Abstract
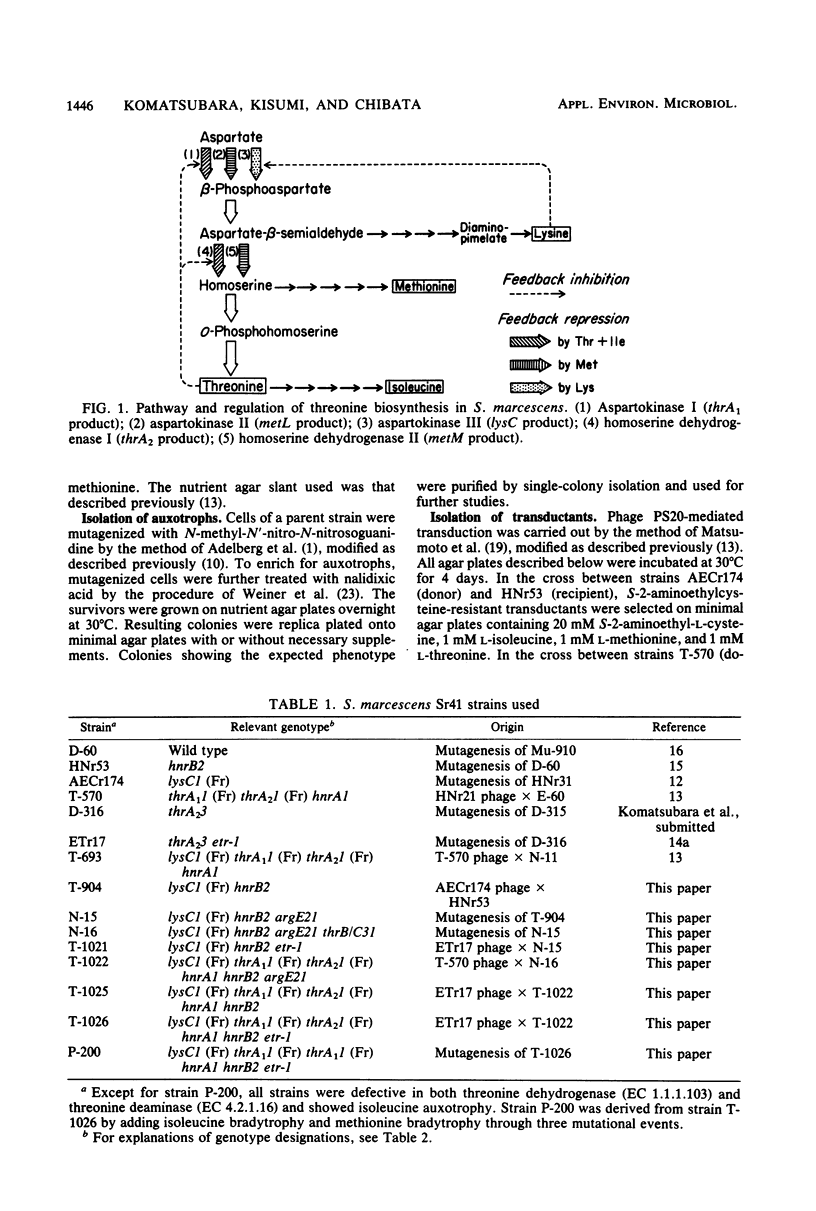
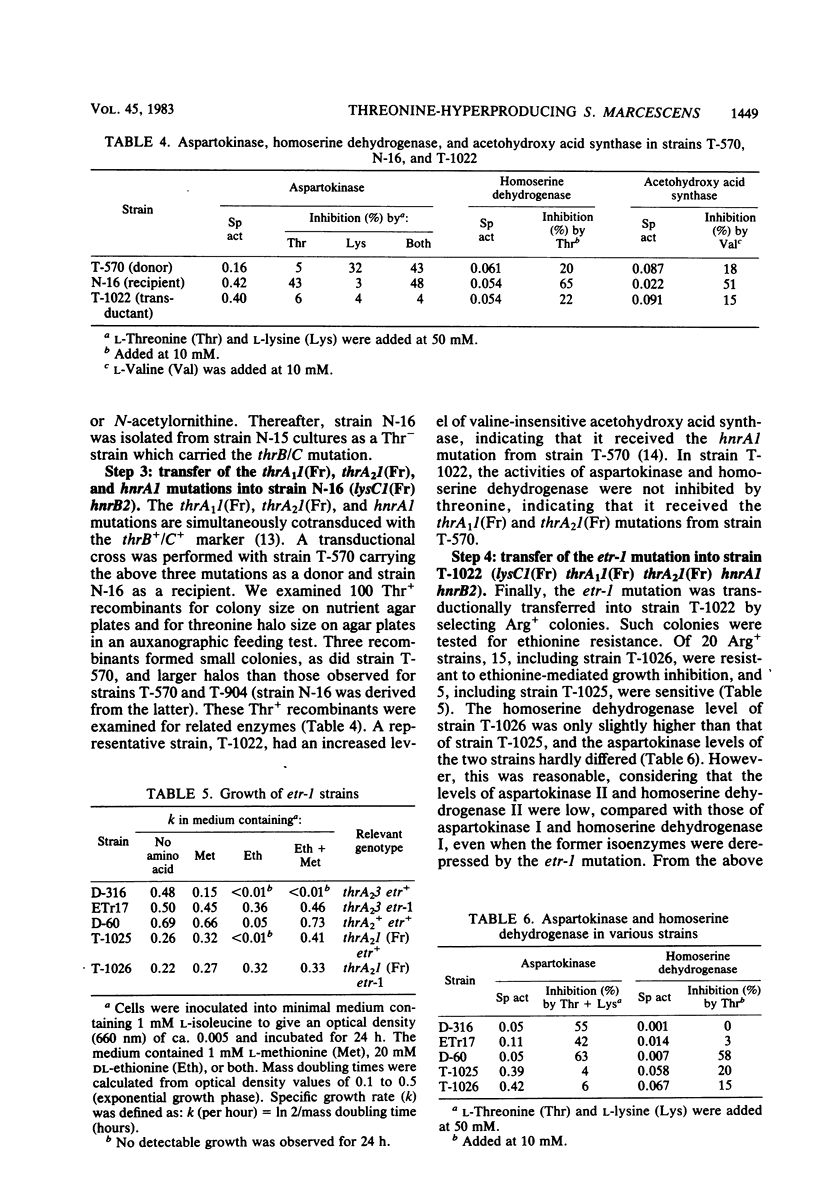
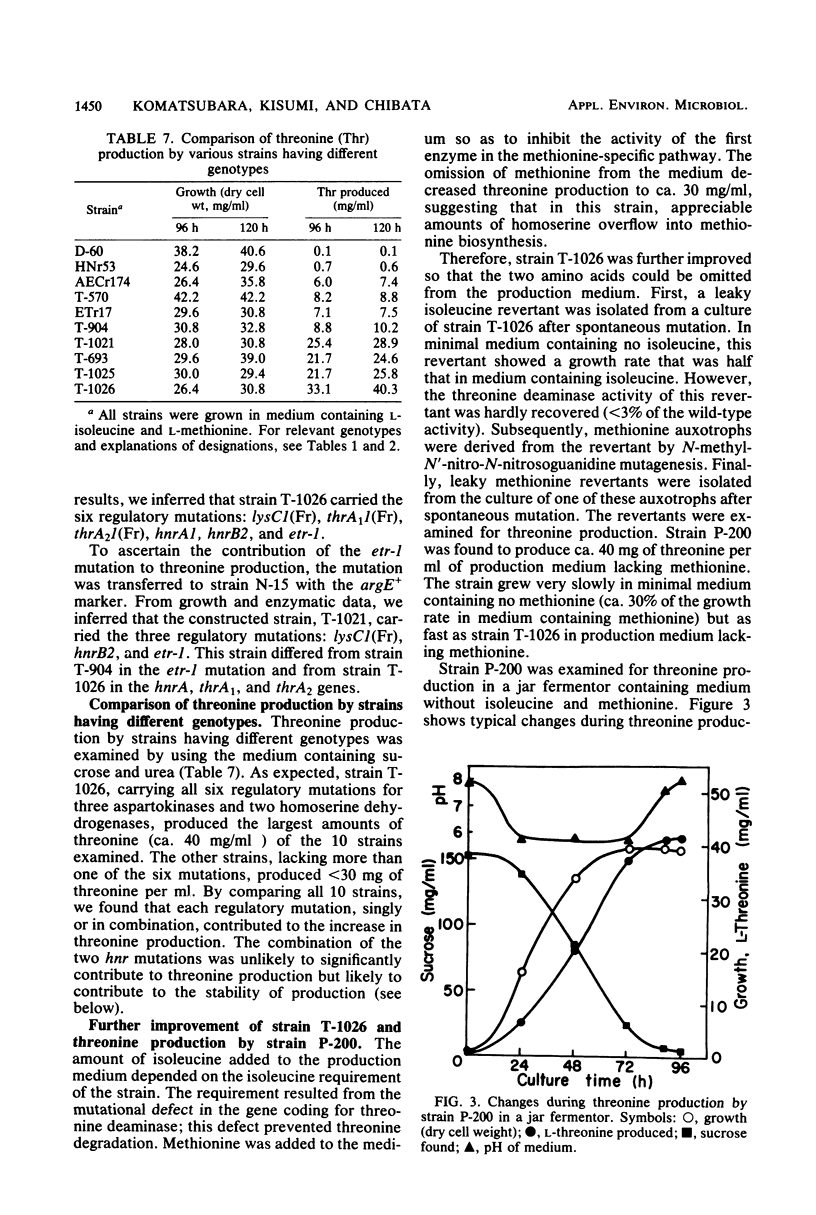
To construct a threonine-hyperproducing strain of Serratia marcescens Sr41, the six regulatory mutations for three aspartokinases and two homoserine dehydrogenases were combined in a single strain by three transductional crosses. The constructed strain, T-1026, carried the lysC1 mutation leading to lack of feedback inhibition and repression of aspartokinase III, the thrA1(1) mutation desensitizing aspartokinase I to feedback inhibition, the thrA2(1) mutation releasing feedback inhibition of homoserine dehydrogenase I, the two hnr mutations derepressing aspartokinase I and homoserine dehydrogenase I, and the etr-1 mutation derepressing aspartokinase II and homoserine dehydrogenase II. The strain produced ca. 40 mg of threonine per ml of medium containing sucrose and urea. Furthermore, the productivity of strain T-1026 was compared with those of strains devoid of more than one of the six regulatory mutations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisumi M., Komatsubara S., Chibata I. Enhancement of isoleucine hydroxamate-mediated growth inhibition and improvement of isoleucine-producing strains of Serratia marcescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):647–653. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.647-653.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisumi M., Komatsubara S., Sugiura M., Chibata I. Isoleucine hydroxamate, an isoleucine antagonist. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):741–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.741-745.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara S., Kisumi M., Chibata I. Participation of lysine-sensitive aspartokinase in threonine production by S-2-aminoethyl cysteine-resistant mutants of Serratia marcescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):777–782. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.777-782.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara S., Kisumi M., Chibata I. Threonine production by ethionine-resistant mutants of Serratia marcescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1437–1444. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1437-1444.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara S., Kisumi M., Chibata I. Transductional construction of a threonine-producing strain of Serratia marcescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1045-1051.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara S., Kisumi M., Chibata I. Transductional construction of an isoleucine-producing strain of Serratia marcescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jul;119(1):51–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara S., Kisumi M., Murata K., Chibata I. Threonine production by regulatory mutants of Serratia marcescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):834–840. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.834-840.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara S., Murata K., Kisumi M., Chibata I. Threonine degradation by Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):318–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.318-323.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Hosogaya S., Suzuki K., Tazaki T. Arginine gene cluster of Serratia marcescens. Jpn J Microbiol. 1975 Feb;19(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1975.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Tazaki T., Hosogaya S. A generalized transducing phage of Serratia marcescens. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;17(6):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thèze J., Saint-Girons I. Threonine locus of Escherichia coli K-12: genetic structure and evidence for an operon. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):990–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.990-998.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbarger H. E. Amino acid biosynthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:532–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. M., Voll M. J., Cook T. M. Nalidixic acid for enrichment of auxotrophs in cultures of Salmonella typhimurium. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):579–581. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.579-581.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


