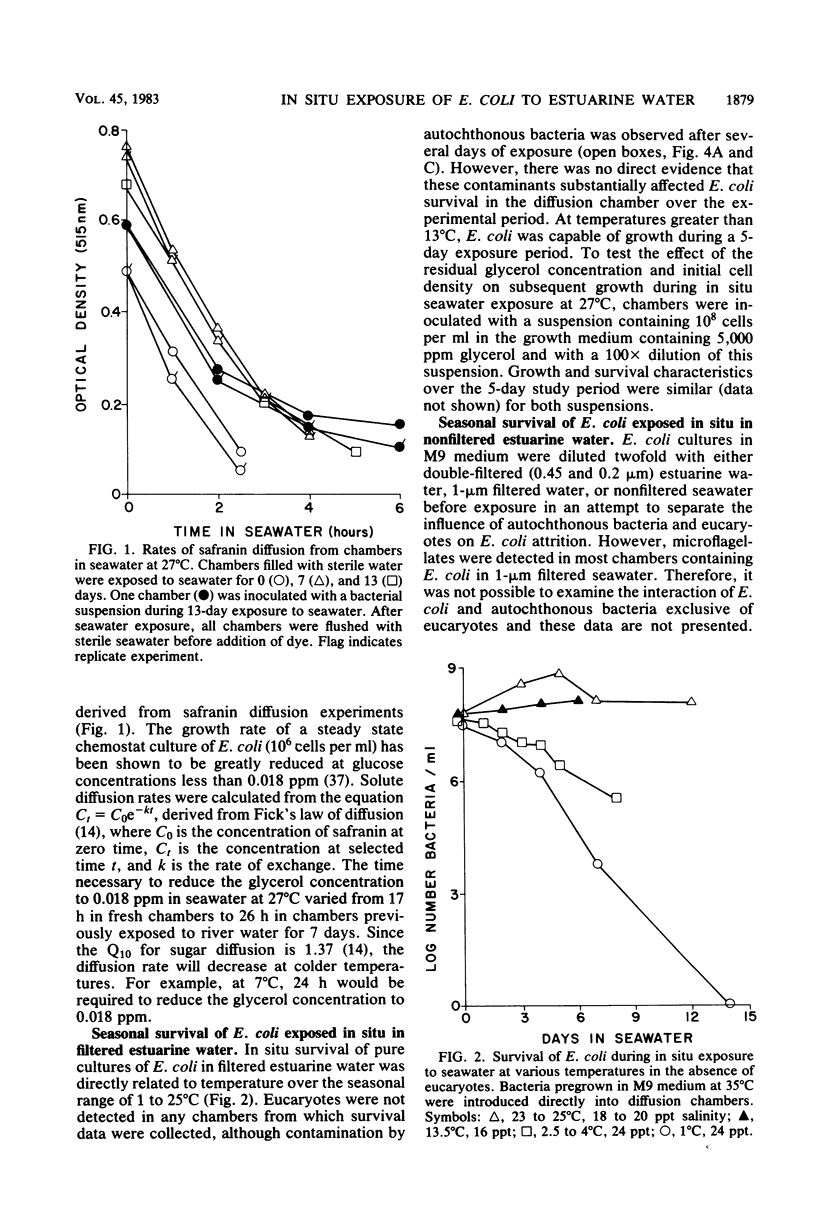
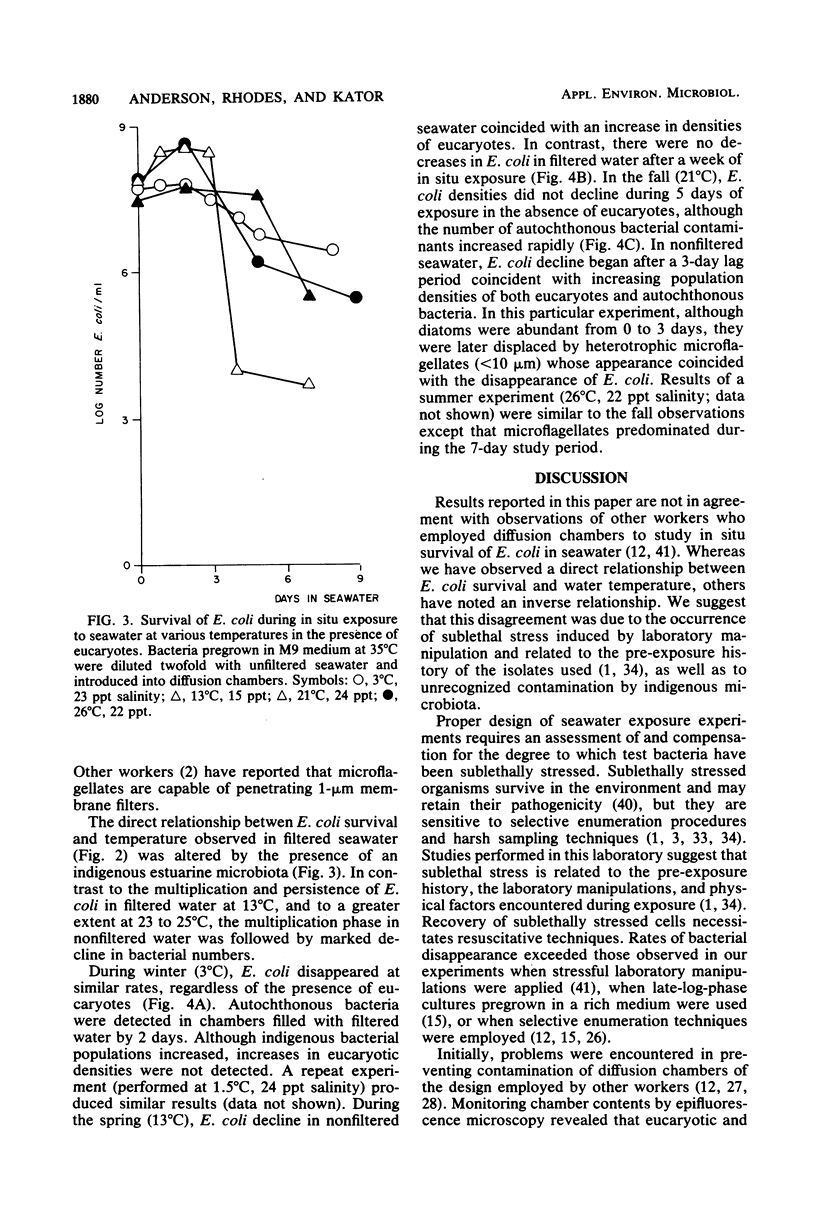
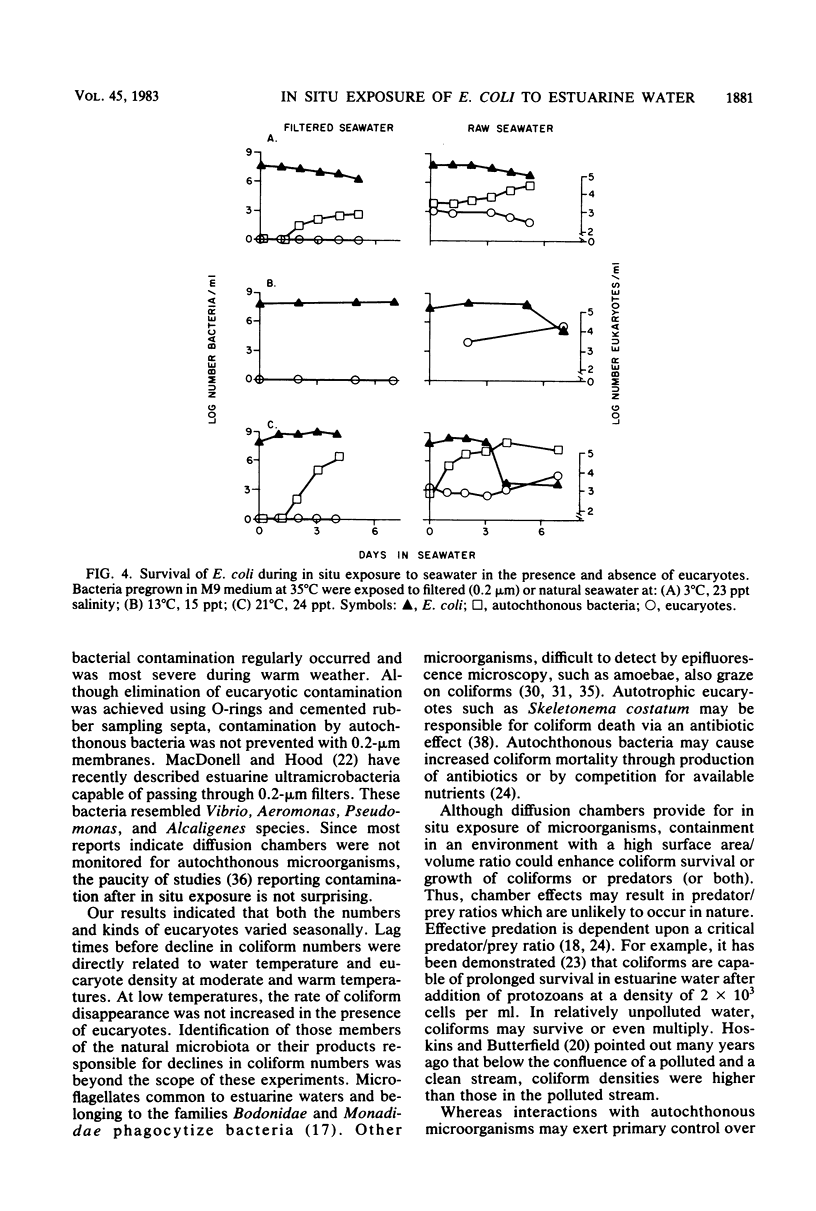
Abstract
Human fecal Escherichia coli isolates were exposed over a seasonal cycle to estuarine water in diffusion chambers filled with double-filtered (0.45 and 0.2 microns) and nonfiltered water. Laboratory manipulations of E. coli cultures before estuarine exposure were reduced to minimize sublethal stress, and nonselective or resuscitative enumeration techniques were employed to maximize recovery of stressed cells. E. coli was capable of extended survival during in situ exposure to estuarine water, provided eucaryotes were excluded from diffusion chambers. Survival was directly related to temperature in absence of the eucaryote component of the natural microbiota. Although it was not possible to prevent eventual bacterial contamination in double-filtered water, there was no direct evidence that such contamination affected E. coli survival. Conversely, E. coli disappearance was most pronounced at warmer temperatures in the presence of the natural microbiota, and decline coincided with increasing eucaryote densities. In contrast, the decline of E. coli during winter was similar in both filtered and nonfiltered seawater.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson I. C., Rhodes M., Kator H. Sublethal stress in Escherichia coli: a function of salinity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1147–1152. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1147-1152.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Evaluation of recovery methods to detect coliforms in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.590-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport C. V., Sparrow E. B., Gordon R. C. Fecal indicator bacteria persistence under natural conditions in an ice-covered river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):527–536. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.527-536.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe L. L., Penrose W. R. "Bactericidal" property of seawater: death or debilitation? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):829–833. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.829-833.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzinger R. M., Cooper R. C. Role of bacteria and protozoa in the removal of Escherichia coli from estuarine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):758–763. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.758-763.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust M. A., Aotaky A. E., Hargadon M. T. Effect of physical parameters on the in situ survival of Escherichia coli MC-6 in an estuarine environment. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):800–806. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.800-806.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granai C., 3rd, Sjogren R. E. In situ and laboratory studies of bacterial survival using a microporous membrane sandwich. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):190–195. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.190-195.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney C. R., Ray B., Speck M. L. Repair detection procedure for enumeration of fecal coliforms and enterococci from seafoods and marine environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):947–953. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.947-953.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuscinski R. B., Mitchell R. Solar radiation induces sublethal injury in Escherichia coli in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):670–674. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.670-674.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonell M. T., Hood M. A. Isolation and characterization of ultramicrobacteria from a gulf coast estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):566–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.566-571.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCambridge J., McMeekin T. A. Effect of solar radiation and predacious microorganisms on survival of fecal and other bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1083–1087. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1083-1087.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCambridge J., McMeekin T. A. Relative effects of bacterial and protozoan predators on survival of Escherichia coli in estuarine water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):907–911. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.907-911.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., Thomson C. A., Stuart D. G. Comparative survival of indicator bacteria and enteric pathogens in well water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):823–829. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.823-829.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters: field and laboratory studies with membrane-filter chambers. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):805–811. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.805-811.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Stuart S. A., Olson S. B. Growth of heterotrophic bacteria and algal extracellular products in oligotrophic waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):383–391. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.383-391.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes M. W., Anderson I. C., Kator H. I. In situ development of sublethal stress in Escherichia coli: effects on enumeration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1870–1876. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1870-1876.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEBURTH J. M., PRAT D. M. Anticoliform activity of sea water associated with the termination of Skeletonema costatum blooms. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Mar;24:498–501. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1962.tb01425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLANETZ L. W., BARTLEY C. H. SURVIVAL OF FECAL STREPTOCCOCCI IN SEA WATER. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehata T. E., Marr A. G. Effect of nutrient concentration on the growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.210-216.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrells K. M., Speck M. L., Warren J. A. Pathogenicity of Salmonella gallinarum after metabolic injury by freezing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.39-43.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos G. J., Swartz R. G. Survival of bacteria in seawater using a diffusion chamber apparatus in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):913–920. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.913-920.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


