Abstract
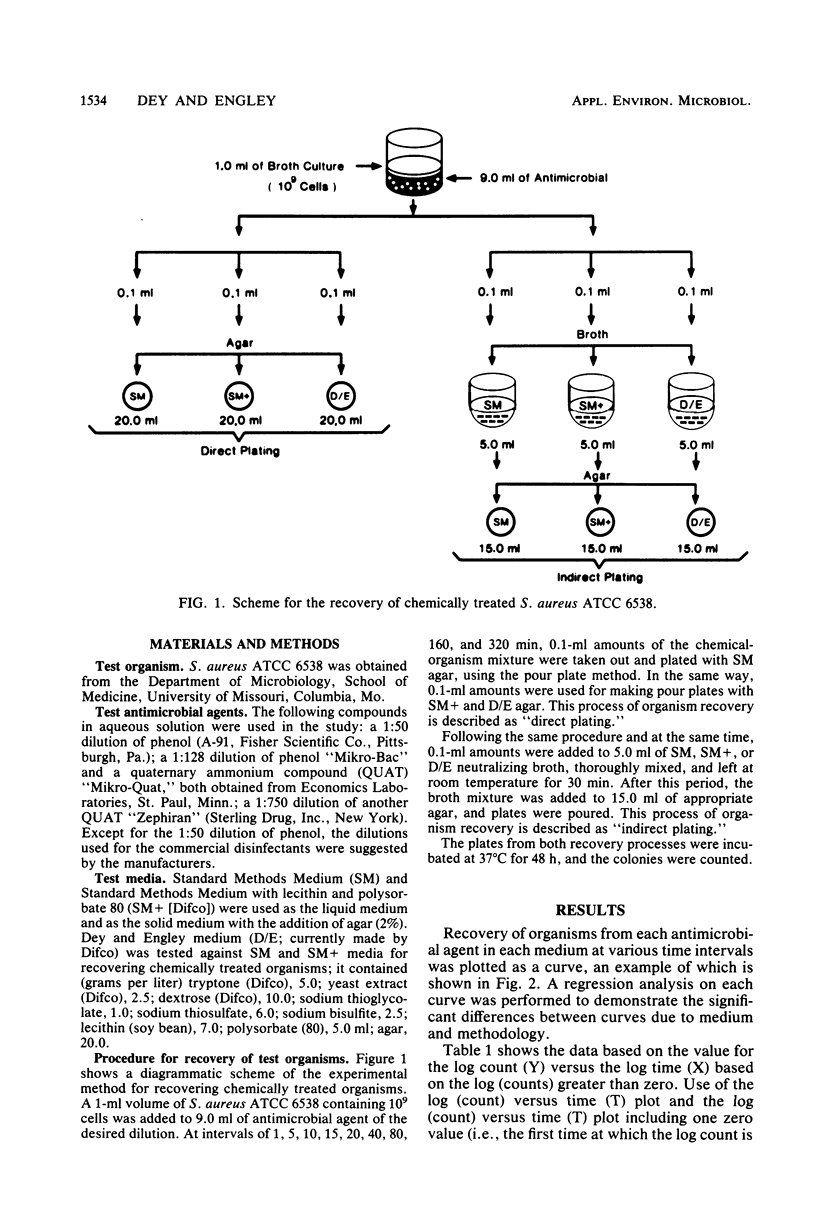
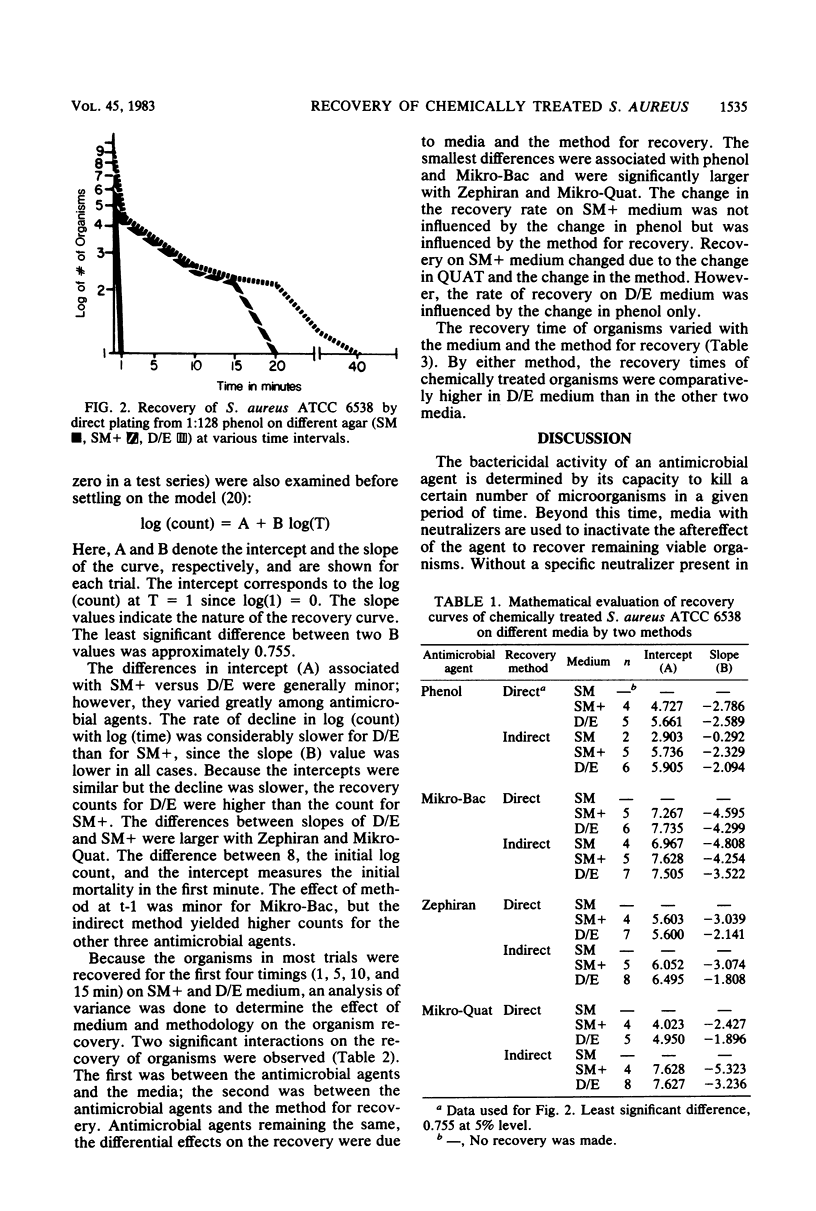
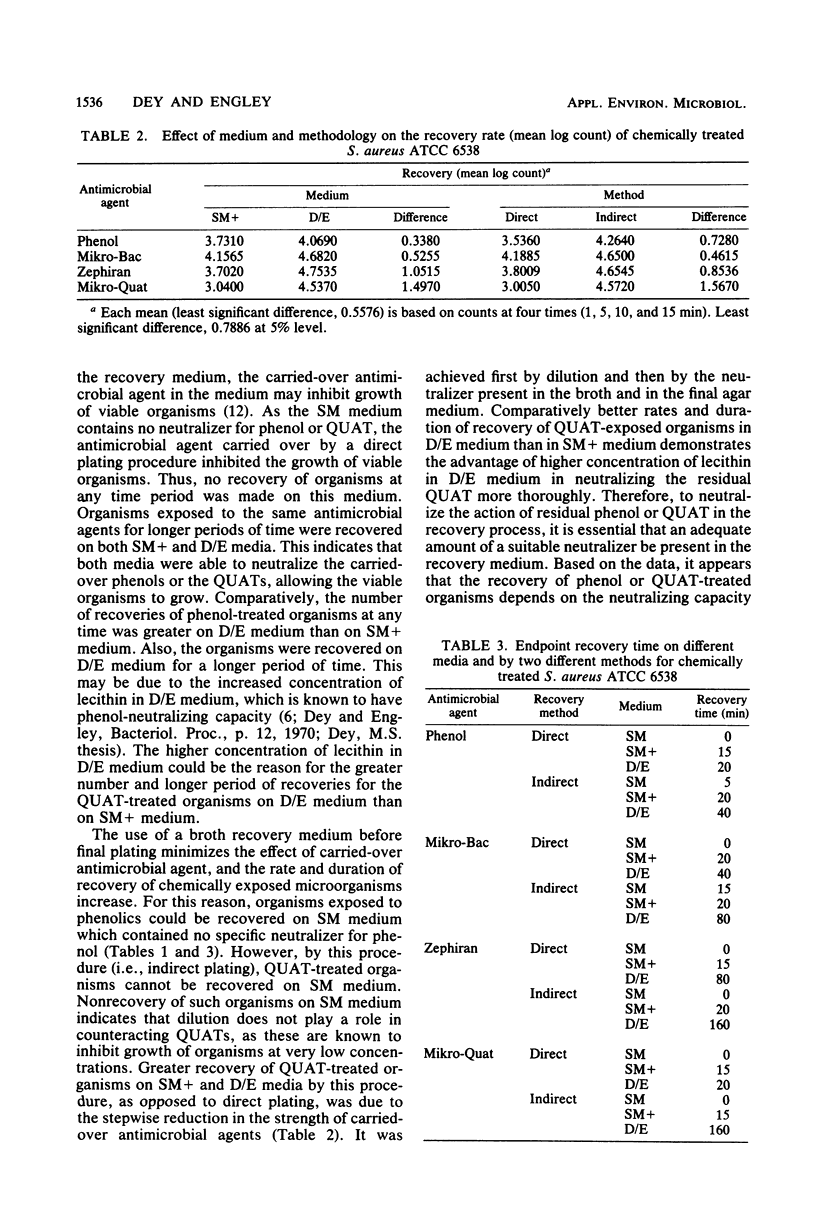
Recovery results of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 treated with phenolics and quaternary ammonium compounds on Dey and Engley (D/E) neutralizing medium at various time intervals were compared by the use of two commonly used media. Two recovery processes were utilized. In one, the chemically treated organisms were plated directly onto an agar medium. In the other, the aliquot was first put in broth and then was plated with agar. By either process, the numbers and the time period for recovery of organism were greater on D/E medium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brummer B. Influence of possible disinfectant transfer on Staphylococcus aureus plate counts after agar contact sampling. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):80–84. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.80-84.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLEY F. B., Jr Evaluation of mercurial compounds as antiseptics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Aug;53(1):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb31945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOTER M. J., NISONGER L. L. A new and direct approach to the evaluation of the germicidal efficiency of semisolid pharmaceuticals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Aug;53(1):112–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb31937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN R. K., PHILLIPS C. R. Evaluation of the paper disc assay procedure and its correlation with phenol coefficients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Aug;53(1):59–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb31932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDSIN R. B., WALTER C. W. In-use testing of bactericidal agents in hospitals. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Mar;9:167–170. doi: 10.1128/am.9.2.167-170.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon I. H. The use of inactivators in the evaluation of disinfectants. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Oct;73(2):189–195. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL H. M., CULBERTSON C. G. Assay of antiseptics at different times after application to human skin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Aug;53(1):207–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb31946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddish G. F. DETERMINING THE GERMICIDAL EFFICIENCY OF DISINFECTANTS. Am J Public Health (N Y) 1926 Mar;16(3):283–286. doi: 10.2105/ajph.16.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. D. Factors influencing the activity of antimicrobial agents: an appraisal. Microbios. 1974 Apr;10(38):151–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh W. Development and validation of a neutralizer system for in vitro evaluation of some antiseptics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):429–434. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


