Abstract
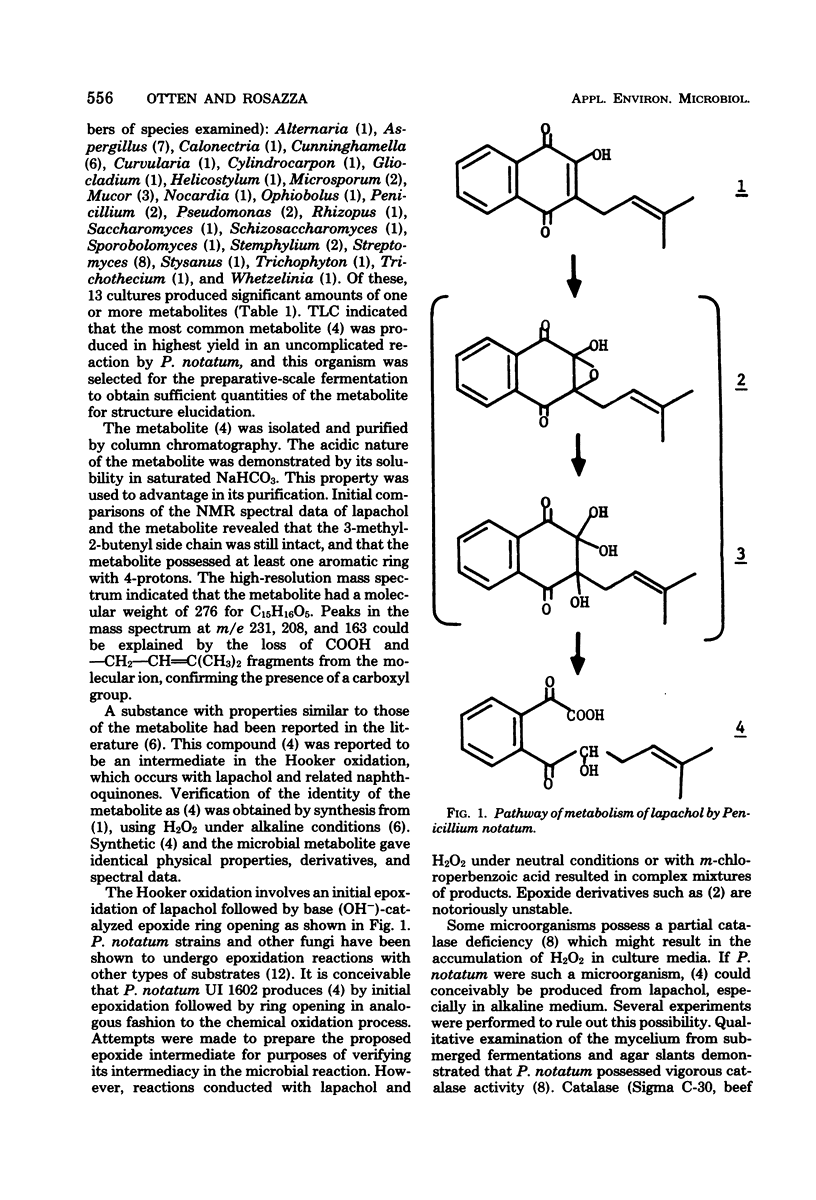
The naphthoquinone lapachol (1) is readily metabolized by several fungi and streptomycetes. Preparative-scale fermentations with Penicillium notatum (UI 1602) provided a major polar metabolite (4), which was isolated and identified as an intermediate of the Hooker oxidation. The metabolite was synthesized by reacting lapachol with hydrogen peroxide under alkaline conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betts R. E., Walters D. E., Rosazza J. P. Microbial transformations of antitumor compounds. 1. Conversion of acronycine to 9-hydroxyacronycine by Cunninghamella echinulata. J Med Chem. 1974 Jun;17(6):599–602. doi: 10.1021/jm00252a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block J. B., Serpick A. A., Miller W., Wiernik P. H. Early clinical studies with lapachol (NSC-11905). Cancer Chemother Rep 2. 1974 Dec;4(4):27–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gledhill W. E., Casida L. E. Predominant Catalase-negative Soil Bacteria. III. Agromyces, gen. n., Microorganisms Intermediary to Actinomyces and Nocardia. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Sep;18(3):340–349. doi: 10.1128/am.18.3.340-349.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Consolaço M., Linardi F., de Oliveira M. M., Sampaio M. R. A lapachol derivative active against mouse lymphocytic leukemia P-388. J Med Chem. 1975 Nov;18(11):1159–1161. doi: 10.1021/jm00245a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lime O. G., Coêlho J. S., d' Albuquerque I. L., de Mello J. F., Martins D. G., Lacerda A. L., de Moraes e Souza M. A. Substâncias antimicrobianas de plantas superiores. XXXV. Atividade antimicrobiana e antitumoral de lawsona (2-hidroxi-1,4-naphthoquinone) em comparaço com o lapachol (2-hidroxi-3-(-3-metil-2-butenil)-1,4-naphthoquinone. Rev Inst Antibiot (Recife) 1971 Jun;11(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


