Abstract
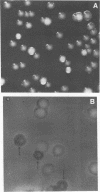
A Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain segregated two unstable colonial variants at high frequency. There is a correlation between colony morphology, encapsulation, Giemsa staining, and bacteriophage resistance.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burt S. J., Woods D. R. R factor transfer to obligate anaerobes from Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):405–409. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Isolation and characterization of ribonuclease I mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant R. B., Riemann H. P. Temperate phages of Clostridium perfringens type C1. Can J Microbiol. 1976 May;22(5):603–610. doi: 10.1139/m76-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES L. M., McDUFF C. R., WILSON J. B. Phenotypic alterations in the colonial morphology of Brucella abortus due to a bacteriophage carrier state. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:860–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.860-866.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. The polysaccharide capsule of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis: immunochemical and morphologic definition. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):79–87. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie H. L., Woods D. R. Isolation of obligate anaerobic faecal bacteria using an anaerobic glove cabinet. S Afr Med J. 1973 Sep 29;47(38):1739–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Identification of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1306–1313. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles C. A., Voros S., Marbell E. C., Amenuvor L. Colony morphology of Vibrio Cholerae on SV medium. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;40(2):213–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb04167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley C. M. A simplified method for the isolation of Bacteroides nodusus from ovine foot-rot and studies on its colony morphology and serology. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;40(3):301–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb04178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]