Abstract
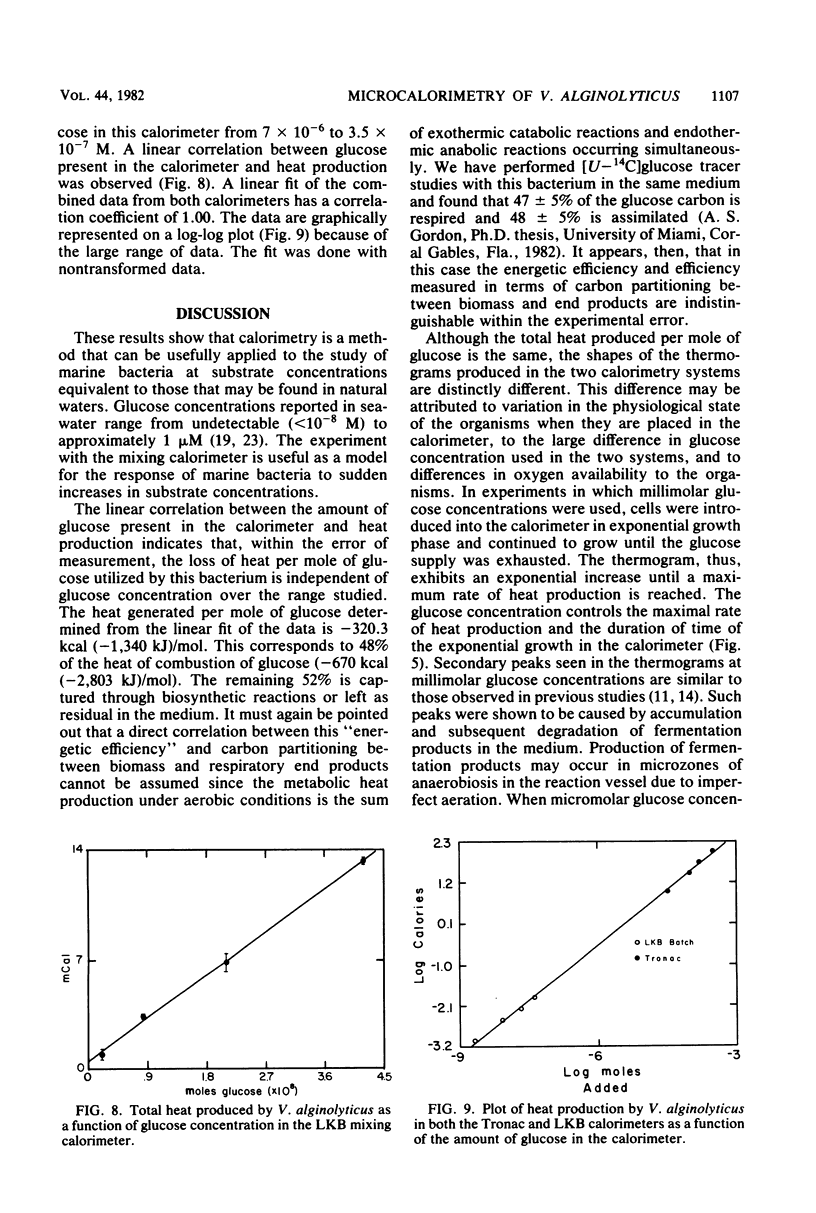
Microcalorimetric measurements of heat production from glucose by Vibrio alginolyticus were made to assess the viability of calorimetry as a technique for studying the metabolism of marine bacteria at organic nutrient concentrations found in marine waters. The results show that the metabolism of glucose by this bacterium can be measured by calorimetry at submicromolar concentrations. A linear correlation between glucose concentration and total heat production was observed over a concentration range of 8 mM to 0.35 μM. It is suggested that these data indicate a constant efficiency of metabolism for this bacterium over the wide range of glucose concentrations studied.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beezer A. E., Newell R. D., Tyrrell H. J. Characterisation and metabolic studies of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces fragilis by flow microcalorimetry. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(1):55–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00400779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belaich A., Belaich J. P. Microcalorimetric study of the anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli: growth thermograms in a synthetic medium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.14-18.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belaich A., Belaich J. P. Microcalorimetric study of the anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli: measurements of the affinity of whole cells for various energy substrates. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.19-24.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belaich J. P., Senez J. C., Murgier M. Microcalorimetric study of glucose permeation in microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1750–1757. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1750-1757.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney C. L., Wang D. I., Mateles R. I. Measurement of heat evolution and correlation with oxygen consumption during microbial growth. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1969 May;11(3):269–281. doi: 10.1002/bit.260110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoun Z., Belaich J. P. Microcalorimetric study of Escherichia coli aerobic growth: kinetics and experimental enthalpy associated with growth on succinic acid. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):377–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.377-380.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessers A., Chiang C., Laudelout H. Calorimetric determination of free energy efficiency in Nitrobacter winogradskyi. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;64(1):71–76. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Few G. A., Yau A. O., Prichard F. E., James A. M. A microcalorimetric study of the growth of Klebsiella aerogenes in simple salts/glucose media. Microbios. 1976;16(63):37–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long R. A., Sprott G. D., Labelle J. L., Martin W. G., Schneider H. Thermal events associated with active membrane transport in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):656–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlvaine P., Langerman N. A calorimetric investigation of the growth of the luminescent bacteria Beneckea harveyi and Photobacterium leiognathi. Biophys J. 1977 Jan;17(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85624-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J., Wiebe W. J. Growth yield and efficiency in chemosynthetic microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:155–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry B. F., Beezer A. E., Miles R. J. Flow microcalorimetric studies of yeast growth: fundamental aspects. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;47(3):527–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


