Abstract
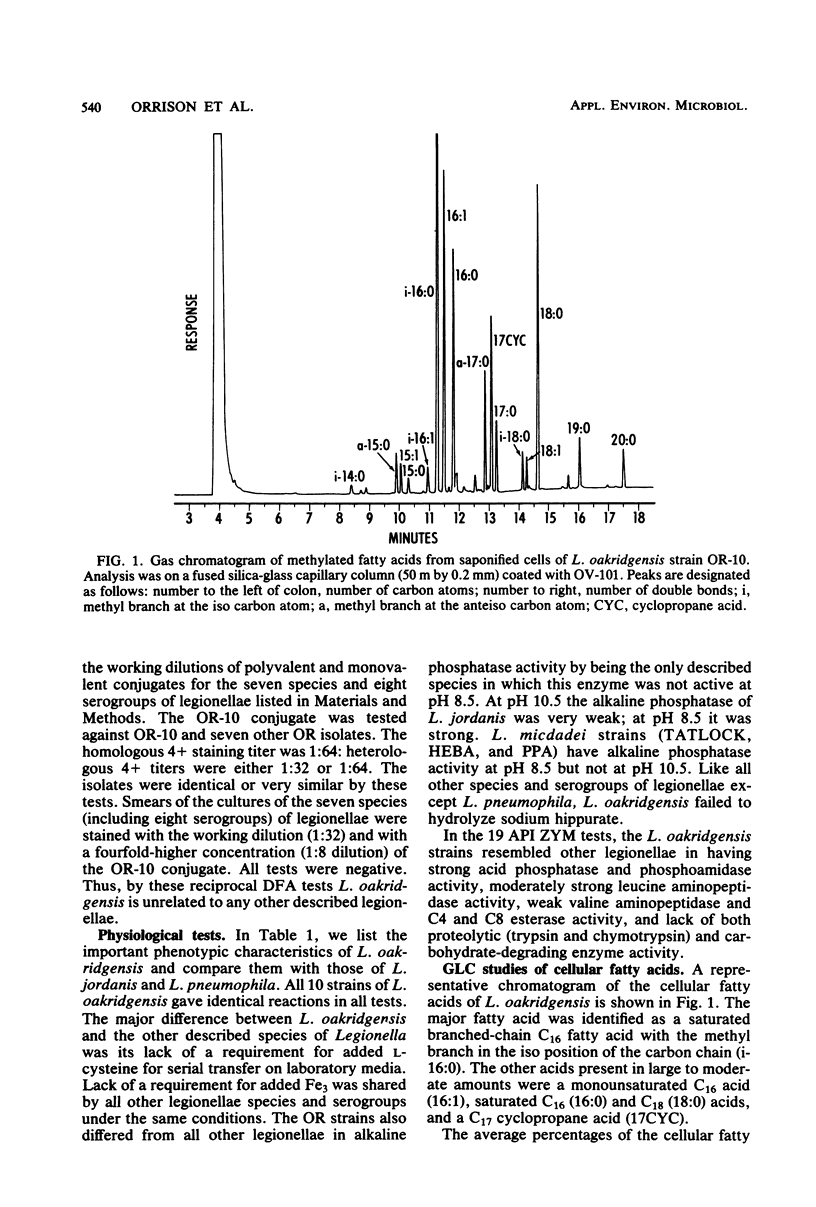
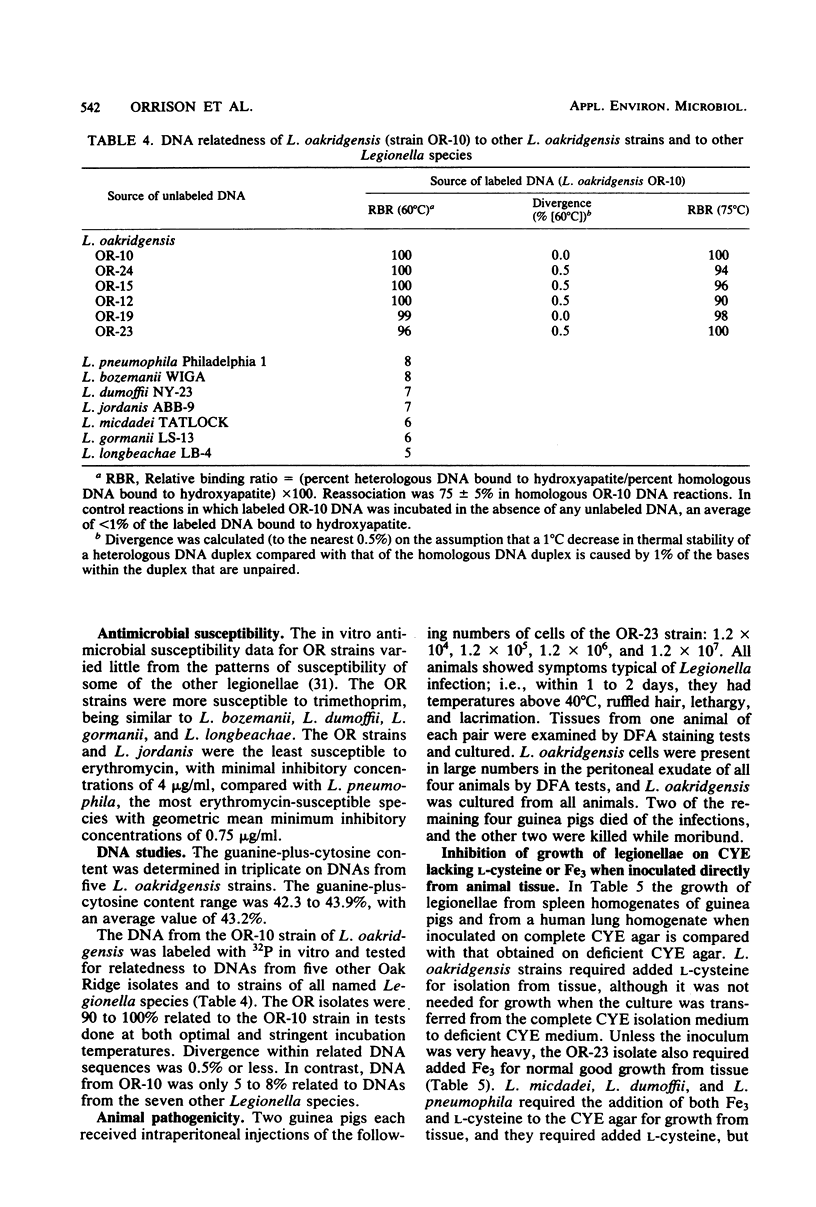
We describe a new species of Legionella represented by 10 strains isolated from industrial cooling towers. Legionella oakridgensis differed genetically from the other seven species of Legionella in DNA hybridization studies and differed serologically in direct fluorescent-antibody tests. The new species, unlike all other species except L. jordanis, did not require added L-cysteine for growth in serial transfer on charcoal-yeast extract agar. L. oakridgensis, as well as three other species tested, required L-cysteine for primary isolation from animal tissues. L. oakridgensis was the only species of Legionella that failed to produce alkaline phosphatase at pH 8.5. In all other respects, it resembled other species of Legionella, including having a high content of branched-chain cellular fatty acids and being pathogenic for guinea pigs. These bacteria have not yet been associated with human disease, but they are potential causes of legionellosis.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B., Rasheed J. K. Aromatic substrate specificity of browning by cultures of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):619–620. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band J. D., LaVenture M., Davis J. P., Mallison G. F., Skaliy P., Hayes P. S., Schell W. L., Weiss H., Greenberg D. J., Fraser D. W. Epidemic Legionnaires' disease. Airborne transmission down a chimney. JAMA. 1981 Jun 19;245(23):2404–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Sorg R. J., Thomason B. M., Hicklin M. D., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J., Wulf M. R. Recognition of a second serogroup of Legionella longbeachae. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):674–677. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.674-677.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Blackmon J. A., Hicklin M. D., Cole R. M., Callaway C. S. Ultrastructure of the agent of Legionnaires' disease in the human lung. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;71(1):43–50. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Gorman G. W., Orrison L. H., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Wilkinson H. W., Johnson S. E., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella jordanis: a new species of Legionella isolated from water and sewage. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):290–297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.290-297.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. A. A simplified Leifson flagella stain. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):632–634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.632-634.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Fraser D. W., Skaliy P., Perlino C. A., Elsea W. R., Mallison G. F., Hayes P. S. Legionnaires' disease outbreak at an Atlanta, Georgia, Country Club: evidence for spread from an evaporative condenser. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Apr;111(4):425–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Mallison G. F., Weeks R. M., Levy J. S., Wong E. W., Schaffner W. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):365–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, McKinney R. M., Skaliy P., Gorman G. W. A fifth serogroup of Legionella pneumophila. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):58–59. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick T. H., Gregg M. B., Berman B., Mallison G., Rhodes W. W., Jr, Kassanoff I. Pontiac fever. An epidemic of unknown etiology in a health department: I. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Feb;107(2):149–160. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A. Hippurate hydrolysis by Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):240–242. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.240-242.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R. Dihydroxy and monohydroxy fatty acids in Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):373–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.373-381.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Porschen R. K., Edelstein P. H., Bissett M. L., Harris P. P., Bondell S. P., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Ein M. E., Lindquist D. S. Legionella longbeachae species nova, another etiologic agent of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):739–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thacker L., Harris P. P., Lewallen K. R., Hebert G. A., Edelstein P. H., Thomason B. M. Four serogroups of Legionnaires' disease bacteria defined by direct immunofluorescence. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):621–624. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A., Feeley J. C., Wong E. S., Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella gormanii sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.718-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W. Gas-liquid chromatography as an analytical tool in microbiology. J Chromatogr. 1981 Jan 9;203:337–347. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Karr D. E., Dees S. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of Legionella longbeachae sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):692–694. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.692-694.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Samuels S. B., Liddle J., McKinney R. M. Occurrence of branched-cahin hydroxy fatty acids in Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1018-1024.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B., Dees S. B., McDougal L. K., Dodd D. J. Characteristics of environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.109-115.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Allen R. G. Liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):19–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.19-21.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


