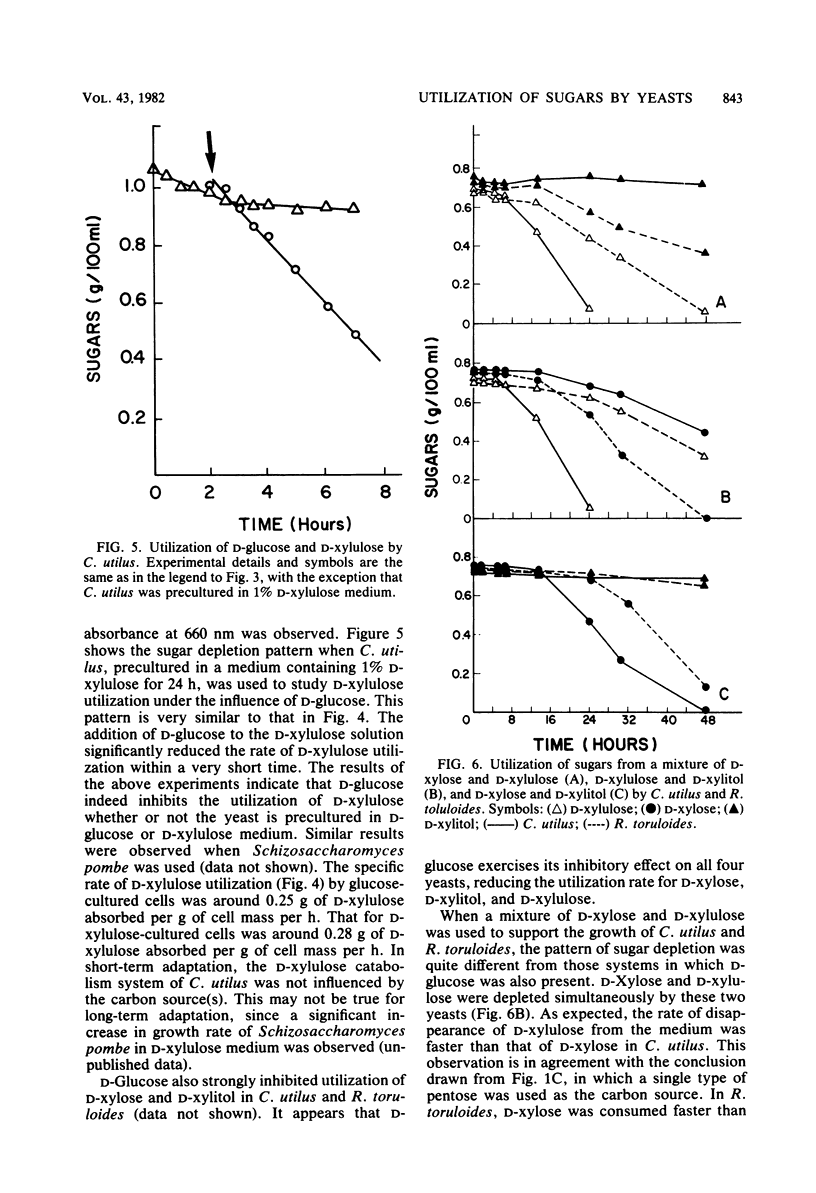
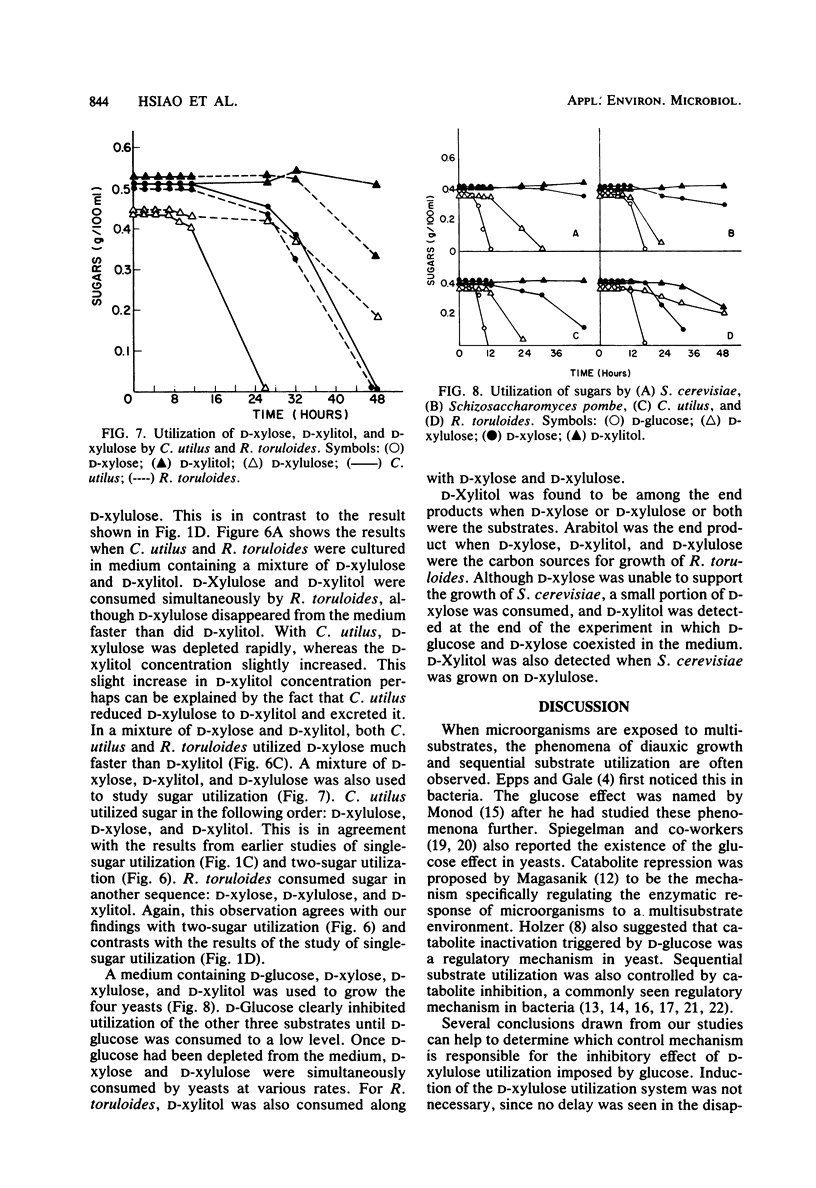
Four yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Candida utilus, and Rhodotorula toruloides) were tested for their ability to grow and consume D-glucose, D-xylose, D-xylulose, and D-xylitol. Sequential utilization of substrates was observed when D-glucose as mixed with D-xylulose as the carbon source. Catabolite inhibition was tentatively concluded to be responsible for this regulatory mechanism. D-Glucose was also found to inhibit the utilization of D-xylose and D-xylitol in C. utilus and R. toruloides. D-Xylose, D-xylitol, and D-xylulose were consumed simultaneously by R. toruloides and C. utilus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAKRAVORTY M., VEIGA L. A., BACILA M., HORECKER B. L. Pentose metabolism in Candida. II. The diphosphopyridine nucleotide-specific polyol dehydrogenase of Candida utilis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1014–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang L. C., Hsiao H. Y., Ueng P. P., Tsao G. T. Enzymatic and Microbial Preparation of d-Xylulose from d-Xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):66–69. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.66-69.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo V. P. Relationship between sugar structure and competition for the sugar transport system in Bakers' yeast. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):603–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.603-611.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epps H. M., Gale E. F. The influence of the presence of glucose during growth on the enzymic activities of Escherichia coli: comparison of the effect with that produced by fermentation acids. Biochem J. 1942 Sep;36(7-9):619–623. doi: 10.1042/bj0360619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong C. S., Chen L. F., Flickinger M. C., Chiang L. C., Tsao G. T. Production of Ethanol from d-Xylose by Using d-Xylose Isomerase and Yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):430–436. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.430-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCHSTER R. M., WATSON R. W. Enzymatic isomerization of D-xylose to D-xylulose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jan;48(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis J. F., Paigen K. Catabolite inhibition: a general phenomenon in the control of carbohydrate utilization. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):902–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.902-913.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis J. F., Paigen K. Site of catabolite inhibition of carbohydrate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):885–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.885-887.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of substrate affinities among several rumen bacteria: a possible determinant of rumen bacterial competition. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):531–536. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.531-536.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Substrate preferences in rumen bacteria: evidence of catabolite regulatory mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):319–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.319-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standing C. N., Fredrickson A. G., Tsuchiya H. M. Batch- and continuous-culture transients for two substrate systems. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):354–359. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.354-359.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumm-Zollinger E. Effects of inhibition and repression on the utilization of substrates by heterogeneous bacterial communities. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):654–664. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.654-664.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. Y., Schneider H. Growth of yeasts on D-xylulose 1. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Sep;26(9):1165–1168. doi: 10.1139/m80-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. Y., Shopsis C., Schneider H. Fermentation of a pentose by yeasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):248–254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


