Abstract
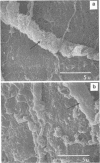
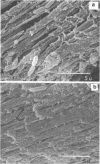
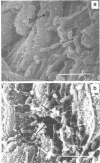
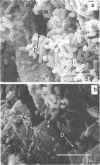
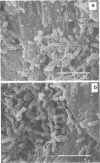
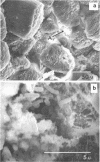
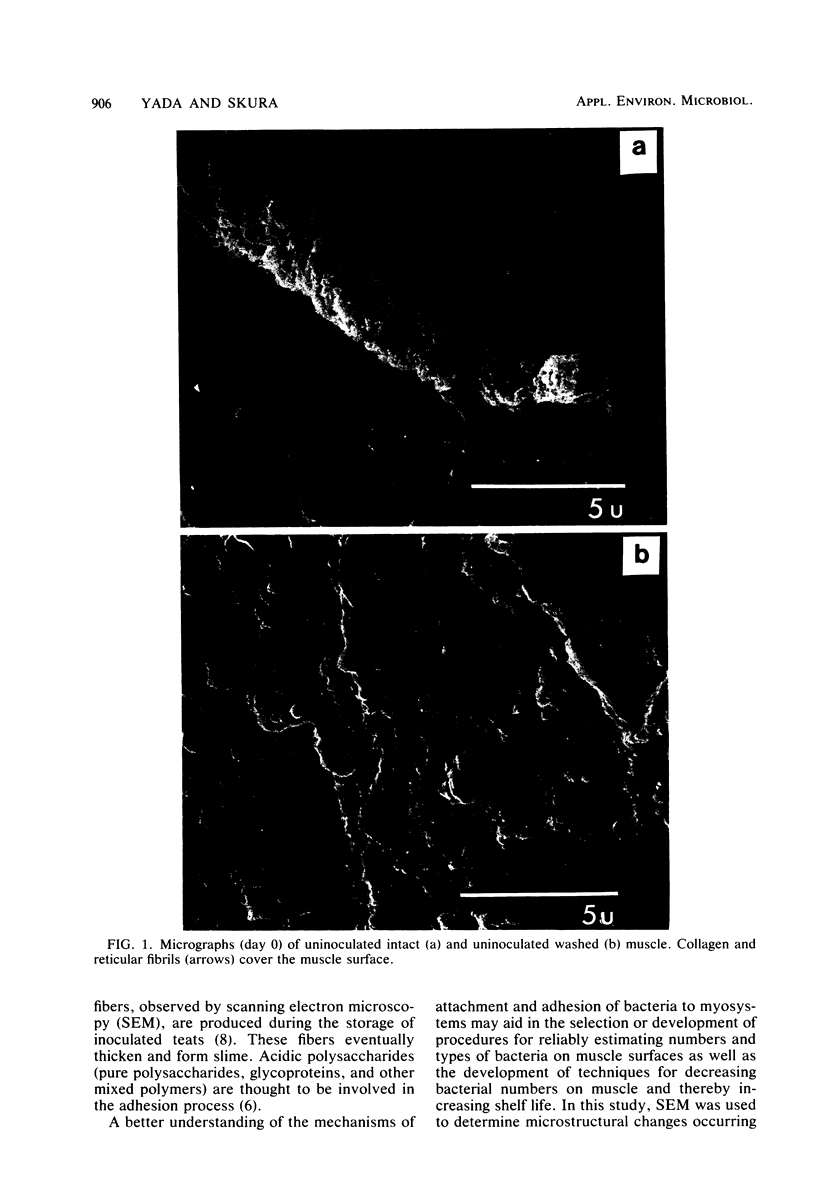
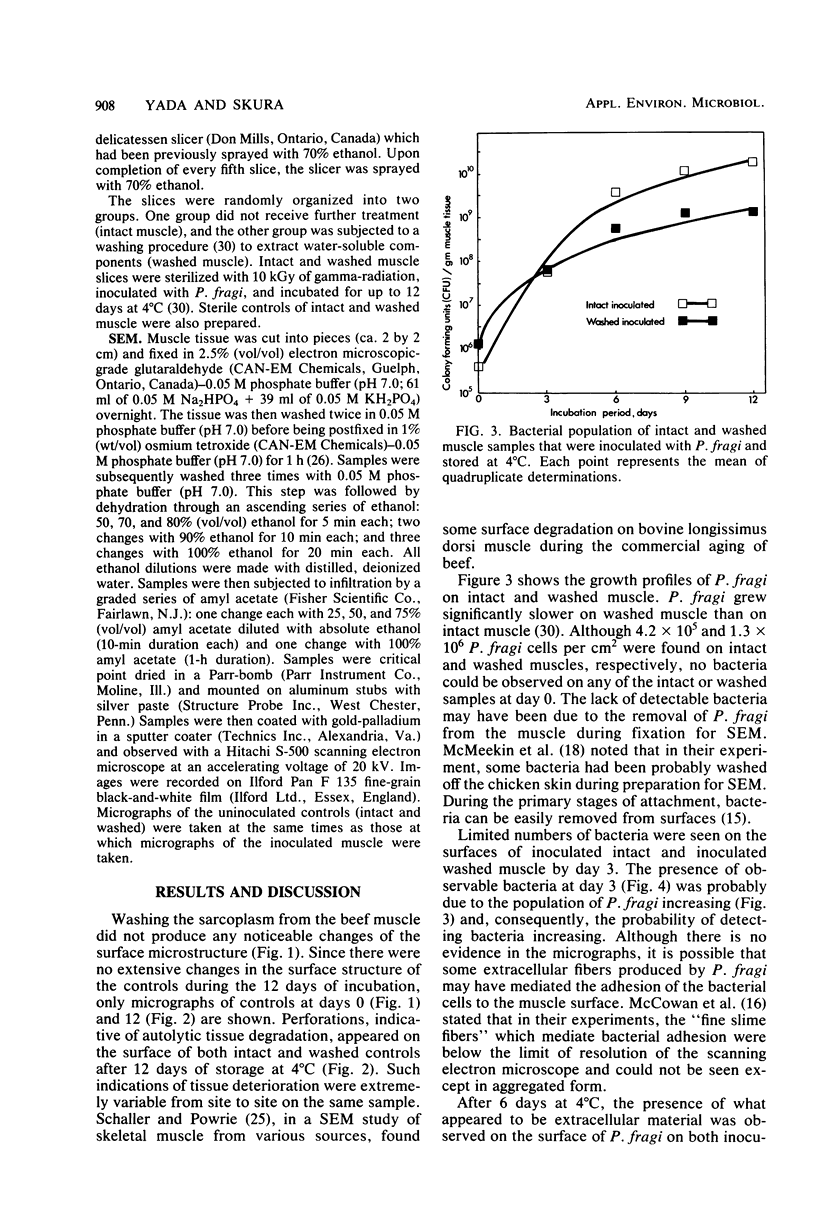
Intact bovine longissimus dorsi muscle strips used 24 h postmortem were washed to remove sarcoplasmic fluid or left intact and were either left uninoculated or inoculated with Pseudomonas fragi ATCC 4973. The effects of decreased sarcoplasm concentration on growth of P. fragi and consequent microstructural changes of beef muscle during aerobic storage at 4 degrees C for 12 days were evaluated. P. fragi grew slower on washed muscle than on intact muscle. Scanning electron micrographs revealed surface degradation of both intact inoculated and washed inoculated muscle only in areas of localized colonization. Extracellular fibrils appeared to mediate adhesion of P fragi to the muscle surface as well as cell-to-cell attachment within microcolonies. P. fragi was also observed growing between muscle fibers.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avens J. S., Miller B. F. Quantifying bacteria on poultry carcass skin. Poult Sci. 1970 Sep;49(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.3382/ps.0491309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinema M. H., Zevenhuizen L. P. Formation of cellulose fibrils by gram-negative bacteria and their role in bacterial flocculation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(1):42–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00409087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill C. O., Newton K. G. The development of aerobic spoilage flora on meat stored at chill temperatures. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill C. O. Substrate limitation of bacterial growth at meat surfaces. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;41(3):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCowan R. P., Cheng K. J., Bailey C. B., Costerton J. W. Adhesion of bacteria to epithelial cell surfaces within the reticulo-rumen of cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):149–155. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.149-155.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCowan R. P., Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Colonization of a portion of the bovine tongue by unusual filamentous bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1224–1229. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1224-1229.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMeekin T. A., Thomas C. J., McCall D. Scanning electron microscopy of microorganisms on chicken skin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;46(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb02600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Kampelmacher E. H. Attachment of some bacterial strains to the skin of broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci. 1974 Nov;15(6):573–585. doi: 10.1080/00071667408416148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Kampelmacher E. H. Further studies on the attachment of bacteria to skin. Br Poult Sci. 1975 Sep;16(5):487–496. doi: 10.1080/00071667508416217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Kampelmacher E. H., van Schothorst M. Studies on sampling methods used in the control of hygiene in poultry processing. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;39(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. T. Microbiological sampling of poultry carcasses. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;35(4):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Rem L. T. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. I. Montmorillonite and kaolinite on bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):547–563. doi: 10.1139/m66-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrant P. J., Pearson A. M., Price J. F., Lechowich R. V. Action of Pseudomonas fragi on the proteins of pig muscle. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):224–228. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.224-228.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. J., McMeekin T. A. Spoilage of chicken skin at 2 degrees C: electron microscopic study. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):492–503. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.492-503.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E. The Effect of Solid Surfaces upon Bacterial Activity. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):39–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.39-56.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]