Abstract
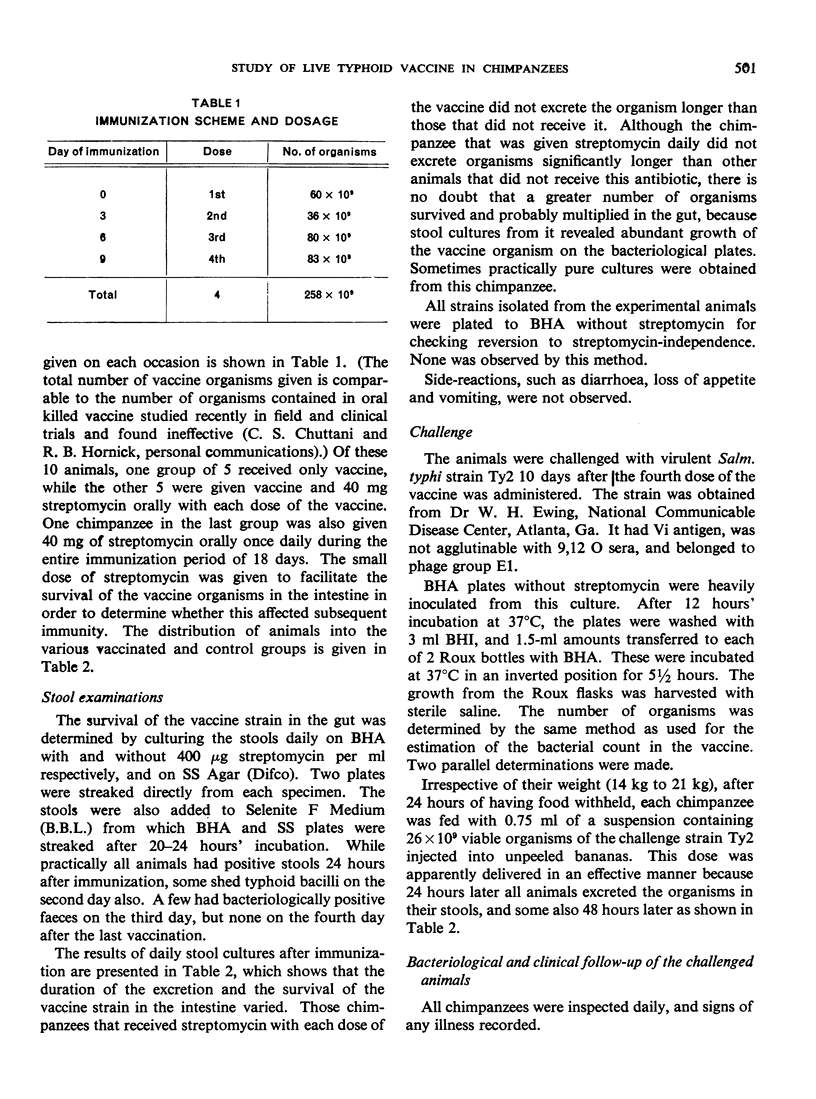
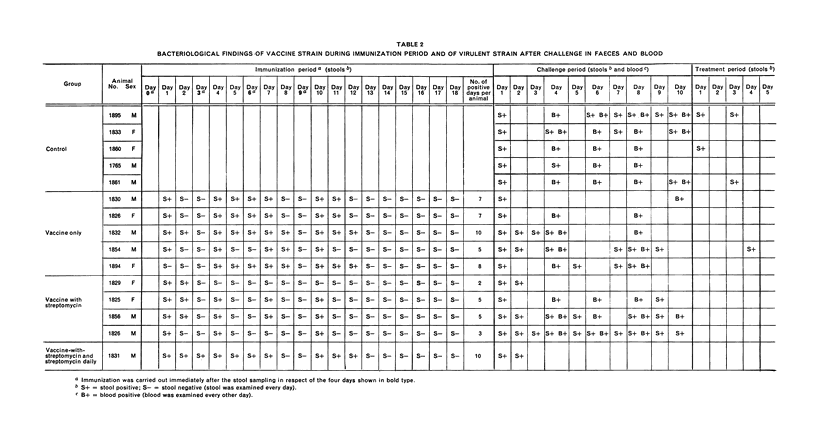
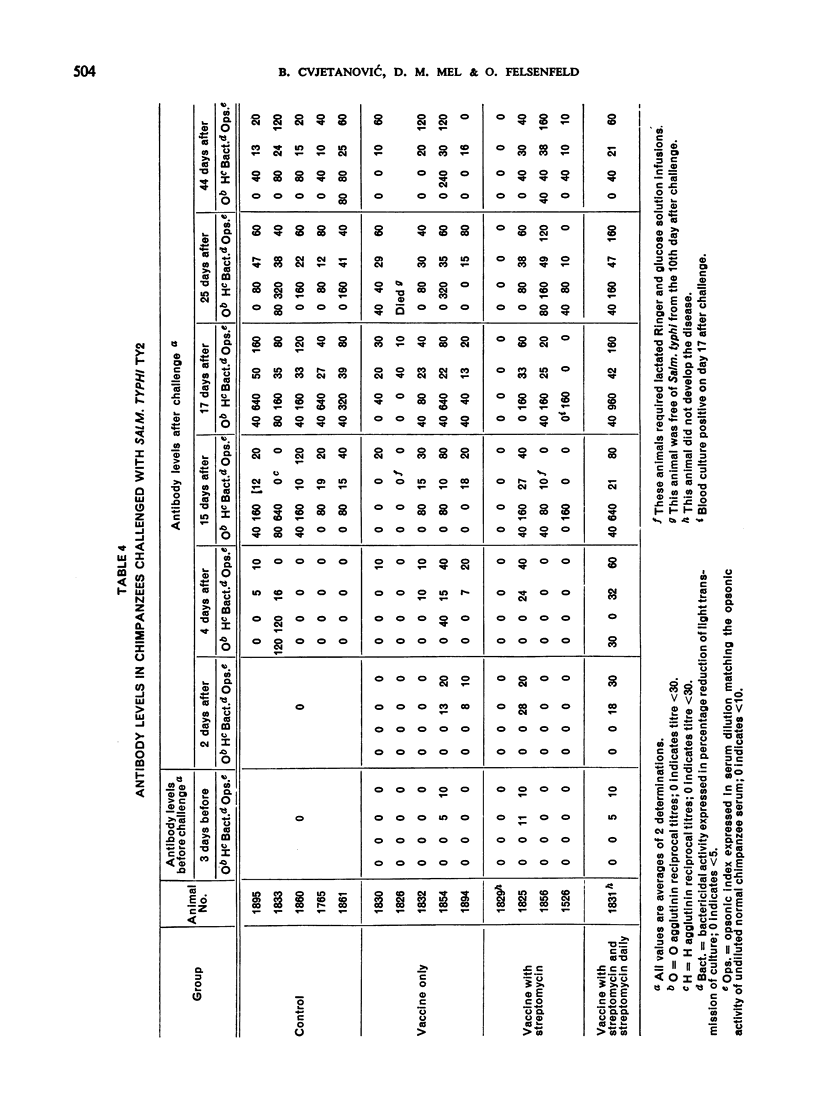
Streptomycin-dependent Salmonella typhi containing O and H antigens was administered as a live oral antityphoid vaccine to chimpanzees. Five animals served as controls; 5 others received the vaccine 4 times at 3-day intervals; 4 further animals were given 4 doses of vaccine at 3-day intervals together with streptomycin; and 1 animal received the 4 doses of vaccine and a daily dose of streptomycin. The individual vaccine doses varied between 36×109 and 82×109 organisms, totalling about 258×109 Salm. typhi per animal. The chimpanzees were challenged with 26×109 cells of the virulent Salm. typhi Ty2 strain 10 days after immunization and followed up bacteriologically, serologically and clinically. It was observed that after this very heavy challenge the immunized animals that had received streptomycin with the vaccine were protected to some degree against the infection and showed fewer symptoms. The animal that received vaccine and streptomycin daily did not develop the disease.
The authors point out that, while the strain used may have potential usefulness for the protection of man, further studies are needed to confirm the innocuity of the vaccine, to reduce the strain's reversion to streptomycin-independence, and to determine the relative effectiveness of different immunization dosages and schedules.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CVJETANOVIC B., UEMURA K. THE PRESENT STATUS OF FIELD AND LABORATORY STUDIES OF TYPHOID AND PARATYPHOID VACCINES WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STUDIES SPONSORED BY WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:29–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSALL G., CARLSON M. C., FORMAL S. B., BENENSON A. S. Laboratory tests of typhoid vaccines used in a controlled field study. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;20:1017–1032. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSALL G., GAINES S., LANDY M., TIGERTT W. D., SPRINZ H., TRAPANI R. J., MANDEL A. D., BENENSON A. S. Studies on infection and immunity in experimental typhoid fever. I. Typhoid fever in chimpanzees orally infected with Salmonella typhosa. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:143–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAROLCEK J., ODLER I., DRASKOVICOVA M., LUZOVA D. POU ZITIE S'EROLOGICKO-IMUNOBIOLOGICK'YCH MET'OD V DIAGNOSTIKE T'YFOV'EHO BACILONOSI CSTVA. Cesk Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 1963 Jul;12:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., ROSEN F. S. ASSOCIATION OF "NATURAL" ANTIBODIES TO GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA WITH THE GAMMA-1-MACROGLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:619–626. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., TREFFERS H. P. Quantitative studies on the bactericidal actions of serum and complement. I. A rapid photometric growth assay for bactericidal activity. J Immunol. 1956 Jan;76(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Papo R. G., Terzin A. L., Vuksić L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 2. Safety tests and reactogenicity studies on a live dysentery vaccine intended for use in field trials. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):637–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M. Infectivity and antigenicity of streptomycin-dependent Salmonella typhosa. J Infect Dis. 1967 Feb;117(1):101–107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOZER B. T., CAMMACK K. A., SMITH H. Separation of antigens by immunological specificity. 2. Release of antigen and antibody from their complexes by aqueous carbon dioxide. Biochem J. 1962 Jul;84:80–80. doi: 10.1042/bj0840080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VLADOIANU I. R., DIMACHE G., ANTOHI S., VLADOIANU C., ZARMA O. LABORATORY TESTS ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL VACCINATION OF YOUNG CHILDREN AGAINST TYPHOID AND PARATYPHOID A AND B. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:37–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


