Abstract
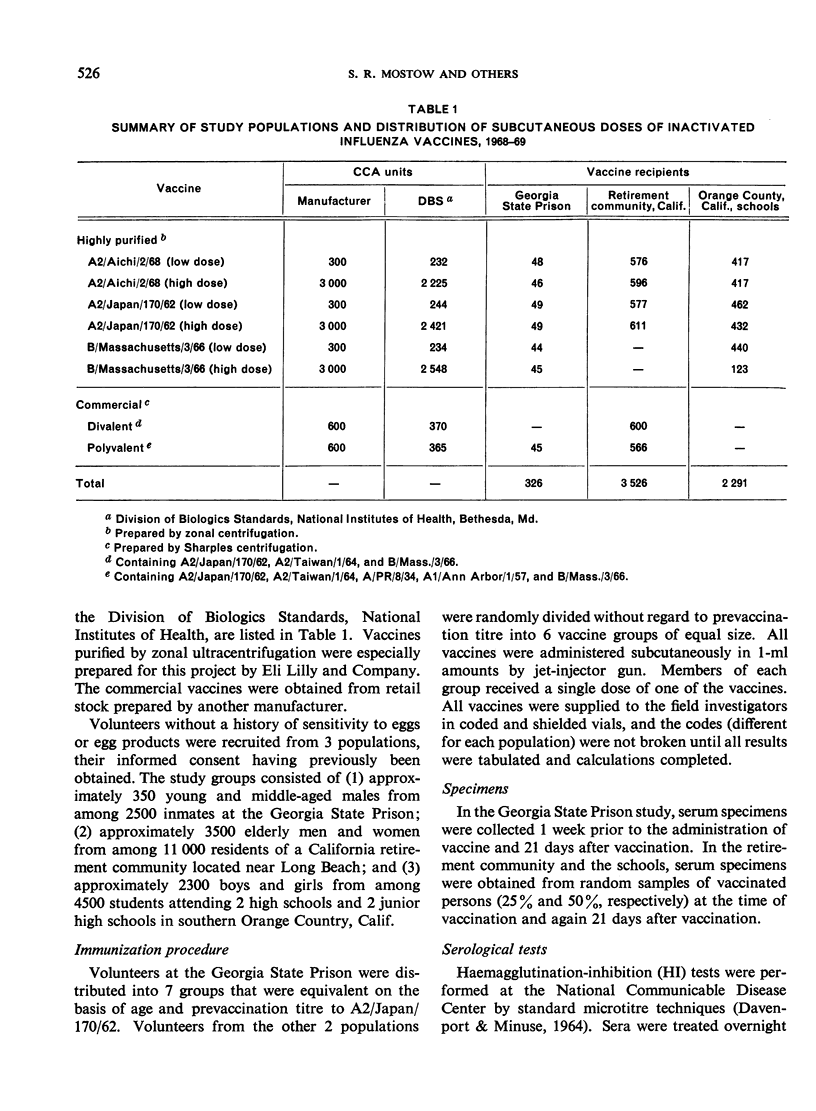
High (3000 CCA units) and standard low (300 CCA units) doses of formalin-inactivated influenza vaccines purified by zonal ultracentrifugation were evaluated in a double-blind manner for adverse reactions and antibody responses in a high school population and in 2 adult populations.
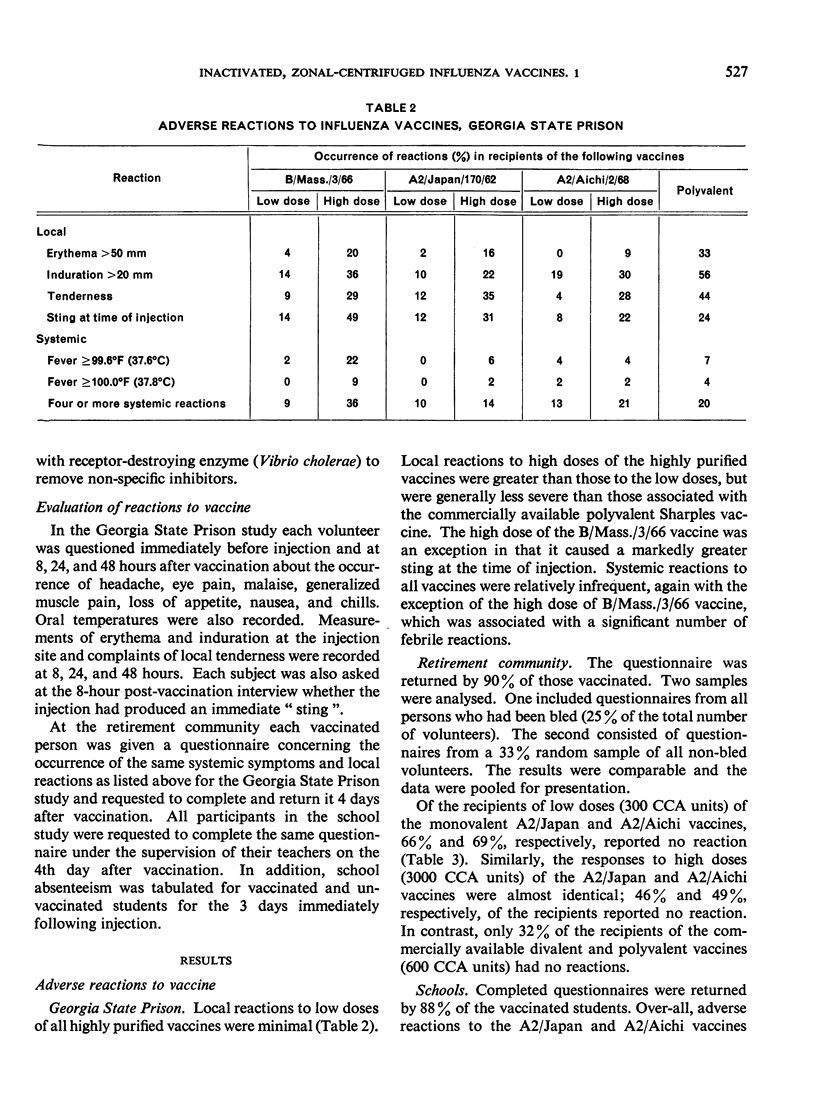
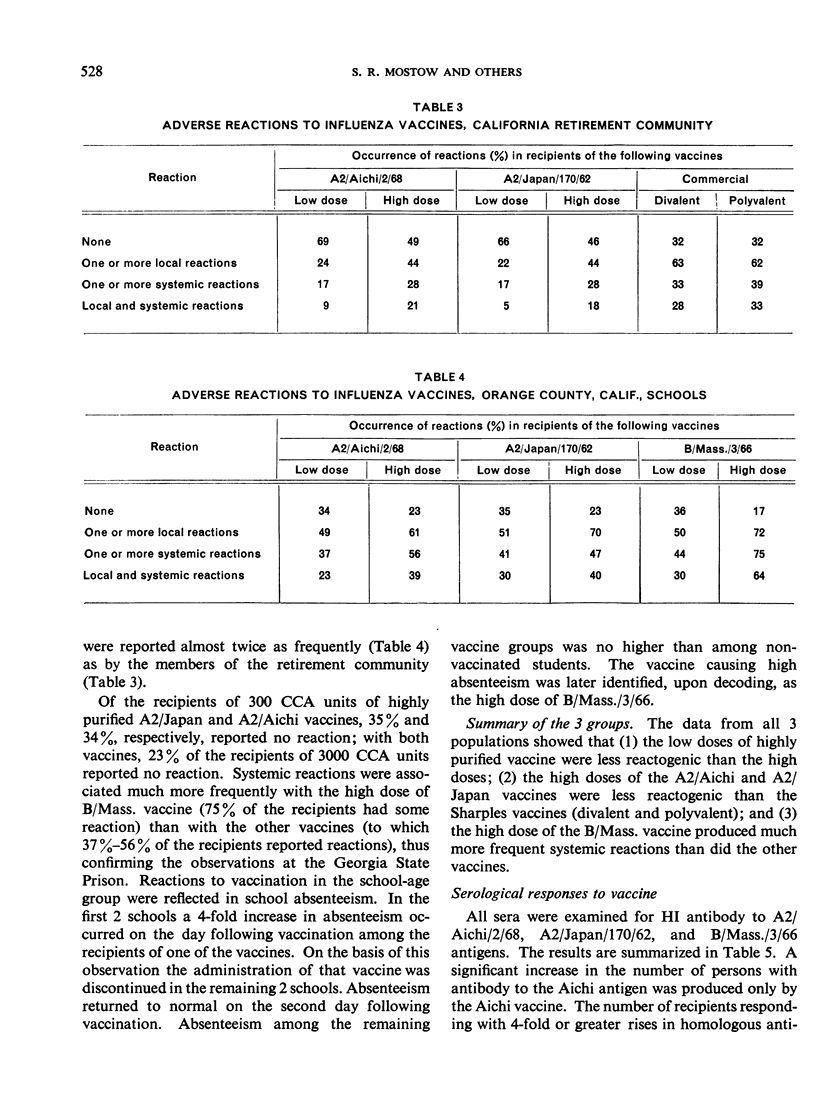
The fewest local and systemic reactions were produced by subcutaneous administration of the low doses of purified monovalent A2/Aichi/2/68, A2/Japan/170/62, and B/Massachusetts/3/66 vaccines. The high doses of A2/Japan and A2/Aichi vaccines produced 2-3-fold greater incidence of adverse reactions but did not exceed that observed with the commercial vaccines. The 3000 CCA units of B/Mass. vaccine produced more frequent and more severe systemic reactions than the polyvalent vaccine.
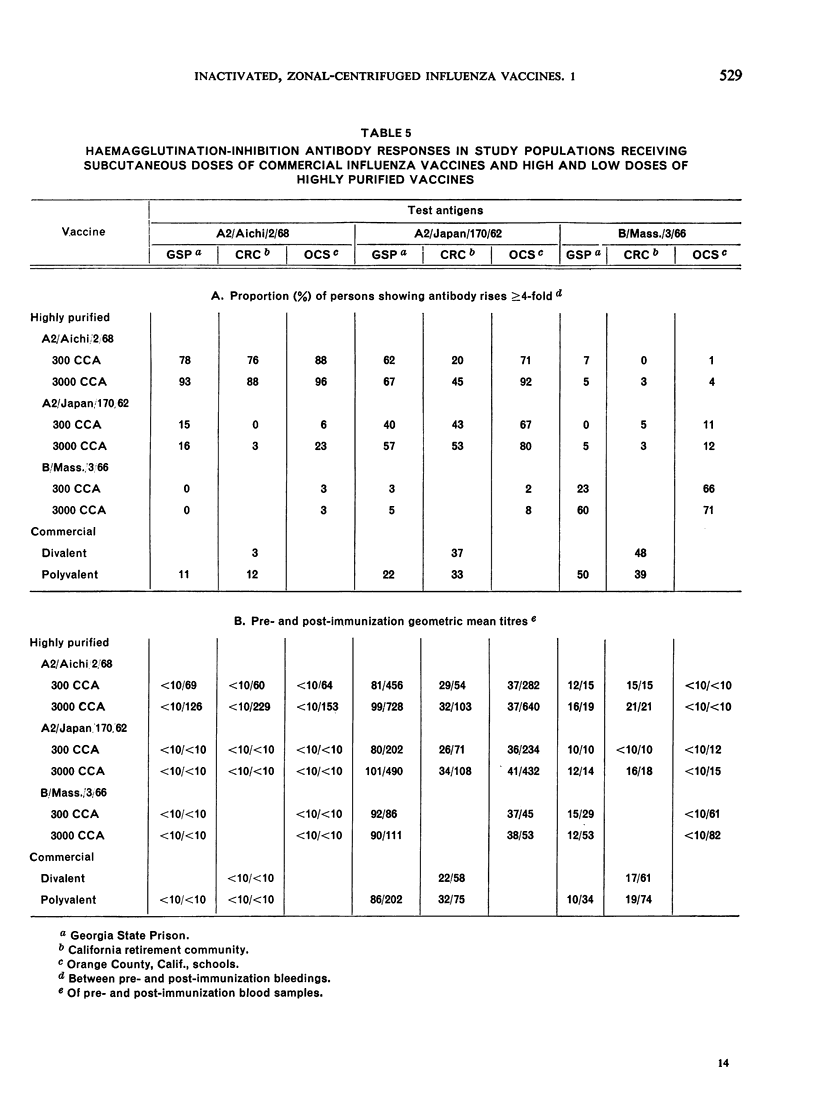
Neither the A2/Japan vaccine nor the commercial vaccines stimulated a significant serum antibody response to A2/Aichi.
The homologous serum antibody response to an Aichi vaccine was excellent in all 3 populations. A2/Aichi vaccines produced higher heterologous A2/Japan titres than did the A2/Japan vaccines. It was demonstrated that high doses of purified influenza vaccine can be given safely, and that 10-fold increases in vaccine concentration produce 2-3-fold increases in antibody titre.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Peck F. B., Jr Purified influenza virus vaccine. A study of viral reactivity and antigenicity. JAMA. 1968 Dec 2;206(10):2277–2282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Baker R. S., Van Frank R. M., Newlin T. E., Cline G. B., Anderson N. G. Purification of large quantities of influenza virus by density gradient centrifugation. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1207-1216.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


