Abstract
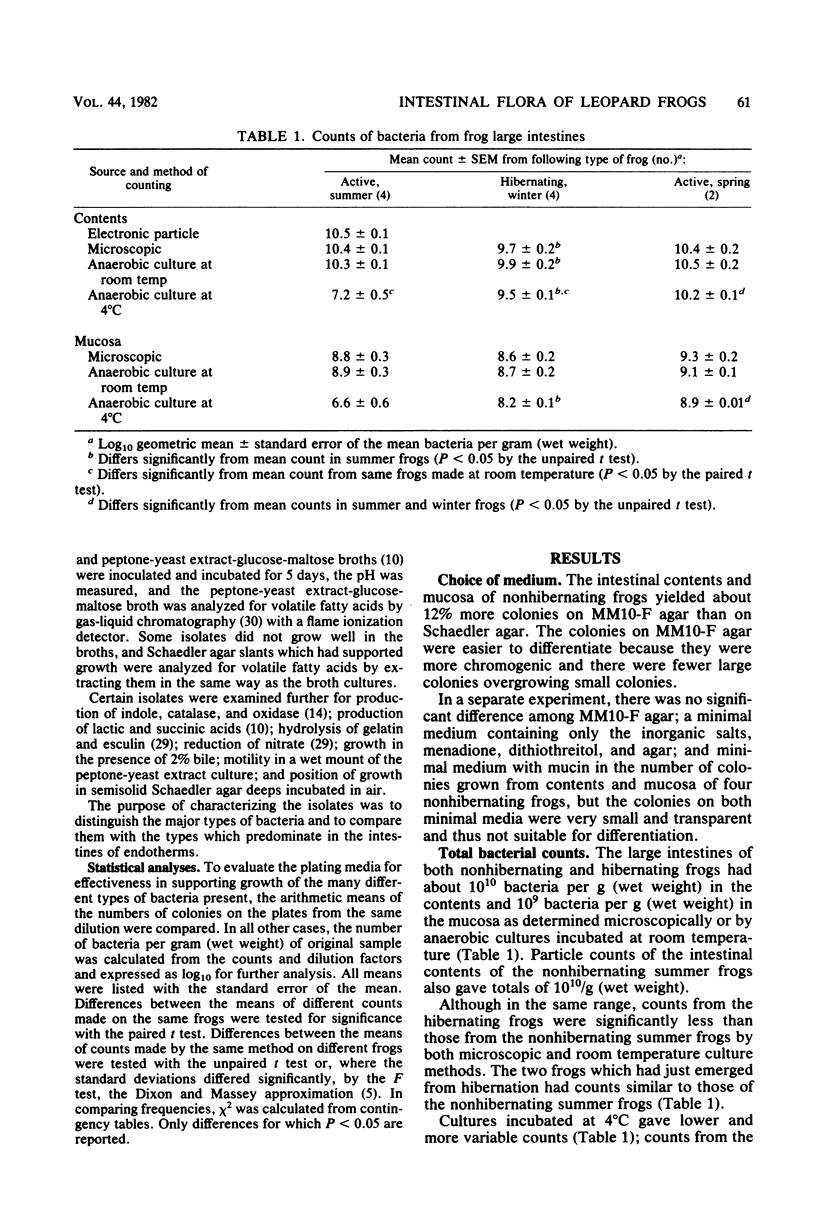
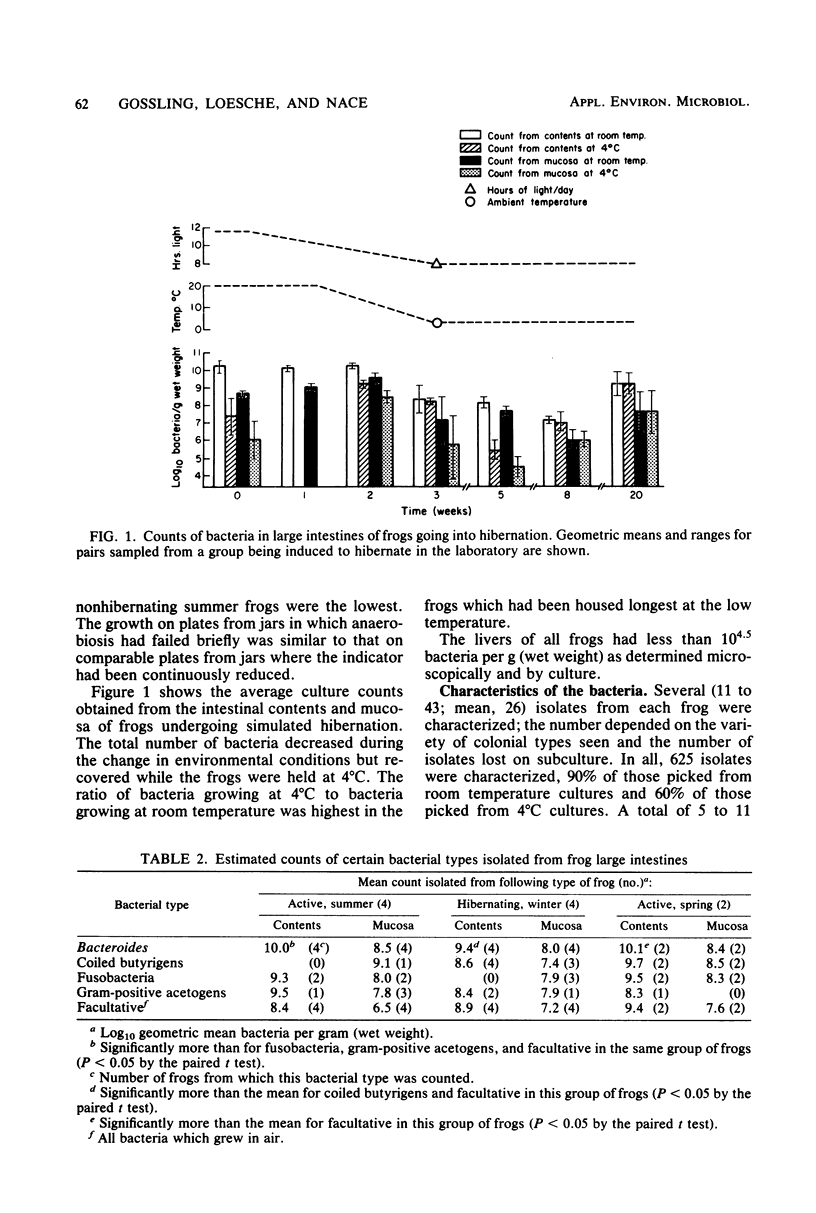
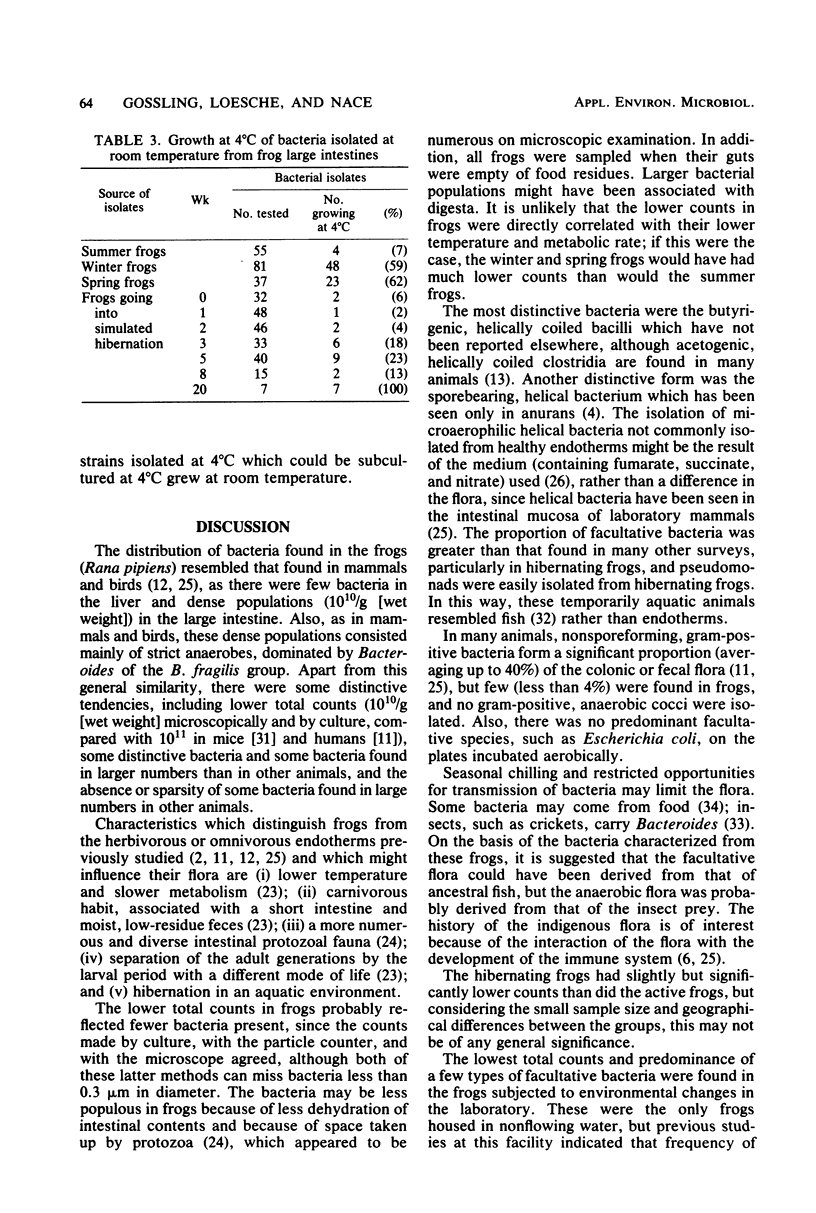
The bacteria in the large intestines of 10 northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens) were enumerated and partially characterized. Four nonhibernating frogs were collected in the summer, four hibernating frogs were collected in the winter, and two frogs just emerged from hibernation were collected in the spring. All frogs had about 10(10) bacteria per g (wet weight) of intestinal contents and about 10(9) bacteria per g (wet weight) of mucosal scraping, although the counts from the winter frogs were slightly less than those from the other two groups of frogs. Another group of 14 summer frogs, after treatment to induce hibernation, showed a drop in bacterial counts accompanied by a change in the composition of the flora. In most frogs, Bacteroides was the dominant organism. Other bacteria repeatedly isolated at high dilutions were strict anaerobes, including butyrigenic and acetogenic helically coiled bacteria; fusobacteria; and acetogenic, small, gram-positive bacilli. These data indicate that the intestinal flora of frogs is similar to that of mammals and birds and that this flora can be maintained at temperatures close to freezing.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on gastrointestinal motility. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):301–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Impey C. S., Stevens B. J. Factors affecting the incidence and anti-salmonella activity of the anaerobic caecal flora of the young chick. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Apr;82(2):263–283. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELAPORTE B. ETUDE COMPAR'EE DE GRANDS SPIRILLES FORMANT DES SPORES: SPOROSPIRILLUM (SPIRILLUM) PRAECLARUM (COLLIN) N.G., SPOROSPIRILLUM GYRINI N.SP. ET SPOROSPIRILLUM BISPORUM N.SP. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Aug;107:246–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. L., Gibbs T. J., Van Dyck P. C. Rana pipiens: health and disease. Lab Anim Care. 1966 Apr;16(2):142–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Amborski R. L., Amborski G. F., Culley D. D. Microbiological studies on septicemic bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). Am J Vet Res. 1974 Sep;35(9):1241–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussong D., Damaré J. M., Limpert R. J., Sladen W. J., Weiner R. M., Colwell R. R. Microbial impact of Canada geese (Branta canadensis) and whistling swans (Cygnus columbianus columbianus) on aquatic ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):14–20. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.14-20.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Straffon L. H. Longitudinal investigation of the role of Streptococcus mutans in human fissure decay. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):498–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.498-507.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Kaneuchi C. Ecology of the bifidobacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Nov;30(11):1799–1810. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.11.1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrovsky D. S., Snyder J. A., Iwata T., Izaka K. I., Maglott D. S., Nace G. W. Frog lysozyme. I. Its identification, occurrence as isozymes, and quantitative distribution in tissues of the leopard frog, Rana pipiens. J Exp Zool. 1976 Feb;195(2):279–290. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401950213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smibert R. M. The genus Campylobacter. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:673–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., Harrison J. H. Frog lysozyme. V. Isolation and some physical and immunochemical properties of lysozyme isozymes of the leopard frog, Rana pipiens. J Exp Zool. 1977 Oct;202(1):89–96. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402020111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Bacteriology of human experimental gingivitis: effect of plaque age. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):821–829. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.821-829.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Survival of human dental plaque flora in various transport media. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):638–644. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.638-644.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Svanberg M., Svanberg G. The predominant cultivable dental plaque flora of beagle dogs with gingivitis. J Periodontal Res. 1980 Mar;15(2):123–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1980.tb00266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Savage D. C. Influences of dietary and environmental stress on microbial populations in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):591–598. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.591-598.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J. Facultative anaerobic bacteria in the digestive tract of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) maintained in fresh water under defined culture conditions. Appl Microbiol. 1975 May;29(5):663–668. doi: 10.1128/am.29.5.663-668.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich R. G., Buthala D. A., Klug M. J. Microbiota Associated with the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Common House Cricket, Acheta domestica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):246–254. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.246-254.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Waaij D., Cohen B. J., Nace G. W. Colonization patterns of aerobic gram-negative bacteria in the cloaca of Rana pipiens. Lab Anim Sci. 1974 Apr;24(2):307–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


