Abstract
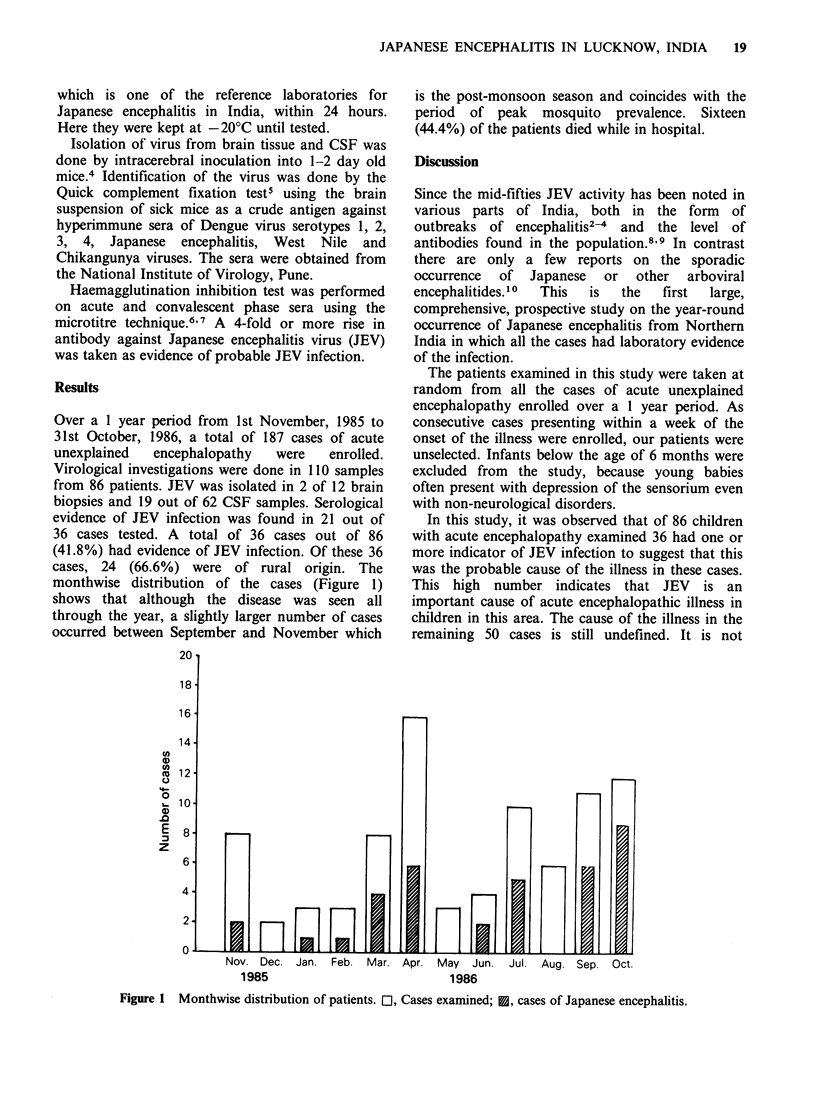
Eighty-six randomly selected children between 6 months and 12 years of age admitted with acute unexplained encephalopathy over a one year period were examined for evidence of Japanese encephalitis. One or more indicators of the infection were present in 36 (41.8%). Viral isolation from brain tissue was possible in 2 of 12 patients and from cerebrospinal fluid in 19 out of 62 patients. Serological evidence of probable Japanese encephalitis was found in 21 out of 36 patients. Japanese encephalitis is an important cause of acute childhood encephalopathy in the Lucknow area, where it is probably endemic.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee K., Desai P. K. Survey of arbovirus antibodies in South India. Indian J Med Res. 1973 Mar;61(3):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas S. K., Bose S. N., Bose M., Roychoudhury D., Nundy N. K., Mukherji S., Saha S. C., Sarkar R., Banerji N., Chatterji R. Epidemic of Japanese encephalitis in Bankura (1973): clinico-pathological findings. Indian J Med Res. 1976 Jun;64(6):801–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASCENKOV N. I. JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS IN THE USSR. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:161–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John T. J., Feldman R. A., Patoria N. K., Christopher S., George S. Enteroviruses and acute encephalopathy syndrome in Nagpur. Indian J Pediatr. 1984 Nov-Dec;51(413):627–631. doi: 10.1007/BF02776376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kant L., Mukherji D. Japanese encephalitis: containing the growing threat. Indian J Pediatr. 1986 Sep-Oct;53(5):543–545. doi: 10.1007/BF02748656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketel W. B., Ognibene A. J. Japanese B encephalitis in Vietnam. Am J Med Sci. 1971 May;261(5):271–279. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197105000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono R., Kim K. H. Comparative epidemiological features of Japanese encephalitis in the Republic of Korea, China (Taiwan) and Japan. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(2):263–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Chaturvedi U. C., Tandon H. O., Agarwal A. K., Mathur G. P., Nag D., Prasad A., Mittal V. P. Japanese encephalitis epidemic in Uttar Pradesh, India during 1978. Indian J Med Res. 1982 Feb;75:161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAVRI K., JADHAV M., WEBB J. K., GEORGE S. Herpes simplex encephalitis: isolation of virus from a fatal case in South India. Indian J Med Res. 1963 Mar;51:223–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. L., Rodrigues F. M., Nambiapan M., Nagarajan M., Ghalsasi G. R., Rodrigues J. J., Pinto B. D., Rao C. V., Gupta N. P. Aetiology of the 1978 outbreak of encephalitis in Tirunelveli and other districts of Tamil Nadu. Indian J Med Res. 1982 Jul;76:36–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh B. H., Rodrigues F. M., Padbidri V. S., Gupta N. P., Sundaram K. R., Ghosh S. N. Antibodies to arboviruses in humans of Rajasthan. Indian J Med Res. 1978 Feb;67:175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


