Abstract
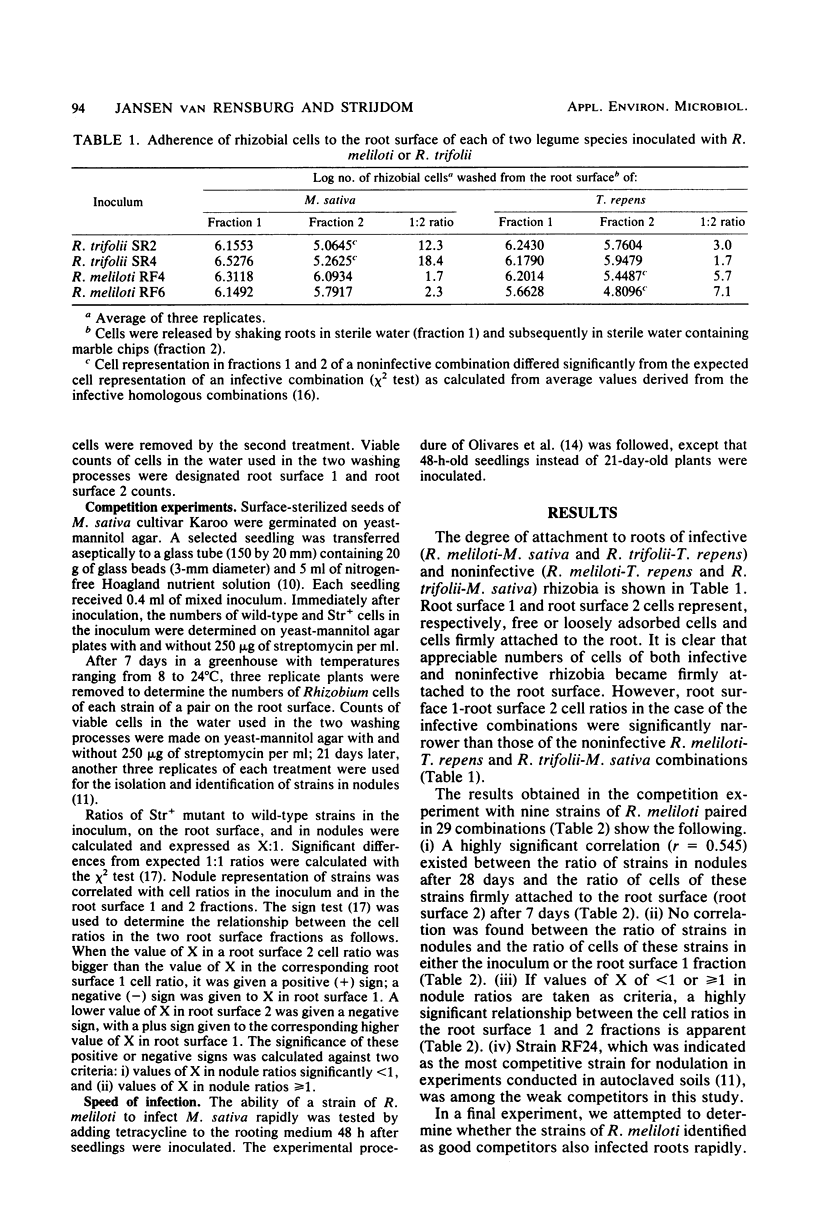
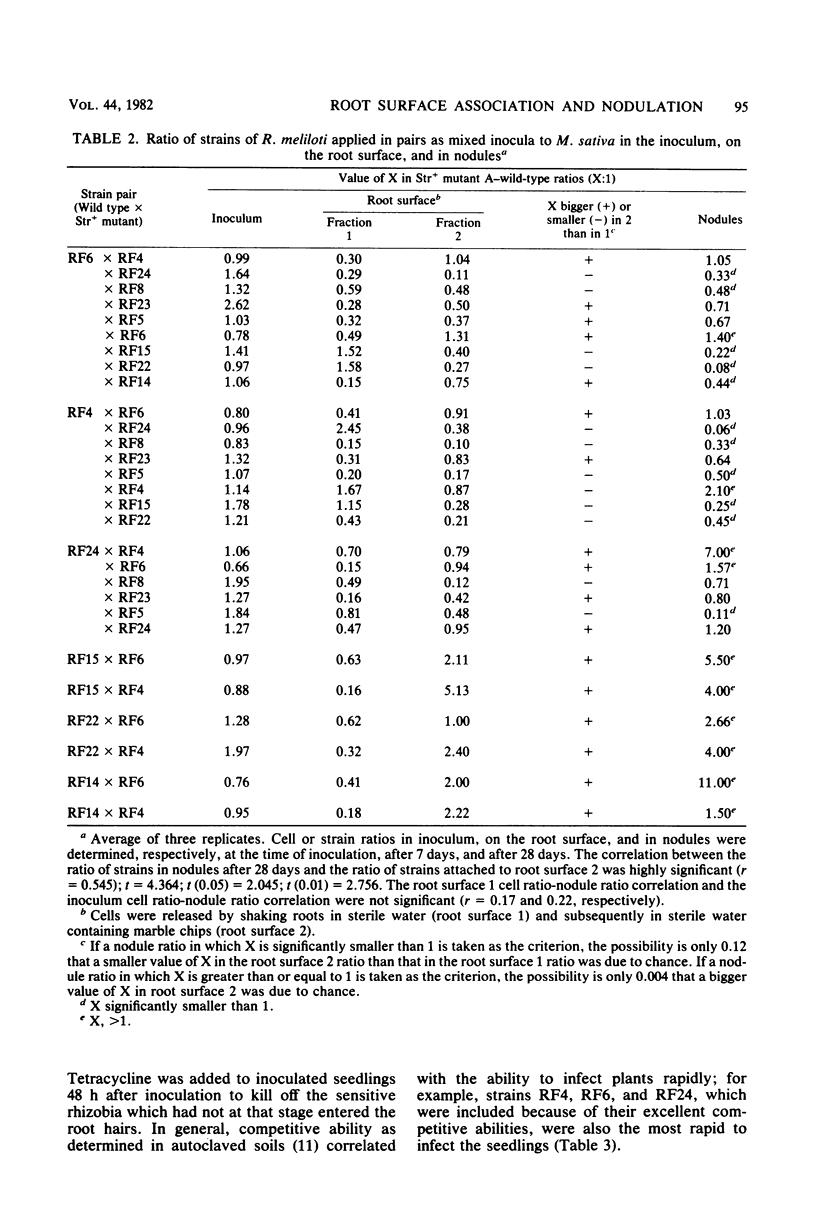
Nine strains of Rhizobium meliloti, ranging in competitive ability on Medicago sativa from excellent to poor in autoclaved soils, were paired in 29 combinations and used to inoculate M. sativa in a liquid rooting medium. A positive correlation (r = 0.545) between strain ratios in nodules after 28 days and root surface cell ratios after 7 days was determined. Two cell fractions from the root surface, representing loosely and firmly adhering cells, were investigated. Infectivity was linked to the more firmly adhering cells. A significant relationship was established between the cell ratios of competing strains in the two fractions. In another experiment, adherence of cells of both infective and noninfective Rhizobium strains to roots of M. sativa and Trifolium repens was demonstrated; the ratios of loosely to firmly adhering cells on the root surface were significantly narrower with the infective combinations than with noninfective strain-legume associations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Turgeon B. G., Bauer W. D. Early Events in the Infection of Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr) by Rhizobium japonicum: I. LOCALIZATION OF INFECTIBLE ROOT CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Napoli C. A., Hubbell D. H. Adsorption of bacteria to roots as related to host specificity in the Rhizobium-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.166-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivares J., Casadesús J., Bedmar E. J. Method for Testing Degree of Infectivity of Rhizobium meliloti Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):967–970. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.967-970.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


