Abstract
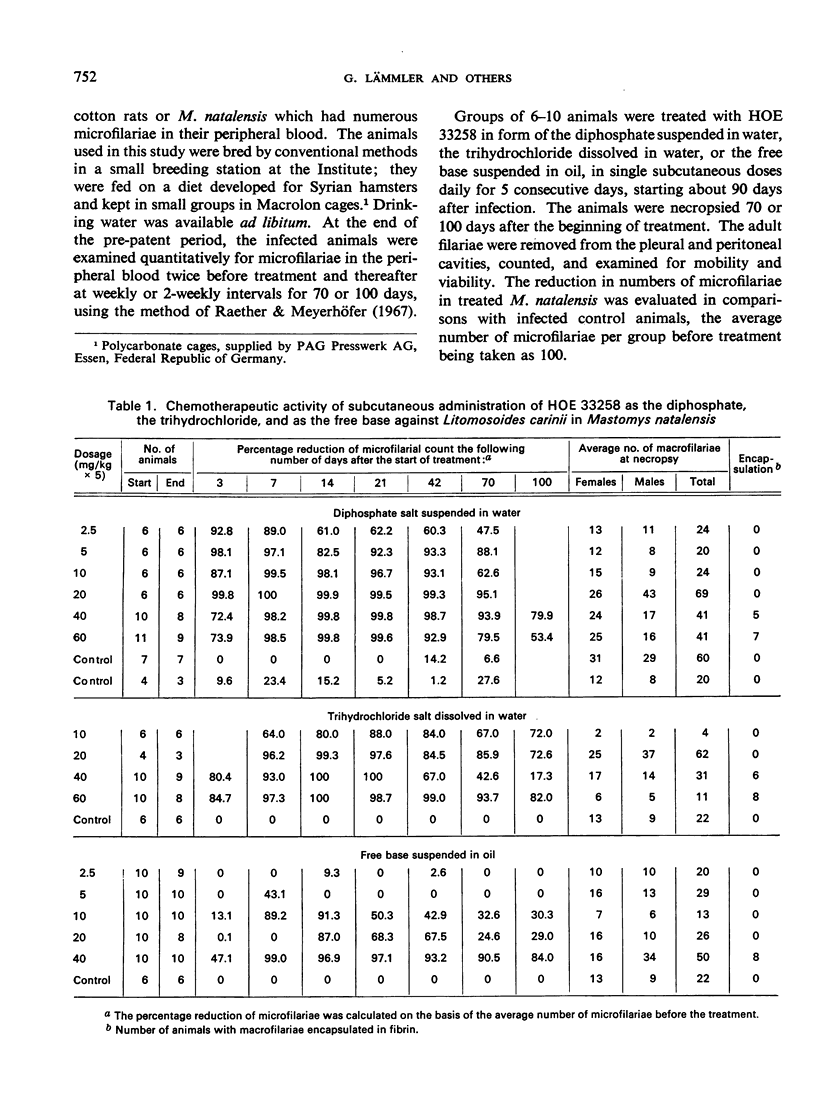
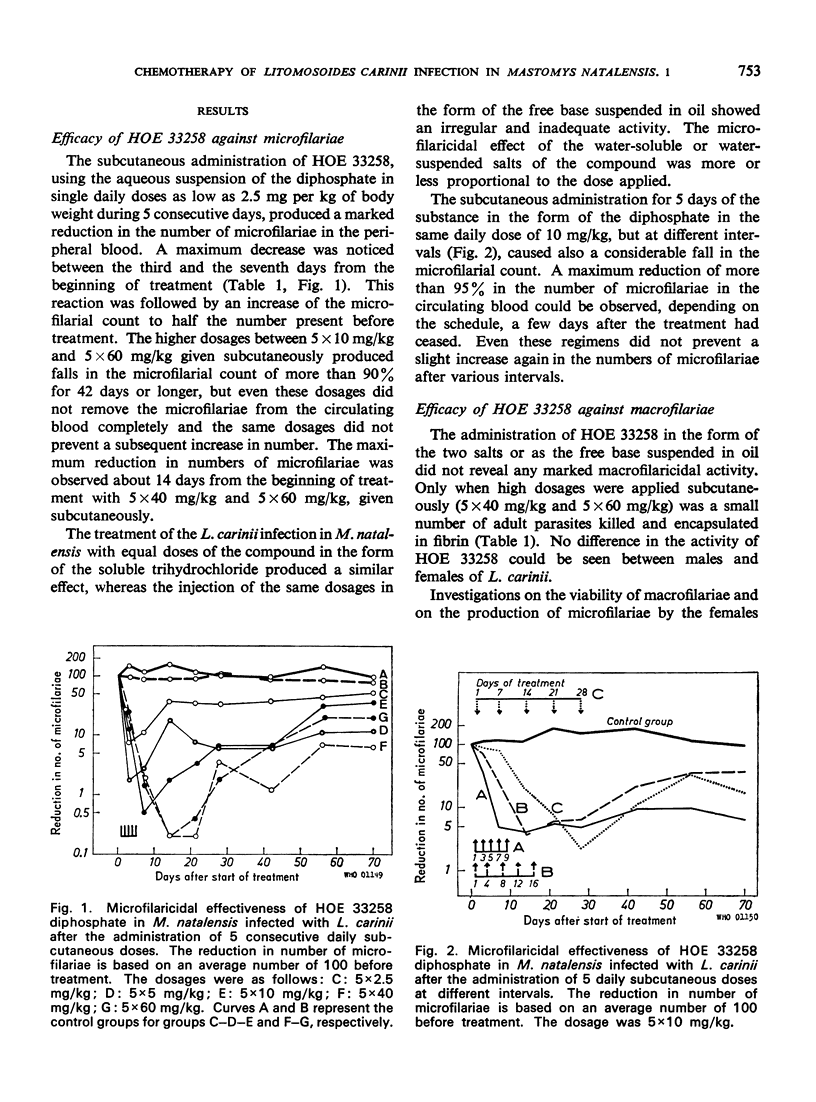
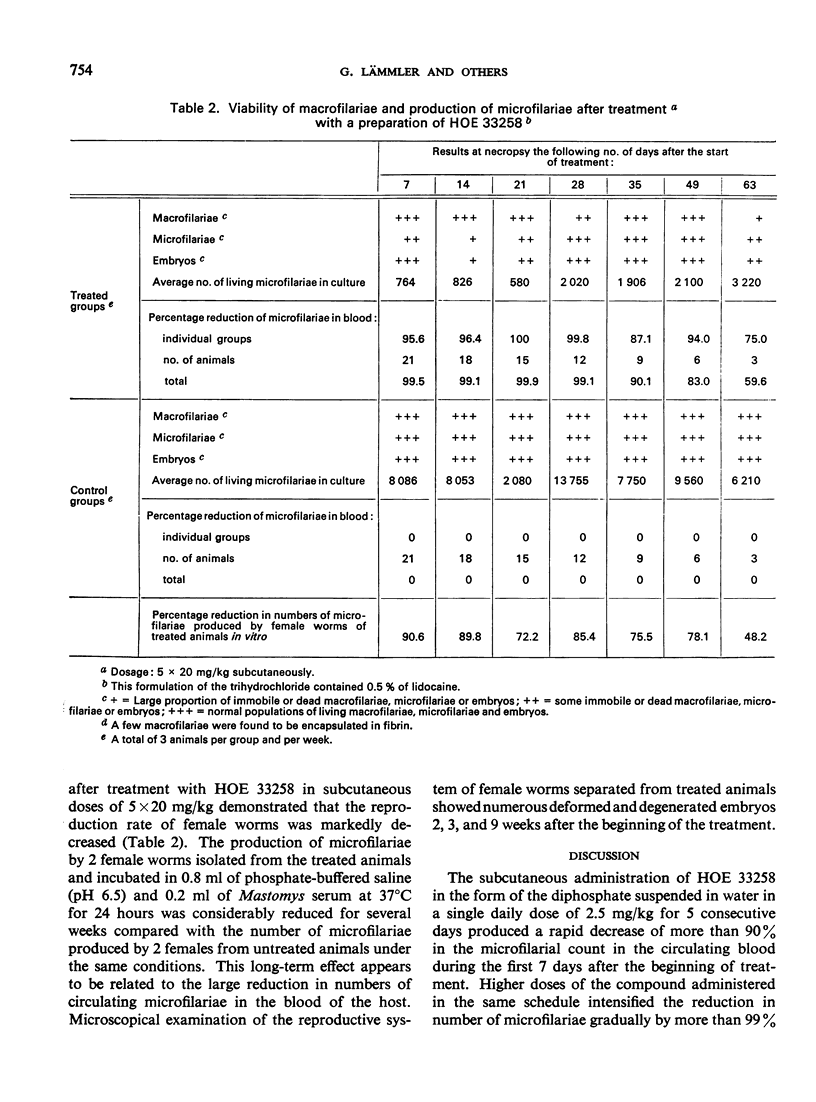
The antifilarial action of 2-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-benzimidazolyl]-6-(1-methyl-4-piperazyl) benzimidazole (HOE 33258) was investigated in Mastomys natalensis infected with Litomosoides carinii. The subcutaneous administration of HOE 33258 in a single daily dose for 5 consecutive days, or at other intervals, produced, depending on the dosage, a rapid reduction in the number of microfilariae in the circulating blood. The reduction amounted to more than 90% within 7-14 days after the treatment was started or at the end of the dosage schedule. The small, slow increase in the microfilarial count during a period of 6-7 weeks after treatment ended reached not more than half the number present before treatment. HOE 33258 showed marked activity on the reproductive system of mature female worms, although only few macrofilariae were killed by the drug. The results also demonstrated the usefulness of L. carinii infection of M. natalensis as a model for the evaluation of the filaricidal activity of drugs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Foster R., Pringle G., King D. F., Paris J. The therapeutic activity of some nitrofurans in experimental filariasis and trypanosomiasis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1969 Mar;63(1):95–107. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1969.11686604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog A., Schütze H. R. Fluorochromierung von Säugetierchromosomen mit einem basisch substituierte Bis-Benzimidazol-Derivat (Präparat 33258 "Hoechst") Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1968 Oct 1;75(19):476–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler G., Enders B., Zahner H. Analytische Untersuchungen an Litomosoides carinii-Extrakten. Z Parasitenkd. 1969;32(3):254–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00329482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler G., Saupe E., Herzog H. Infektionsversuche mit der Baumwollrattenfilarie Litomosoides carinii bei Mastomys natalensis (Smith, 1834) Z Parasitenkd. 1968;30(4):281–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00259572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler G., Schütze H. R. Vital-Fluorochromierung tierischer Zellkerne mit einem neuen Fluorochrom. Naturwissenschaften. 1969 May;56(5):286–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00633942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler G., Srivastava V. K., Zahner H. The efficacy of various anthelmintics against the parasitic larval stages of Ancylostoma caninum in Mastomys natalensis. Br Vet J. 1970 Aug;126(8):427–439. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)48251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler G., Zahner H., Texdorf I. Infektionsversuche mit Darmnematoden, Cestoden und Trematoden bei Mastomys natalensis (Smith, 1834) Z Parasitenkd. 1968;31(2):166–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raether W., Meyerhöfer W. Quantitative Untersuchungsmethoden zum Nachweis von Mikrofilarien (Litomosoides carinii) mit Hilfe der Zähikammern nach Fuchs-Rosenthal und Jessen sowie Anreicherungsverfahren. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1967 Apr;18(1):99–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahner H., Herzog H., Saupe E., Enders B. Präzipitierende Antikörper im Serum von Mastomys natalensis im Verlauf der Litomosoides carinii-Infektion. Z Parasitenkd. 1970;34(2):128–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00260384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahner H., Schütze H. R., Lämmler G., Enders B. Das Albumin-Globulin-Verhältnis im Serum von Mastomys natalensis (Smith, 1834) im Verlauf einer Litomosoides carinii-Infektion. Z Parasitenkd. 1970;33(4):267–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00331466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


