Abstract
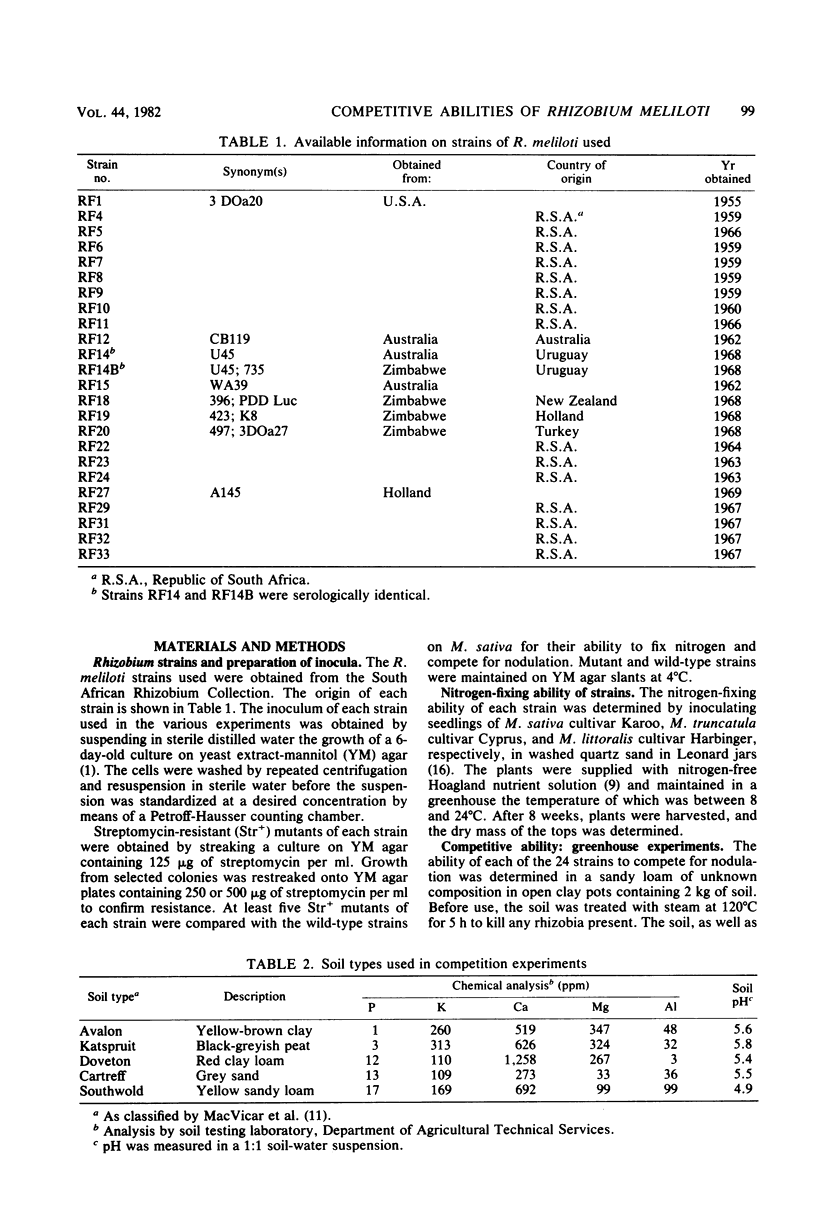
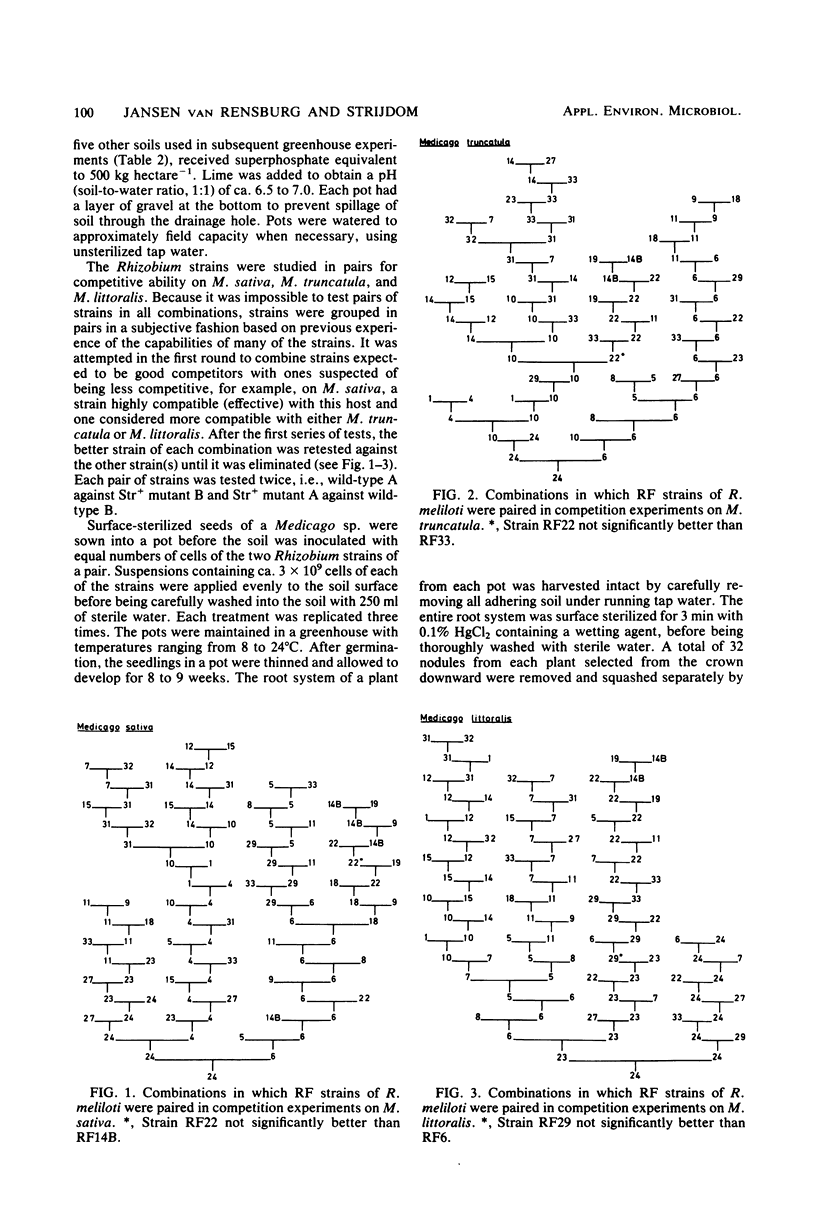
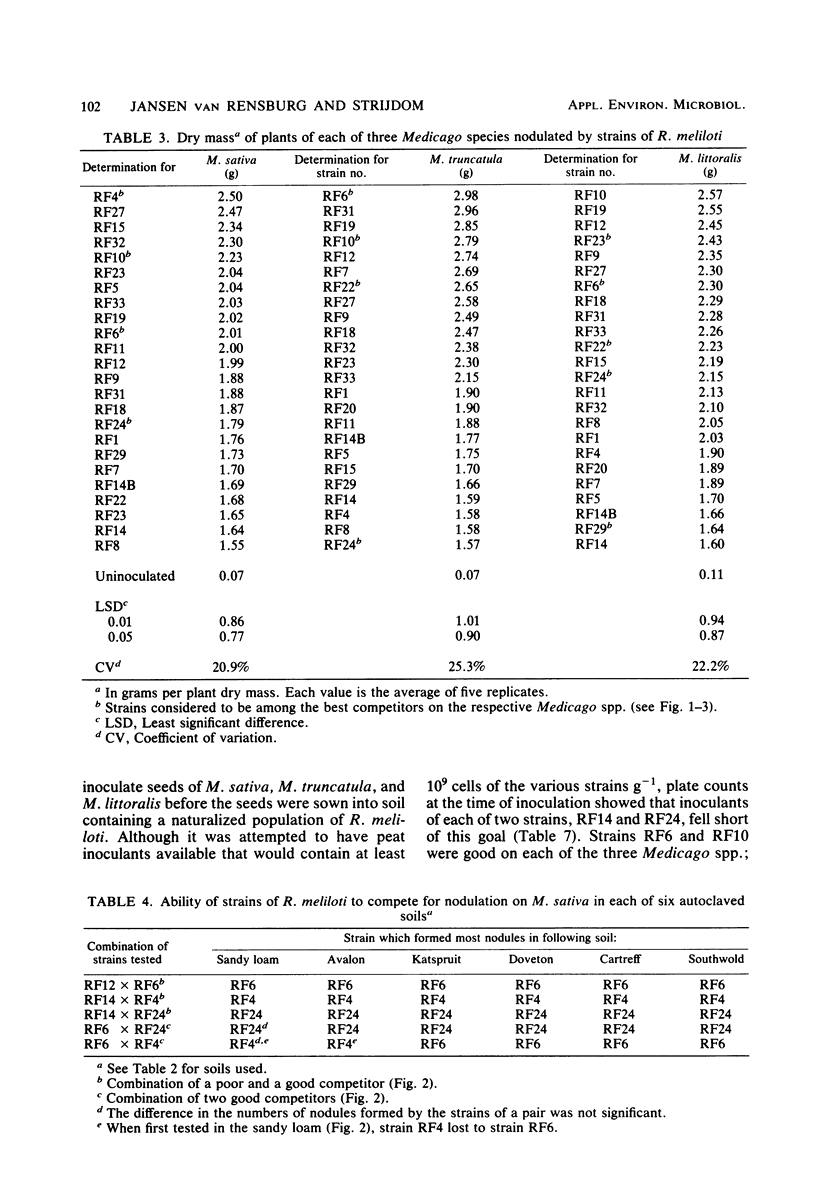
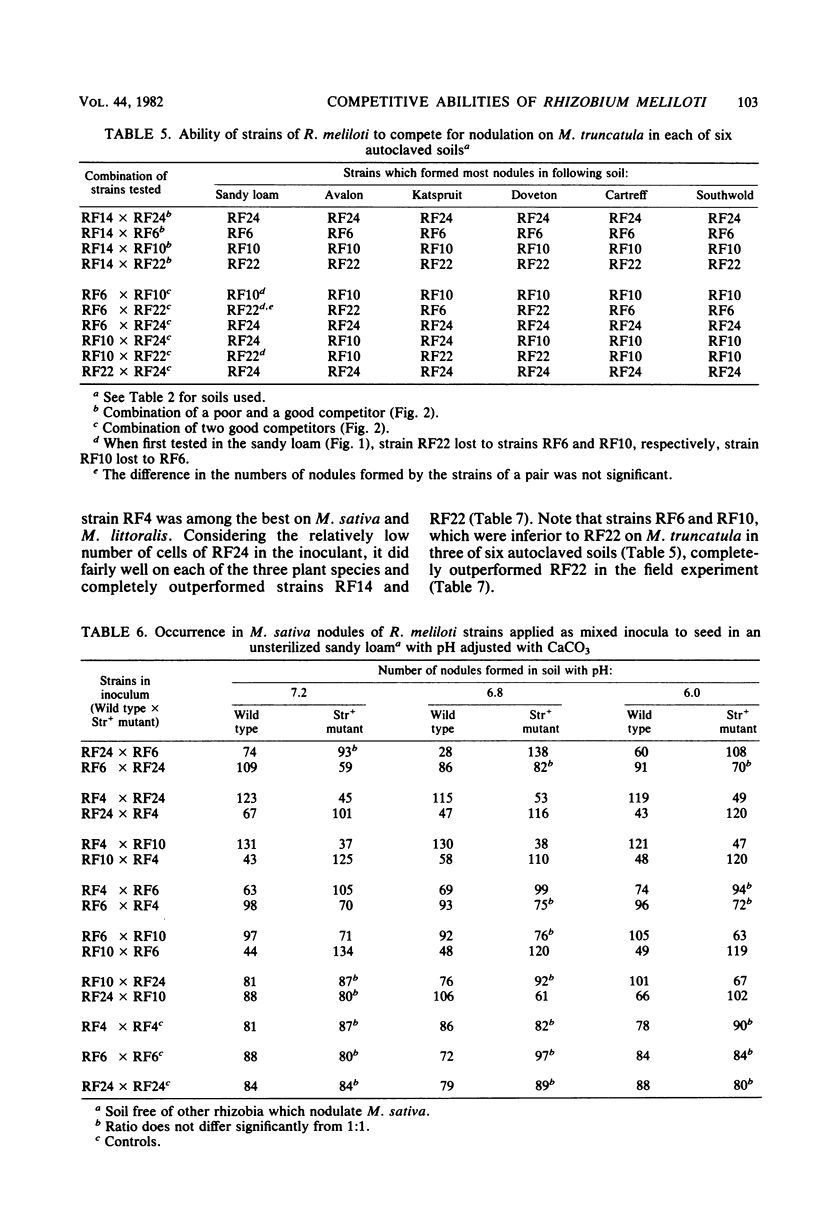
Twenty four strains of Rhizobium meliloti considered to have potential for inoculant production were grouped in pairs and tested for their ability to compete for nodulation on Medicago sativa, Medicago truncatula, and Medicago littoralis. At the outset, each pair of strains, which consisted of a wild type and a selected streptomycin-resistant mutant of another strain, was tested in an autoclaved soil. Six strain pairs, each consisting of a good and a poor competitor, reacted consistently when tested in each of five other autoclaved soils; eight pairs consisting of strains with comparable competitive abilities varied in their reactions in some of the soils, or even in the same soil when retested. An effect of soil pH on competitive ability was observed with some of these strains. Not all of the strains identified as good competitors on one or more of the Medicago spp. in the autoclaved soils were able to nodulate these plants satisfactorily in a field soil containing an established population of R. meliloti. Strain RF24, which seemed to be the best competitor on each of the three Medicago spp., grouped among the less effective strains on two of the legumes. Two strains of R. meliloti frequently used for inoculant production differed markedly with regard to competitive ability; this places some doubt on the relevancy of singling out competitive ability for special attention when selecting a strain for inoculant production.
Full text
PDF