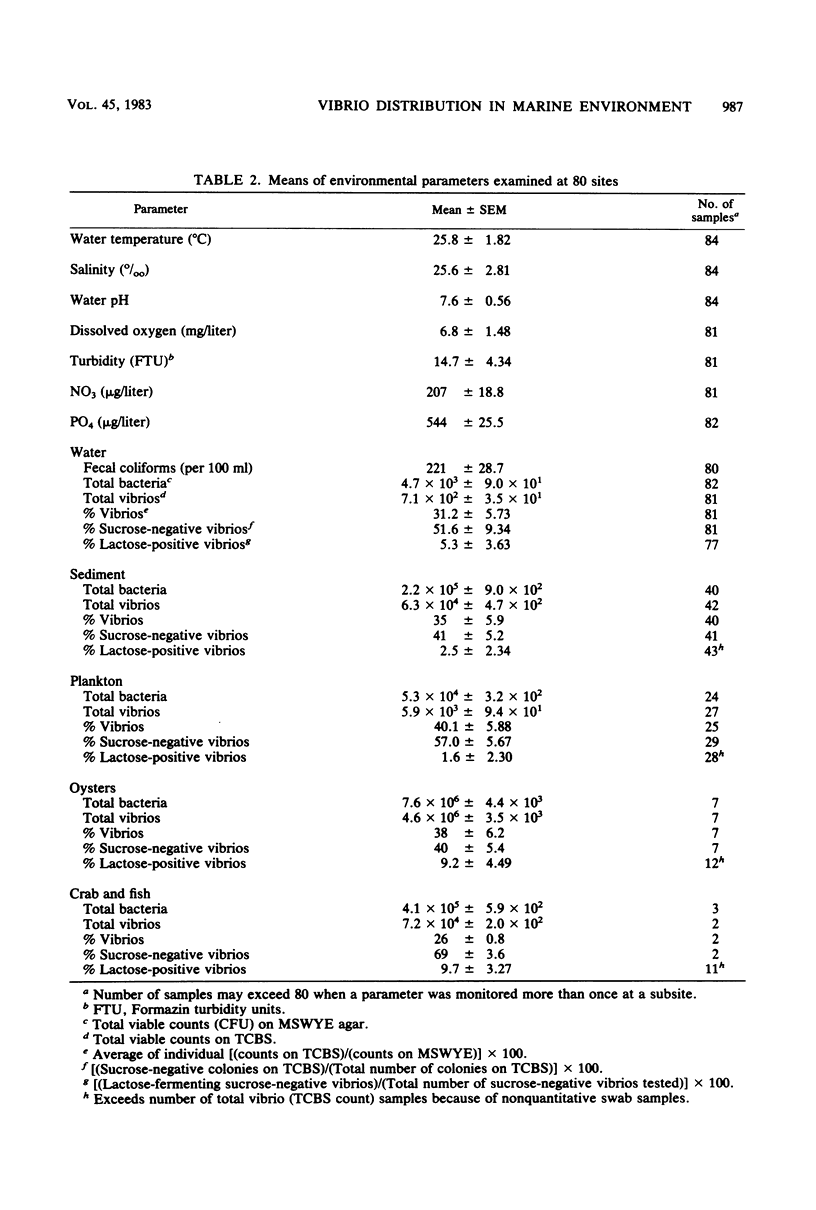
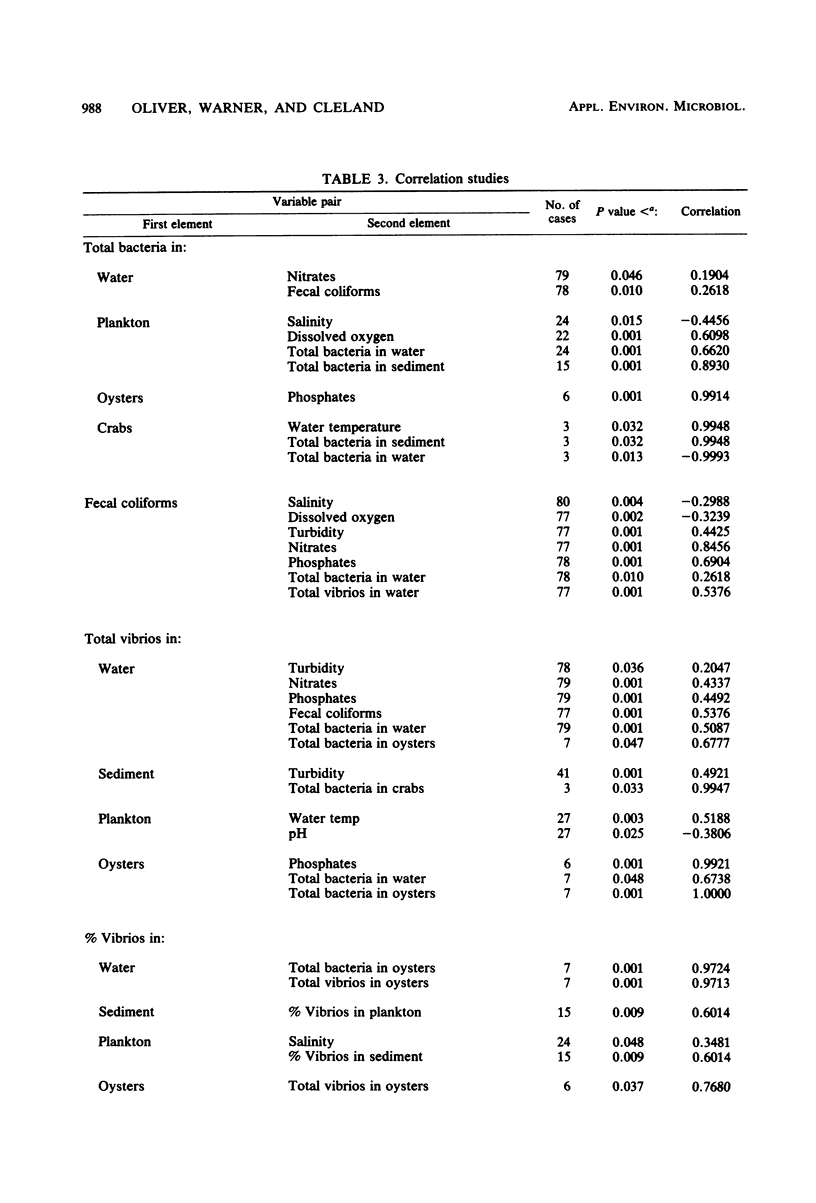
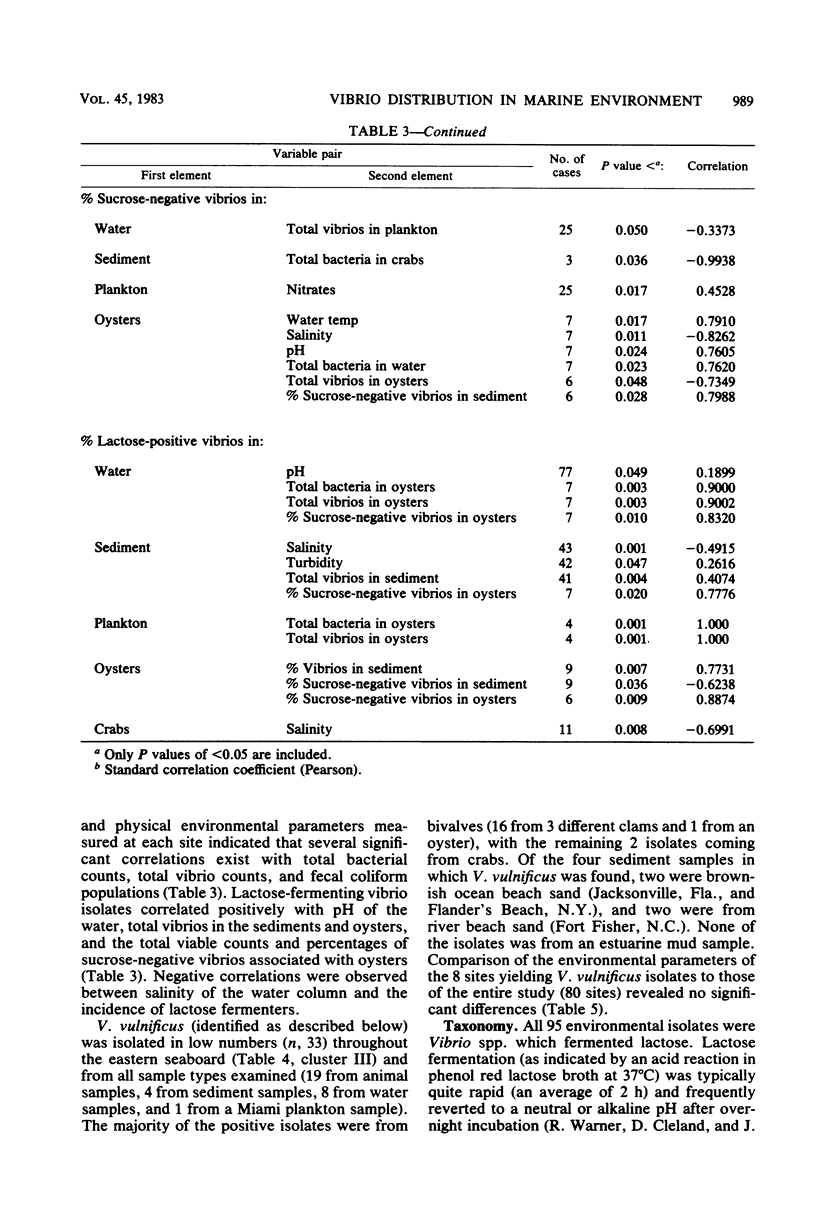
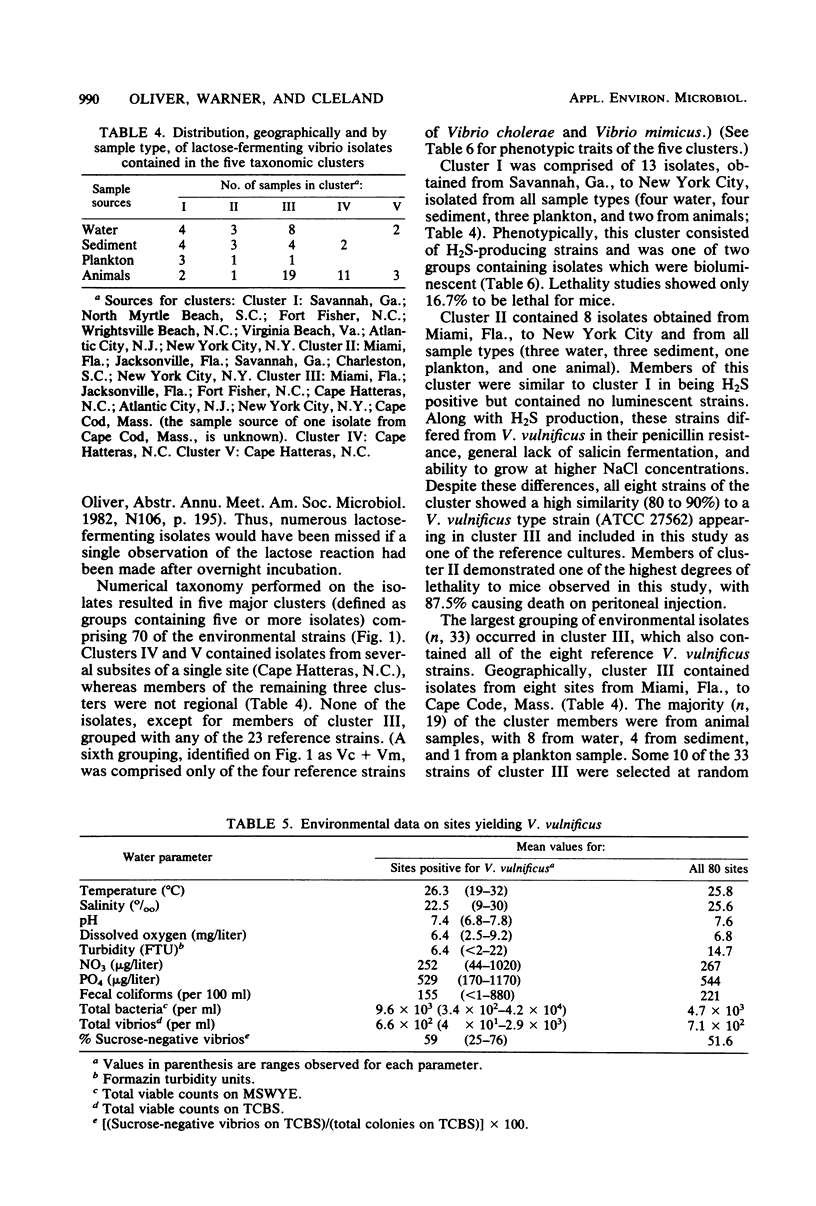
Abstract
During the summer of 1981, 3,887 sucrose-negative vibrios were isolated from seawater, sediment, plankton, and animal samples taken from 80 sites from Miami, Fla., to Portland, Maine. Of these, 4.2% were able to ferment lactose. The lactose-positive strains isolated from the various samples correlated positively with pH and turbidity of the water, vibrios in the sediment and oysters, and total bacterial counts in oysters. Negative correlations were obtained for water salinity. Numerical taxonomy was performed on 95 of the lactose-fermenting environmental isolates and 23 reference strains. Five clusters resulted, with the major cluster containing 33 of the environmental isolates and all of the Vibrio vulnificus reference strains. The 33 isolates, which produced an acid reaction in lactose broth within hours of initial inoculation, represented 20% of all lactose-fermenting vibrios studied. These isolates were nearly identical phenotypically to clinical strains of V. vulnificus studied by the Centers for Disease Control, Atlanta, Ga., and by our laboratory, and their identification was confirmed by DNA-DNA hybridization studies. V. vulnificus was isolated from all sample types and from Miami to Cape Cod, Mass., and comparison of the environmental parameters of the eight subsites yielding this species with those of all 80 subsites revealed no significant differences. The majority of the isolates were obtained from animals, with clams providing most (84%) of these. On injection into mice, 82% of the V. vulnificus isolates resulted in death. Members of the remaining four clusters contained strains which differed from V. vulnificus in such phenotypic traits as luminescence and in urease or H2S production. None of the other reference cultures, including nine other Vibrio species, were contained in the remaining clusters, and these isolates could not be identified. Most of these were also lethal for mice. Phenotypic differences, potential pathogenicity, and geographic distribution of the five clusters were examined. It is concluded that V. vulnificus is a ubiquitous organism, both geographically and in a variety of environmental sources, although it occurs in relatively low numbers. The public health significance of this organism and of the other unidentified lactose-fermenting Vibrio species is discussed.
Full text
PDF

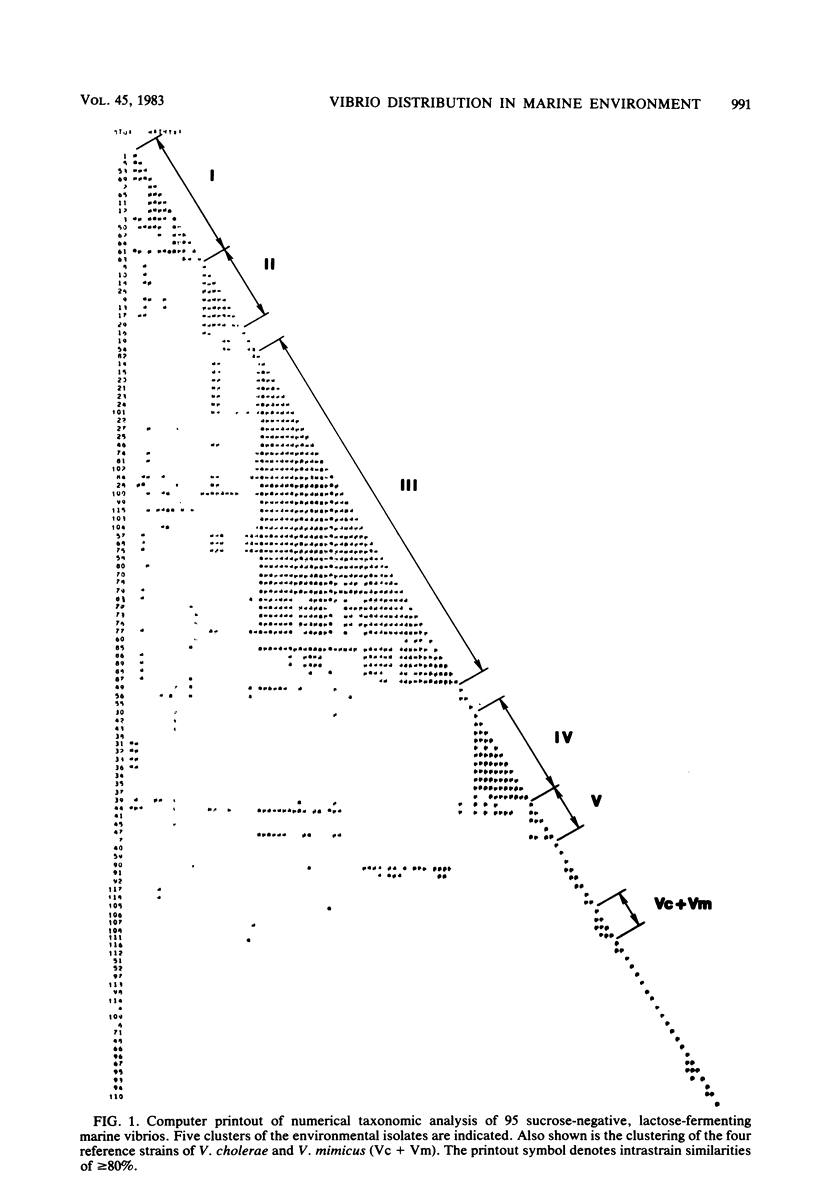
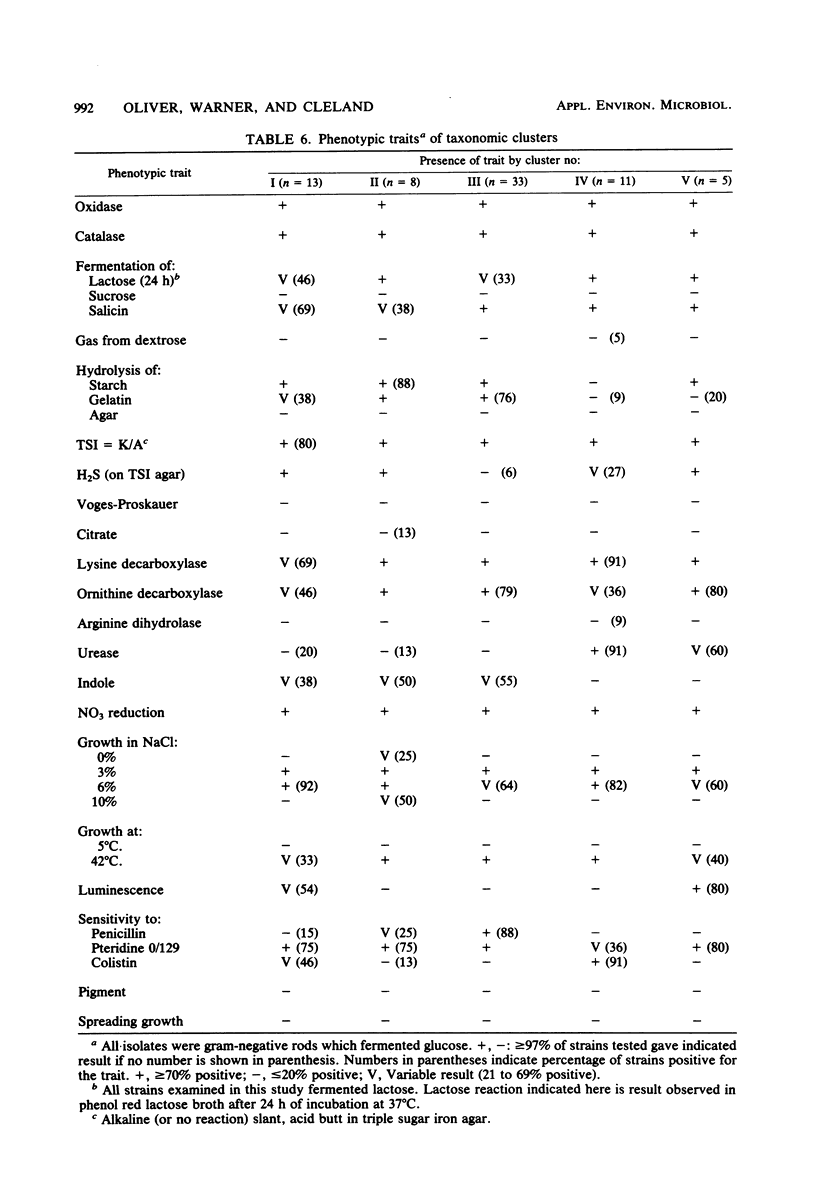

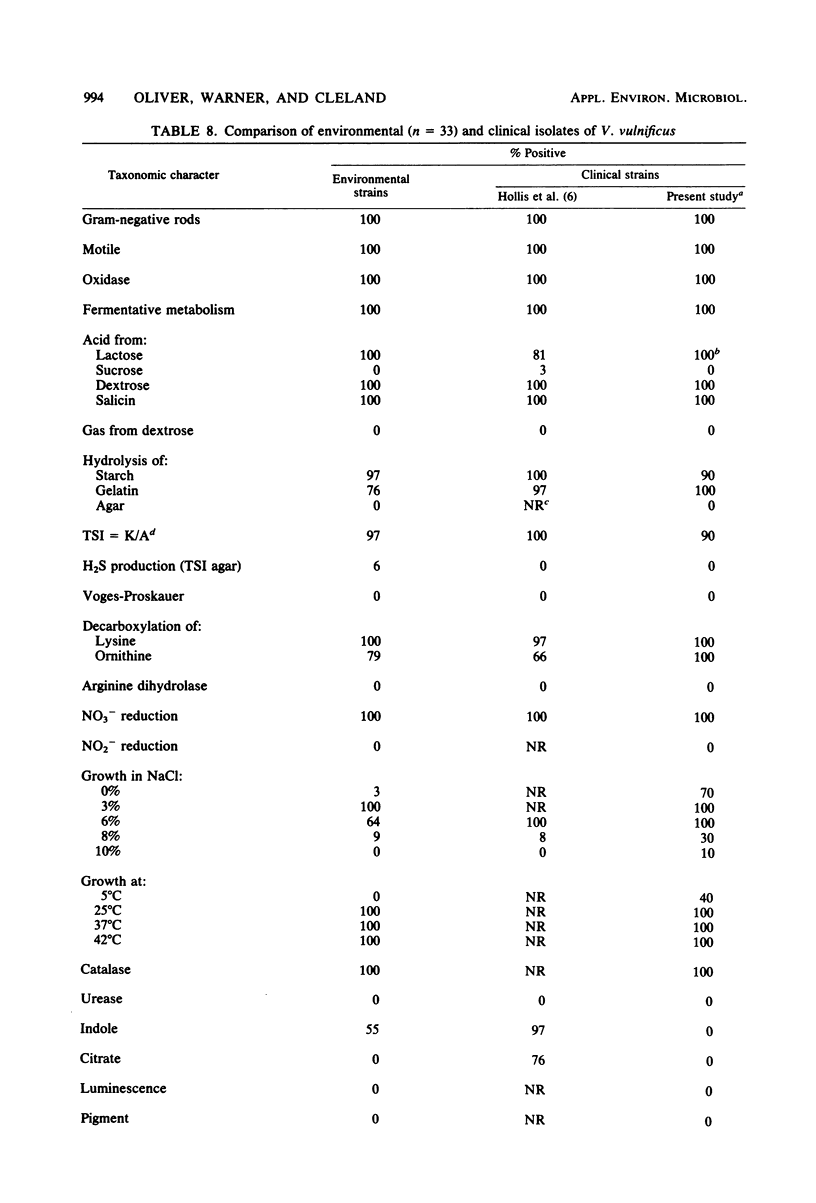
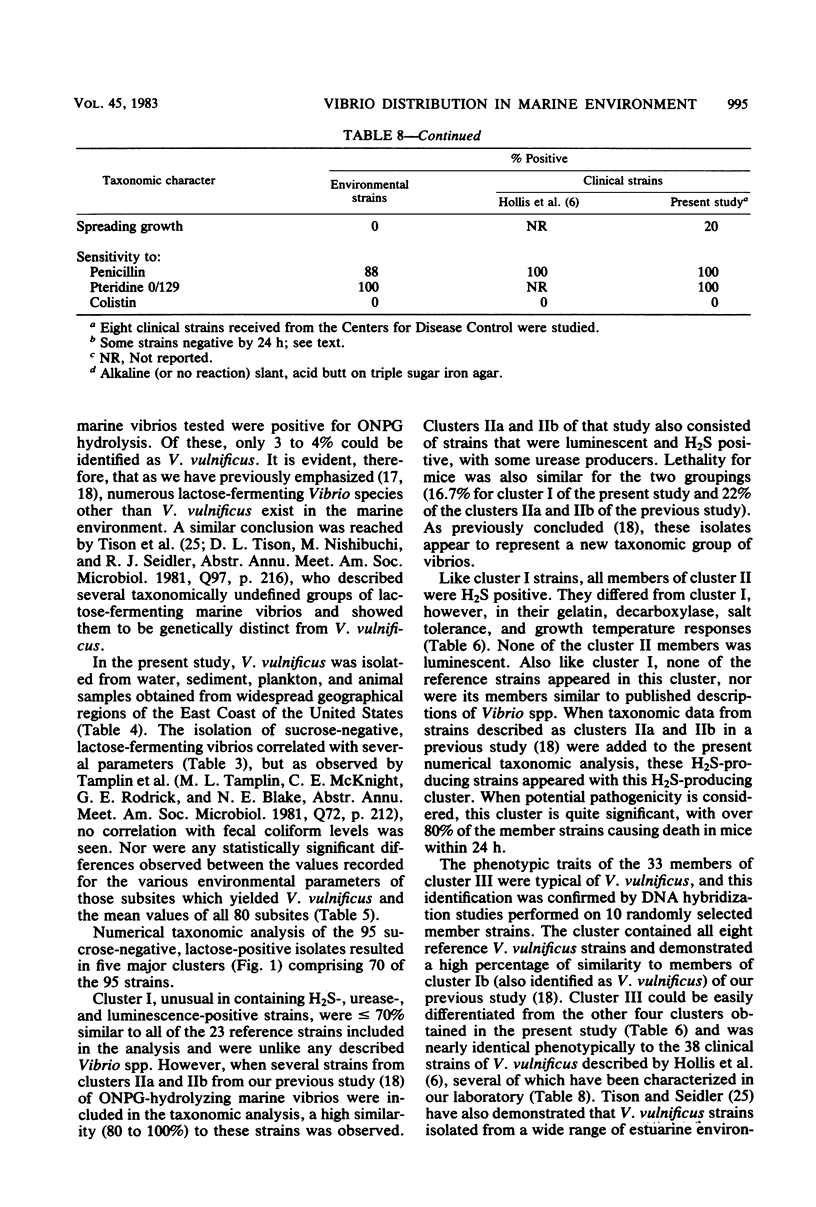



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowdre J. H., Poole M. D., Oliver J. D. Edema and hemoconcentration in mice experimentally infected with Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1193–1199. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1193-1199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus vibrio: numerical taxonomy of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and related Vibrio species. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):410–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.410-433.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. K., Bowen T. E. Halophilic vibrios from human tissue infections on the pacific coast of Australia. Pathology. 1980 Jul;12(3):397–402. doi: 10.3109/00313028009077102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Calia F. M. Hemolytic reaction of clinical and environmental strains of Vibrio vulnificus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):457–459. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.457-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Adsorption of Vibrio parahaemolyticus onto chitin and copepods. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):269–274. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.269-274.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Ecology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.24-32.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Avery D. M. Lactose-positive Vibrio in seawater: a cause of pneumonia and septicemia in a drowning victim. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):278–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.278-280.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., McCormick W. F. Acute bacterial myositis caused by Vibrio vulnificus. JAMA. 1981 Jul 3;246(1):72–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A., Lockwood D. Detection of extracellular toxin(s) produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.583-590.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love M., Teebken-Fisher D., Hose J. E., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hickman F. W., Fanning G. R. Vibrio damsela, a Marine Bacterium, Causes Skin Ulcers on the Damselfish Chromis punctipinnis. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1139–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.214.4525.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Kohno S., Ikeda T., Saruwatari K., Ninomiya H. Fulminating lactose-positive Vibrio septicemia. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1978 Nov;28(6):937–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1978.tb01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens A., Nagler J., Hansen W., Gepts-Friedenreich E. Halophilic, lactose-positive Vibrio in a case of fatal septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):233–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.233-235.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhofer T. R., Podgore J. K. Urea-hydrolyzing Vibrio parahaemolyticus associated with acute gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):581–583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.581-583.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Warner R. A., Cleland D. R. Distribution and ecology of Vibrio vulnificus and other lactose-fermenting marine vibrios in coastal waters of the southeastern United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1404–1414. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1404-1414.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole M. D., Oliver J. D. Experimental pathogenicity and mortality in ligated ileal loop studies of the newly reported halophilic lactose-positive Vibrio sp. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):126–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.126-129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. C., Merkel J. R. Collagenolytic activity of Vibrio vulnificus: potential contribution to its invasiveness. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1155–1156. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1155-1156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Nishibuchi M., Greenwood J. D., Seidler R. J. Vibrio vulnificus biogroup 2: new biogroup pathogenic for eels. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):640–646. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.640-646.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D. Role of iron in the pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):503–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.503-507.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


