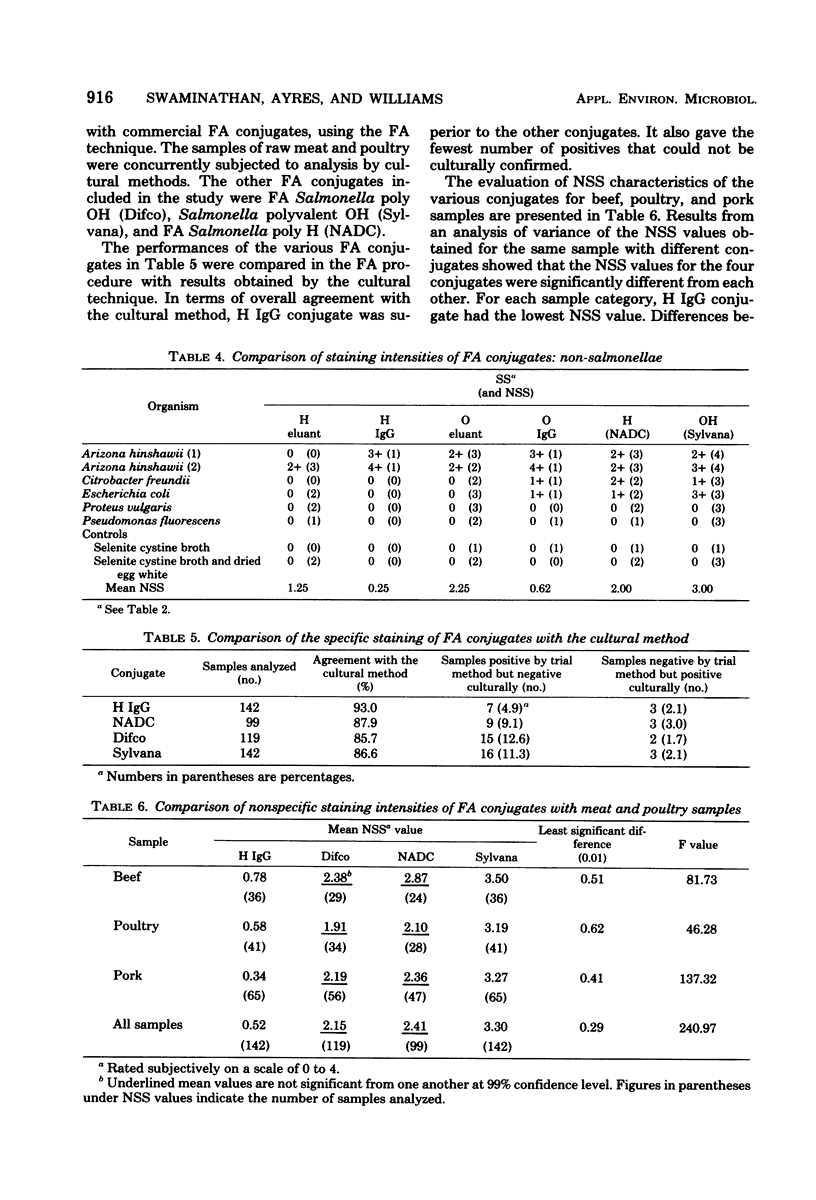
Abstract
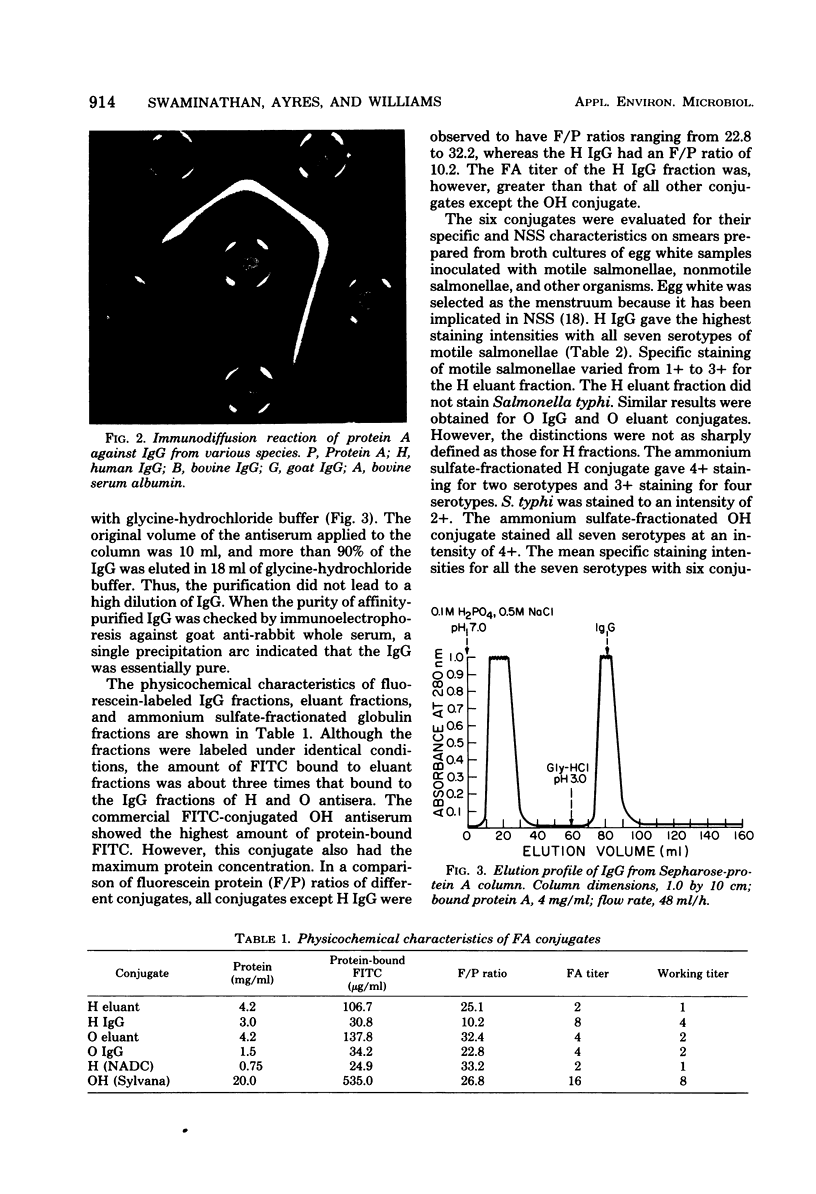
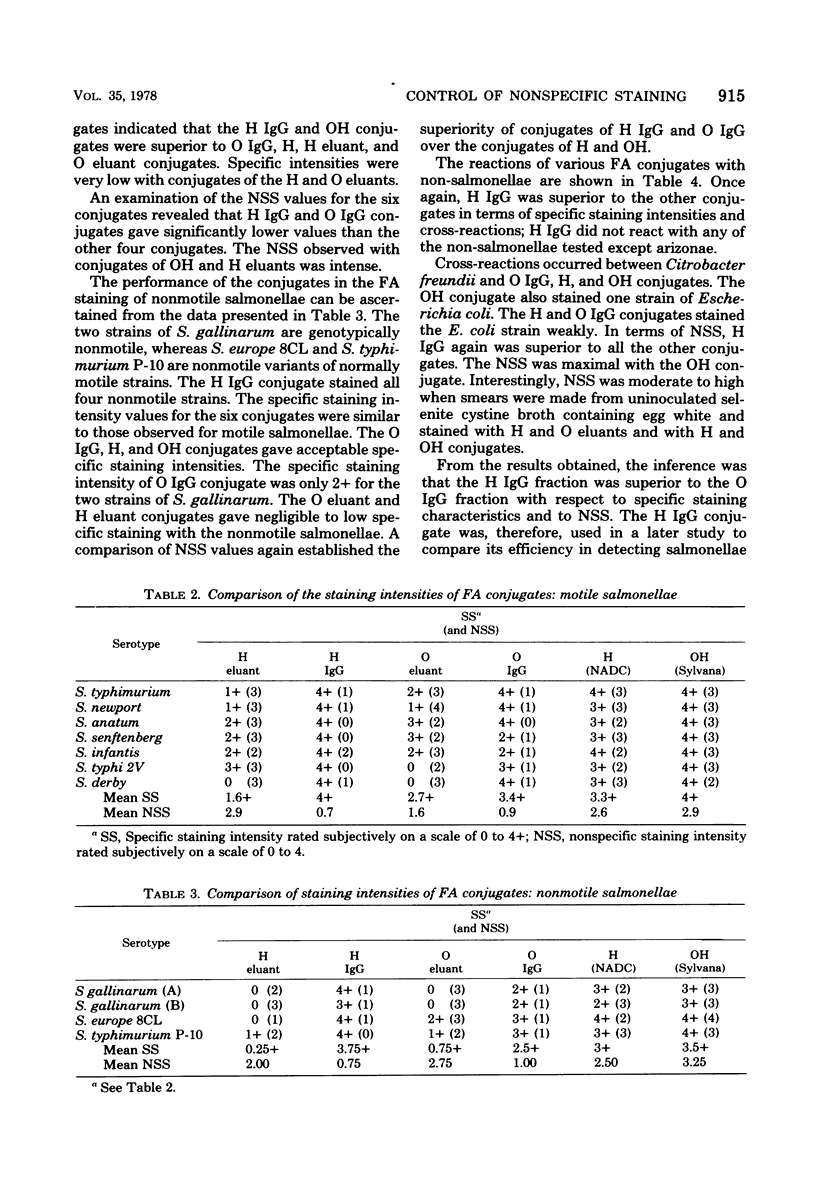
A fluorescent antibody conjugate, prepared from the IgG (immunoglobulin G) fraction of Salmonella polyvalent flagellar antiserum, gave better specific staining intensities and significantly lower nonspecific staining than did conjugates prepared from globulin fractions of ammonium sulfate-fractionated Salmonella polyvalent antisera. IgG was purified by affinity chromatography against protein A, a normal cell wall component of Staphylococcus aureus. Affinity chromatography yielded high-purity IgG in a one-step purification procedure. The conjugate prepared from affinity-purified IgG was compared with commercially available fluorescent antibody conjugates for the detection of salmoneallae in retail samplings of meats and poultry and gave better correlations with the cultural method than did the commercial conjugates.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleksić S., Rohde R. The separation and purification of "Salmonella-Arizona" H-antigens by the DEAE-cellulose column chromatography for the preparation of diagnostic H-antisera with high titres and free of O-antibodies. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Sep;123(3):363–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidson S., Holme T., Wadström T. Influence of cultivation conditions on the production of extracellular proteins by Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Petersson B. A., Sjöquist J. Some physiochemical properties of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK H. F., SHEPARD C. C. A DIALYSIS TECHNIQUE FOR PREPARING FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:642–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Thomason B. M., Gladden J. B., Holsing N., Murlin A. M. Detection of salmonellae in foodstuffs, feces, and water by immunofluorescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:350–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEDMON R. E., HOLMES A. W., DEINHARDT F. PREPARATION OF FLUORESCEIN ISOTHIOCYANATE-LABELED GAMMA-GLOBULIN BY DIALYSIS, GEL FILTRATION, AND IONEXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY IN COMBINATION. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:734–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.734-739.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis E. M., Harrington R., Jr A direct fluorescent antibody test for Salmonella. Arch Environ Health. 1969 Dec;19(6):876–881. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1969.10666946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Wetzstein H. P. Production of potent salmonella H antisera by immunization with flagellae, isolated by immunosorption. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF02120772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
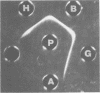
- GRABAR P. Agar-gel diffusion and immunoelectrophoretic analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Dec 16;69(4):591–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb49699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goepfert J. M., Hicks R. Immunofluorescent staining of Salmonella species with flagellar sera. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Oct;18(4):612–617. doi: 10.1128/am.18.4.612-617.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goepfert J. M., Mann M. E., Hicks R. One-day fluorescent-antibody procedure for detecting salmonellae in frozen and dried foods. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Dec;20(6):977–983. doi: 10.1128/am.20.6.977-983.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGLUND J. R., AYRES J. C., PATON A. M., KRAFT A. A., QUINN L. Y. DETECTION OF SALMONELLA IN EGGS AND EGG PRODUCTS WITH FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Sep;12:447–450. doi: 10.1128/am.12.5.447-450.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R., Jr, Ellis E. M. Immunofluorescence technique for detection of Salmonellae in tissues of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Feb;33(2):445–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pittman B., Cherry W. B. Factors affecting the degree of nonspecific staining given by fluorescein isothiocyanate labelled globulins. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1204–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pittman B., Cherry W. B. The definition and application of evaluation techniques as a guide for the improvement of fluorescent antibody reagents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:54–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Sjödahl J., Sjöquist J. Immunologically active and structurally similar fragments of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):395–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insalata N. F., Mahnke C. W., Dunlap W. G. Rapid, direct fluorescent-antibody method for the detection of salmonellae in food and feeds. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):645–649. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.645-649.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insalata N. F., Schulte S. J., Berman J. H. Immunofluorescence technique for the detection of salmonellae in various foods. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1145–1149. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1145-1149.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A., Nilsson G., Thore A., Morein B. Quantification of the inhibitory effect of eriochrome black and sodium nitrite on non-specific immunofluorescent staining. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Oct;83(5):482–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Spillane J. T., Pearce G. W. A simple method for determining the labeling efficiency of fluorescein isothiocyanate products. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman B., Herbert G. A., Cherry W. B., Taylor G. C. The quantitation of nonspecific staining as a guide for improvement of fluorescent antibody conjugates. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1196–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Meloun B., Hjelm H. Protein A isolated from Staphylococcus aureus after digestion with lysostaphin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason B. M. Evaluation of frozen fixed smears for use in fluorescent antibody studies of salmonellae. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):418–419. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.418-419.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason B. M., Hebert G. A., Cherry W. B. Evaluation of a semiautomated system for direct fluorescent antibody detection of salmonellae. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):557–564. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.557-564.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason B. M., Wells J. G. Preparation and testing of polyvalent conjugates for fluorescent-antibody detection of salmonellae. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):876–884. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.876-884.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]