Abstract
Coeliac disease is exacerbated by wheat gluten. A review of methods for the purification, identification and quantitation of wheat proteins to investigate coeliac disease is presented. Recent developments including amino acid sequencing and expression of wheat protein peptides in E. coli should permit characterization of the cereal peptide that exacerbates coeliac disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand B. S., Piris J., Truelove S. C. The role of various cereals in coeliac disease. Q J Med. 1978 Jan;47(185):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. G., Read A. E. Oats and barley toxicity in coeliac patients. Postgrad Med J. 1976 May;52(607):264–268. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.52.607.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels D., Thompson R. D., Rothstein S. Synthesis of a wheat storage protein subunit in Escherichia coli using novel expression vectors. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels D., Thompson R. D. The characterization of cDNA clones coding for wheat storage proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):2961–2977. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Ellis H. J., Evans D. J., Lennox E. S. A radioimmunoassay for wheat gliadin to assess the suitability of gluten free foods for patients with coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Mar;59(3):703–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Ellis H. J., Evans D. J., Lennox E. S. Relation of antigenic structure of cereal proteins to their toxicity in coeliac patients. Br J Nutr. 1985 Jan;53(1):39–45. doi: 10.1079/bjn19850008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Evans D. J., Fagg N. L., Lennox E. S., Dowling R. H. Clinical testing of gliadin fractions in coeliac patients. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Mar;66(3):357–364. doi: 10.1042/cs0660357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKE W. K., WEIJERS H. A., VAN DE KAMER J. H. Coeliac disease. II. The presence in wheat of a factor having a deleterious effect in cases of coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr. 1953 Jan;42(1):34–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1953.tb05563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
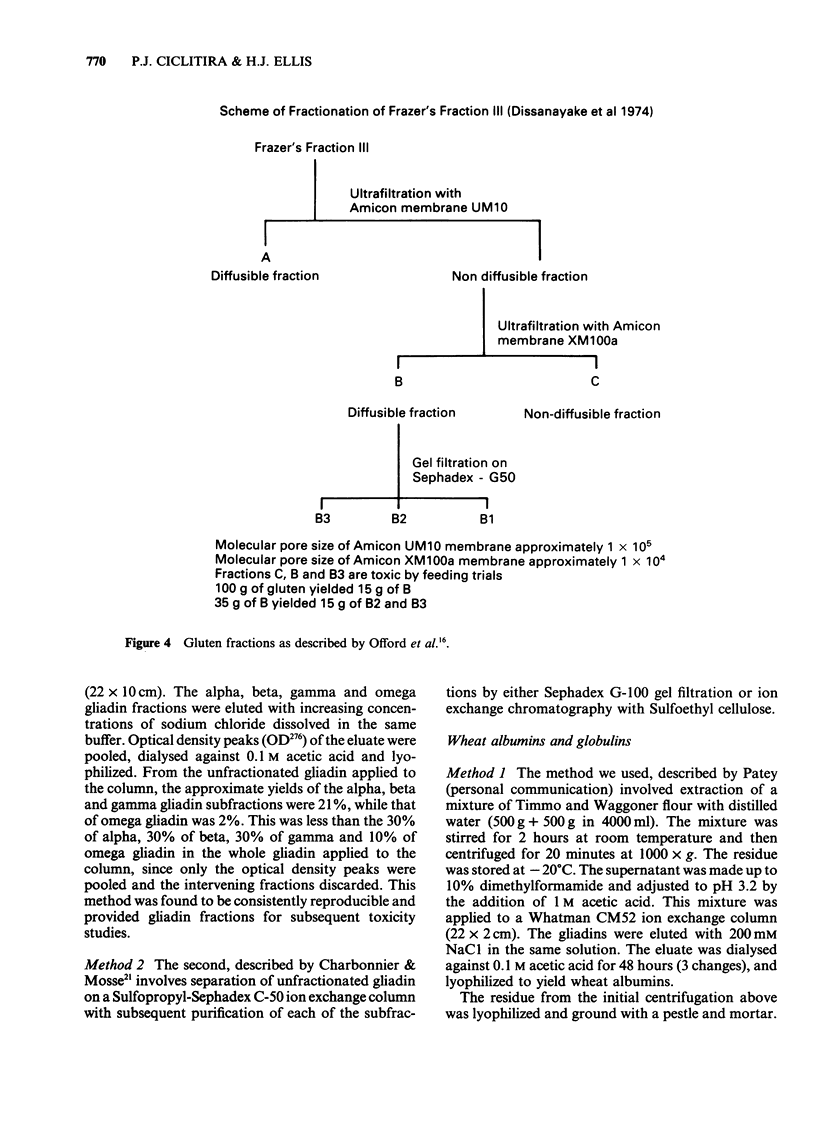
- Dissanayake A. S., Jerrome D. W., Offord R. E., Truelove S. C., Whitehead R. Identifying toxic fractions of wheat gluten and their effect on the jejunal mucosa in coeliac disease. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):931–946. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake A. S., Truelove S. C., Whitehead R. Lack of harmful effect of oats on small-intestinal mucosa in coeliac disease. Br Med J. 1974 Oct 26;4(5938):189–191. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5938.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
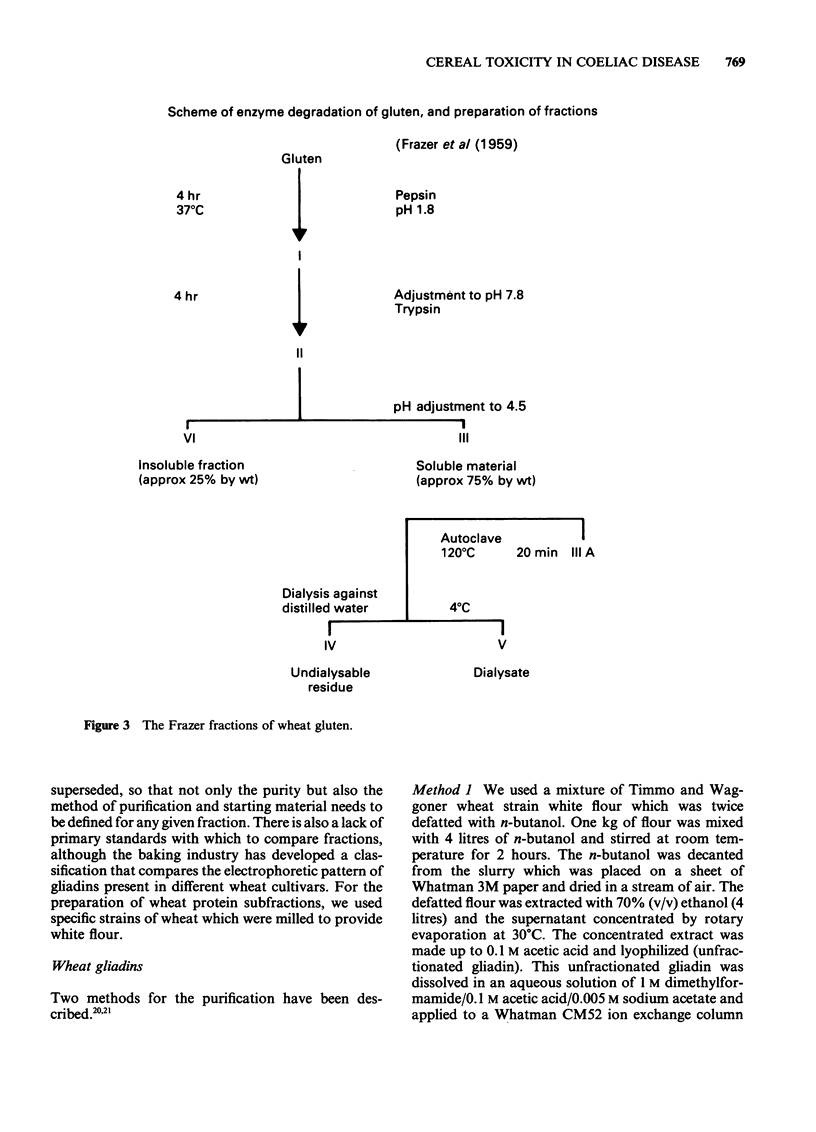
- FRAZER A. C., FLETCHER R. F., ROSS C. A., SHAW B., SAMMONS H. G., SCHNEIDER R. Gluten-induced enteropathy: the effect of partially digested gluten. Lancet. 1959 Sep 5;2(7097):252–255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howdle P. D., Ciclitira P. J., Simpson F. G., Losowsky M. S. Are all gliadins toxic in coeliac disease? An in vitro study of alpha, beta, gamma, and w gliadins. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Jan;19(1):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jos J., Charbonnier L., Mossé J., Olives J. P., de Tand M. F., Rey J. The toxic fraction of gliadin digests in coeliac disease. Isolation by chromatography on Biogel P-10. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Mar 12;119(3):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Hubert J. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D. Possible role for a human adenovirus in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1544–1557. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Schneider R., Cox P. S., Hawkins C. F. Gluten subfractions in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patey A. L., Evans D. J. Large-scale preparation of gliadin proteins. J Sci Food Agric. 1973 Oct;24(10):1229–1233. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740241011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHINER M., DONIACH I. Histopathologic studies in steatorrhea. Gastroenterology. 1960 Mar;38:419–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DE KAMER J. H., WEIJERS H. A. Coeliac disease. V. Some experiments on the cause of the harmful effect of wheat gliadin. Acta Paediatr. 1955 Sep;44(5):465–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1955.tb04269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DE KAMER J. H., WEIJERS H. A., DICKE W. K. Coeliac disease. IV. An investigation into the injurious constituents of wheat in connection with their action on patients with coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr. 1953 May;42(3):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1953.tb05586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOYCHIK J. H., BOUNDY J. A., DIMLER R. J. Starch gel electrophoresis of wheat gluten proteins with concentrated urea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]