Abstract
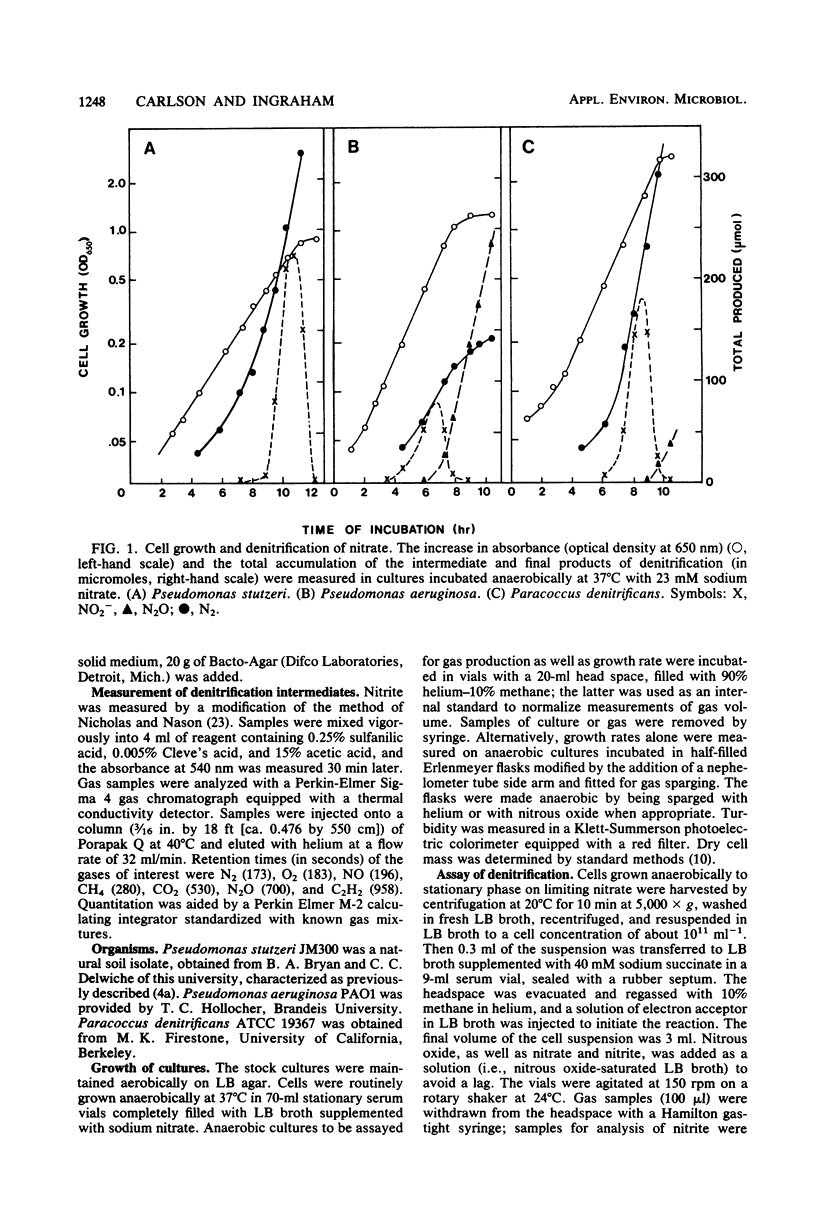
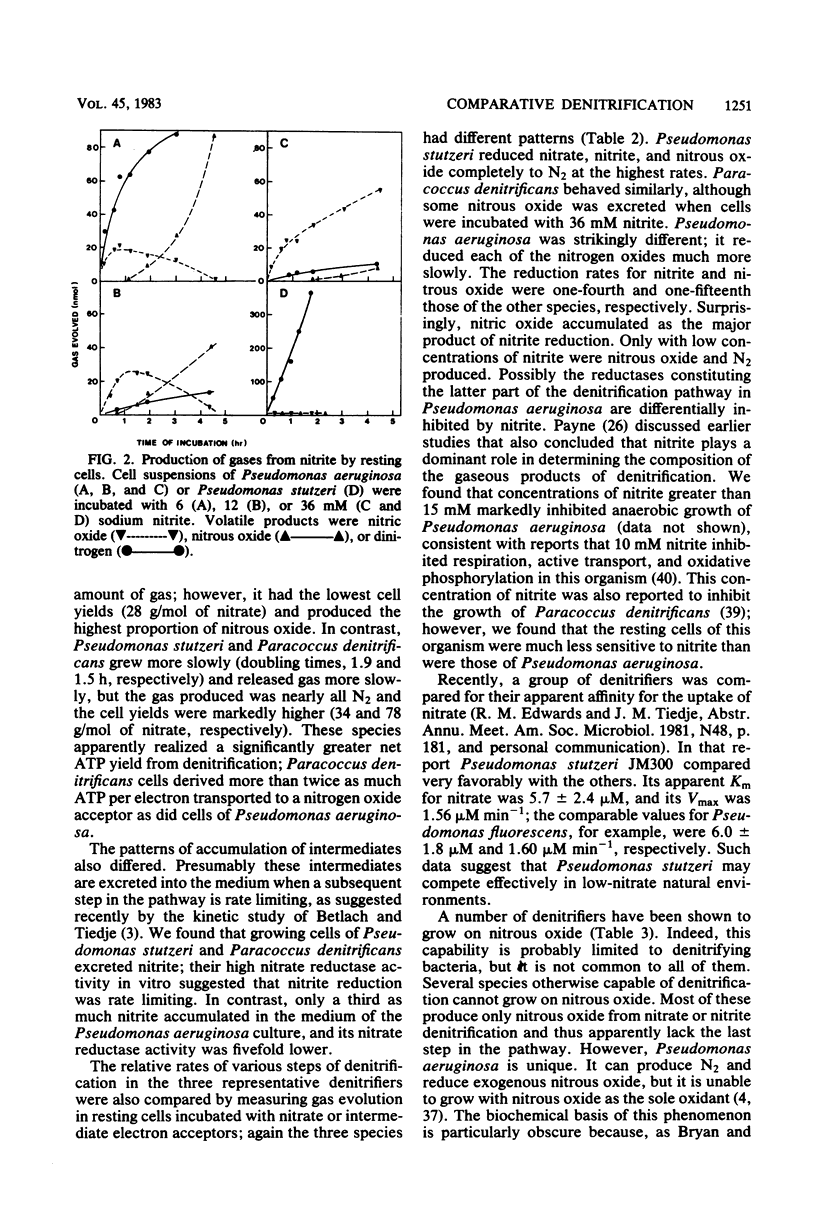
A comparison was made of denitrification by Pseudomonas stutzeri, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Paracoccus denitrificans. Although all three organisms reduced nitrate to dinitrogen gas, they did so at different rates and accumulated different kinds and amounts of intermediates. Their rates of anaerobic growth on nitrate varied about 1.5-fold; concomitant gas production varied more than 8-fold. Cell yields from nitrate varied threefold. Rates of gas production by resting cells incubated with nitrate, nitrite, or nitrous oxide varied 2-, 6-, and 15-fold, respectively, among the three species. The composition of the gas produced also varied markedly: Pseudomonas stutzeri produced only dinitrogen; Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Paracoccus denitrificans produced nitrous oxide as well; and under certain conditions Pseudomonas aeruginosa produced even more nitrous oxide than dinitrogen. Pseudomonas stutzeri and Paracoccus denitrificans rapidly reduced nitrate, nitrite, and nitrous oxide and were able to grow anaerobically when any of these nitrogen oxides were present in the medium. Pseudomonas aeruginosa reduced these oxides slowly and was unable to grow anaerobically at the expense of nitrous oxide. Furthermore, nitric and nitrous oxide reduction by Pseudomonas aeruginosa were exceptionally sensitive to inhibition by nitrite. Thus, although it has been well studied physiologically and genetically, Pseudomonas aeruginosa may not be the best species for studying the later steps of the denitrification pathway.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. B., VAN NIEL C. B. Experiments on bacterial denitrification. J Bacteriol. 1952 Sep;64(3):397–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.3.397-412.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of cytochrome c' from Alcaligenes sp. N.C.I.B. 11015. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):751–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1350751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M. R., Tiedje J. M. Kinetic explanation for accumulation of nitrite, nitric oxide, and nitrous oxide during bacterial denitrification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1074–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1074-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Pierson L. S., Rosen J. J., Ingraham J. L. Pseudomonas stutzeri and related species undergo natural transformation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):93–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.93-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone M. K., Firestone R. B., Tiedje J. M. Nitric oxide as an intermediate in denitrification: evidence from nitrogen-13 isotope exchange. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):10–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90575-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. L. Etude de la dénitrification chez une bactérie thermophile sporulée. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):447–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg E. P., Becker G. E. Nitrous oxide as end product of denitrification by strains of fluorescent pseudomonads. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jul;23(7):903–907. doi: 10.1139/m77-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART L. T., LARSON A. D., MCCLESKEY C. S. DENITRIFICATION BY CORYNEBACTERIUM NEPHRIDII. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1104–1108. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1104-1108.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque M., Aleem M. I. Intermediates of denitrification in the chemoautotroph Thiobacillus denitrificans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 31;94(3):269–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00417456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg N. R. Taxonomic studies of Spirillum lipoferum. Basic Life Sci. 1977;9:463–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE R. H., EVANS H. J. PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF A SOLUBLE NITRATE REDUCTASE FROM RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 1;85:377–389. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T. Studies on denitrification. 8. Some properties of the N2O-anaerobically grown cell. J Biochem. 1971 Jun;69(6):991–1001. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyra C. A., Döbereiner J. Denitrification by N2-fixing Sprillum lipoferum. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Mar;23(3):300–305. doi: 10.1139/m77-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):409–452. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.409-452.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., Bigliardi-Rouvier J., Mandel M., Greenway B., Méténier G., Garcia J. L. The isolation and properties of a denitrifying bacterium of the genus Flavobacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1976;42(3):349–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00394134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., Mandel M., Garcia J. L. Etude de six souches de Agrobacterium tumefaciens et A. radiobacter. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Apr;128A(3):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., Mandel M., Garcia J. L. Etude physiologique et taxonomique de Paracoccus denitrificans. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Aug-Sep;128(2):243–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., Mandel M., Garcia J. L. Etude physiologique et taxonomique de Paracoccus denitrificans. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Aug-Sep;128(2):243–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., Mandel M., Greenway B., Garcia J. L. Isolement à partir du sol étude d'une bactérie déntrifiante appartenant au genre Alcaligenes. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 Oct 27;281(17):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., de Berjac H., Mandel M., Greenway B., Garcia J. L. Une nouvelle bactérie sporulée, dénitrifiante, mésophile: Bacillus azotoformans N. SP. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 Oct;127B(3):351–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. D., Becker G. E. Production of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide during denitrification by Corynebacterium nephridii. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.821-826.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle P. L., Matsumoto H., Holloway B. W. Genetic circularity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):145–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.145-155.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John R. T., Hollocher T. C. Nitrogen 15 tracer studies on the pathway of denitrification in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):212–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. Biochemistry and genetics of nitrate reductase in bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):315–375. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. R., Rowe J. J., Romero P., Eagon R. G. Denitrifying Pseudomonas aeruginosa: some parameters of growth and active transport. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):257–263. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.257-263.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari T. N2O reduction by Vibrio succinogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):81–84. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.81-84.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Verseveld H. W., Meijer E. M., Stouthamer A. H. Energy conservation during nitrate respiration in Paracoccus denitrificans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):17–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00446649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


