Abstract
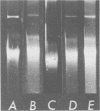
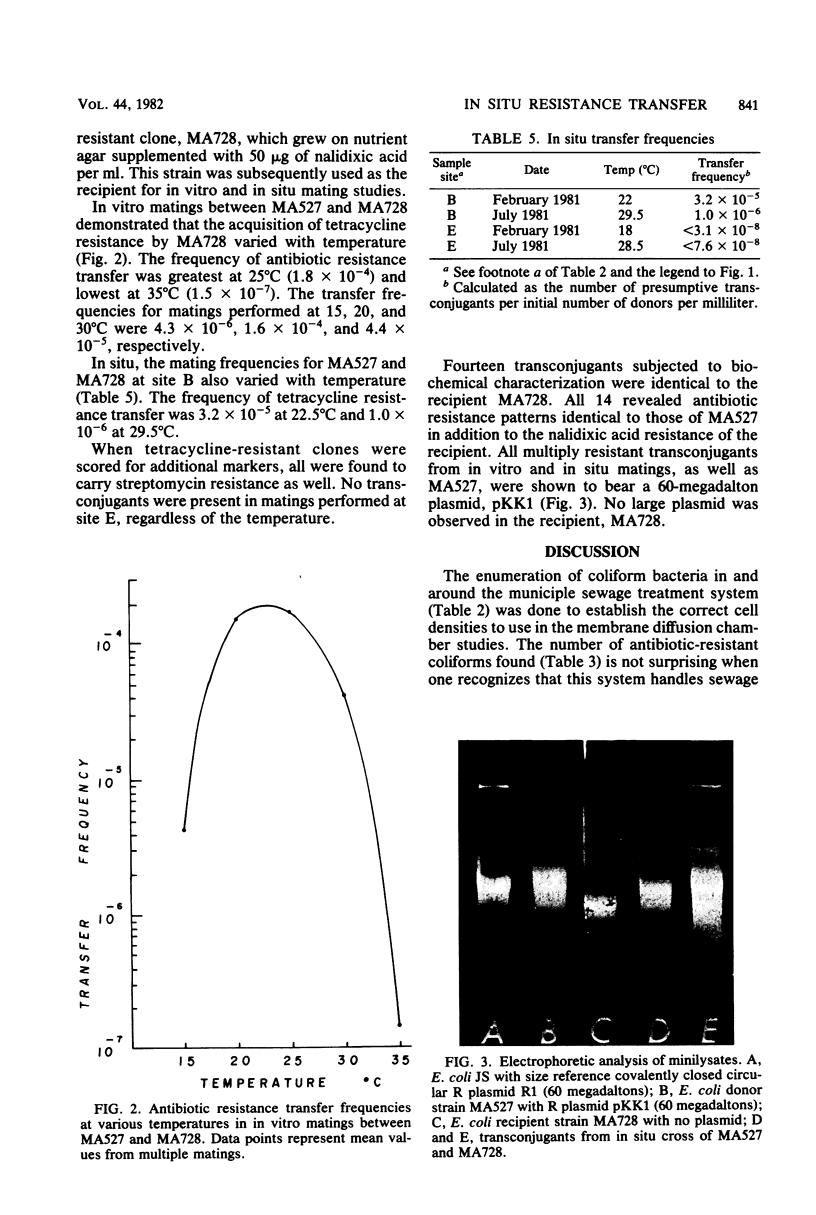
Coliform bacteria were isolated from raw sewage and sewage effluent-receiving waters and tested for their antibiotic susceptibility patterns and their ability to transfer antibiotic resistance to Escherichia coli K-12 C600. An environmental isolate of E. coli (MA527) capable of transferring antibiotic resistance to C600 was mated, both in vitro and in situ, with an antibiotic-sensitive E. coli environmental isolate (MA728). In situ matings were conducted in modified membrane diffusion chambers, in the degritter tank at the Grant Street (Melbourne, Fla.) sewage treatment facility, and in the sewage effluent-receiving waters in Melbourne, Fla. The transfer frequencies in situ were 3.2 x 10(-5) to 1.0 x 10(-6), compared with 1.6 x 10(-4) to 4.4 x 10(-5) observed in vitro. Transfer was shown to occur in raw sewage but was not detected in the effluent-receiving waters. The presence of a 60-megadalton plasmid species in both donor and transconjugants, but not in the recipients, provided physical evidence for the transfer of antibiotic resistance in situ.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S. The ecology of transferable drug resistance in the enterobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:131–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. A., Elkan G. H. Multiple antibiotic resistance in Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):867–870. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.867-870.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. D. Antibiotic resistance among coliform and fecal coliform bacteria isolated from sewage, seawater, and marine shellfish. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):879–884. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corliss T. L., Cohen P. S., Cabelli V. J. R-Plasmid Transfer to and from Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Human Fecal Samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):959–966. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.959-966.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Smith D. I. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial agents. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:469–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust M. A., Aotaky A. E., Hargadon M. T. Effect of physical parameters on the in situ survival of Escherichia coli MC-6 in an estuarine environment. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):800–806. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.800-806.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feary T. W., Sturtevant A. B., Jr, Lankford J. Antibiotic-resistant coliforms in fresh and salt water. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Sep;25(3):215–220. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Gorden R. W., Hazen T. C., Esch G. W. Aeromonas distribution and survival in a thermally altered lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.114-122.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Gorden R. W. Modification of membrane diffusion chambers for deep-water studies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):207–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.207-210.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine T. D., 3rd, Hoadley A. W. Transferable drug resistance associated with coliforms isolated from hospital and domestic sewage. Health Lab Sci. 1976 Oct;13(4):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., Prozesky O. W. Drug resistance of coliform bacteria in hospital and city sewage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helinski D. R. Plasmid determined resistance to antibiotics: molecular properties of R factors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:437–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.002253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasweck K. L., Fliermans C. B. Lactose variability of Escherichia coli in thermally stressed reactor effluent waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):739–746. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.739-746.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton K. B., Richmond M. H., Bevan R., Gillespie W. A. Antibiotic resistance and R factors in coliform bacilli isolated from hospital and domestic sewage. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Feb;7(1):91–103. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters: field and laboratory studies with membrane-filter chambers. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):805–811. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.805-811.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra D. S., Kumar A., Singh I. P. Antibiotic resistance and transfer factor (R+) in E. coli isolated from raw sewage. Indian J Med Res. 1979 Oct;70:559–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S. The R factors. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jan;119(1):89–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. Some environmental consequences of the use of antibiotics: or 'what goes up must come down'. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;35(2):155–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Cabelli V. J. R-plasmid transfer frequencies from environmental isolates of Escherichia coli to laboratory and fecal strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):756–764. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.756-764.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Incidence of R + Escherichia coli in coastal bathing waters of Britain. Nature. 1971 Nov 19;234(5325):155–156. doi: 10.1038/234155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Incidence of river water of Escherichia coli containing R factors. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2281286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z., Green P. Thermosensitive antibiotic resistance plasmids in enterobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):37–47. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A. B., Jr, Feary T. W. Incidence of infectious drug resistance among lactose-fermenting bacteria isolated from raw and treated sewage. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):918–924. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.918-924.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. H. Temperature dependence of mating-pair formation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):222–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.222-224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]