Abstract
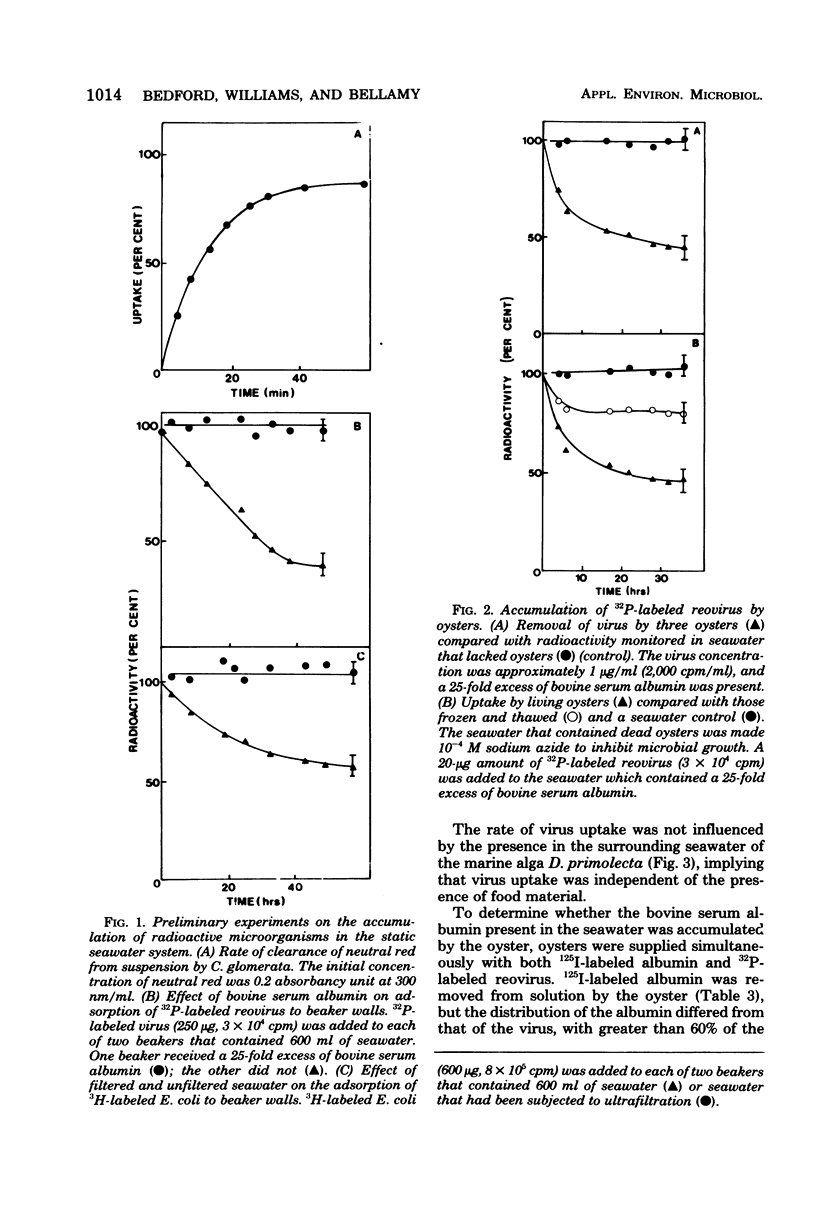
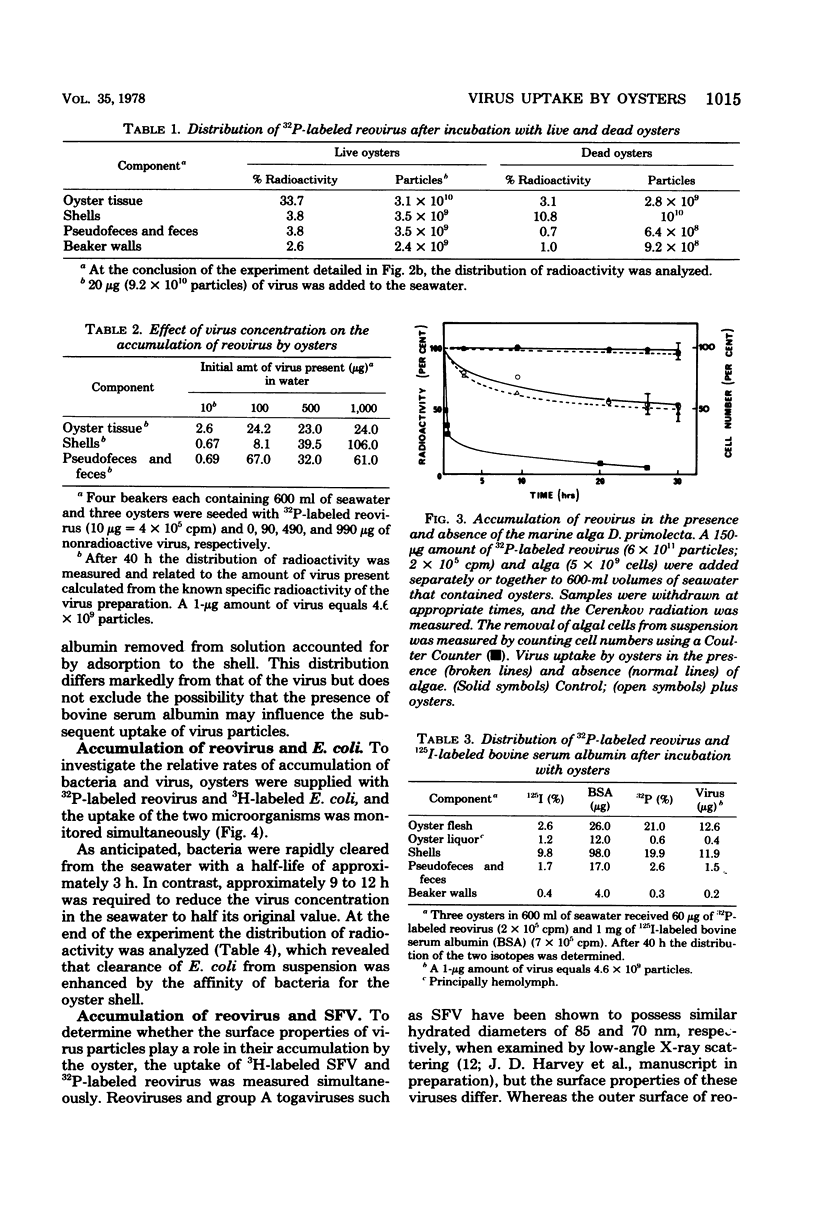
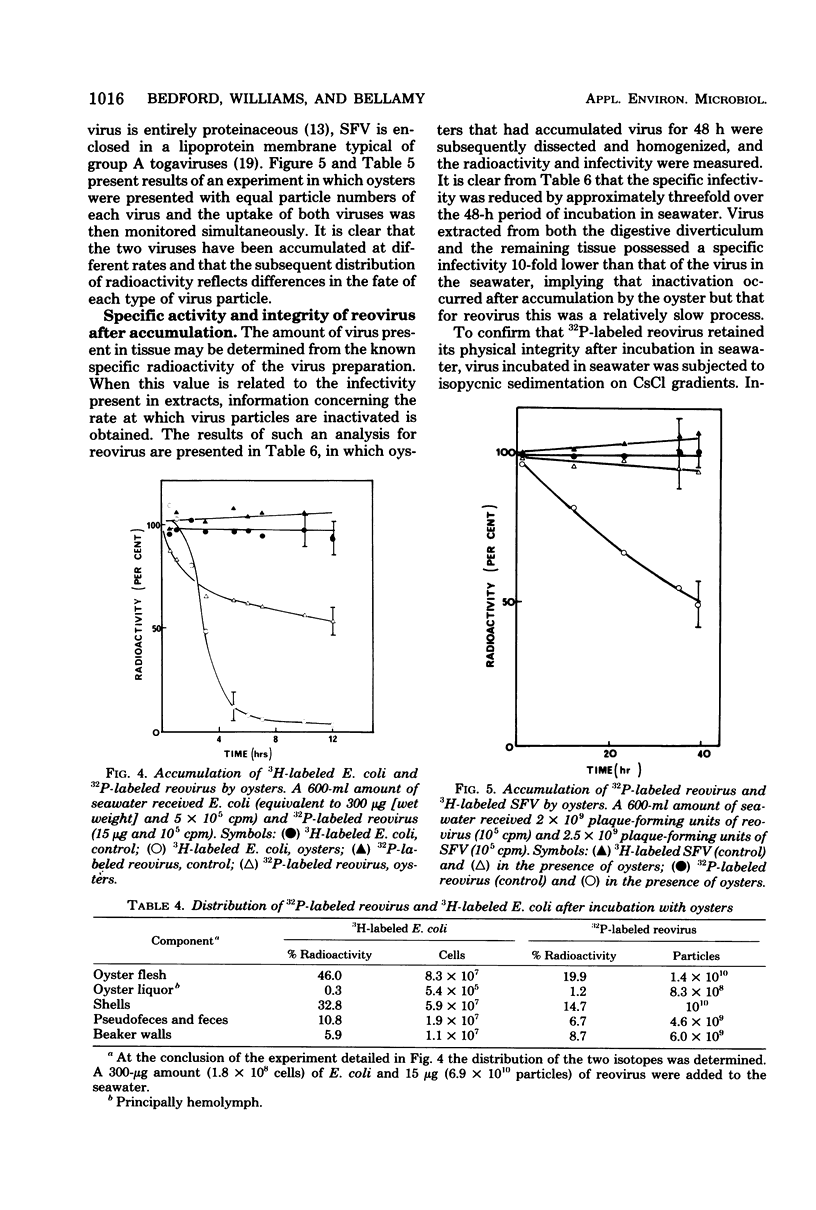
The accumulation of virus by the New Zealand rock oyster Crassostrea glomerata has been studied in a static seawater system using radioactively labeled reovirus type III and Semliki Forest virus. The uptake of virus was found to be less rapid than for the bacterium Escherichia coli and to be unaffected by the presence of the marine alga Dunaliella primolecta in the seawater. Accumulation was dependent on virus concentration, with saturation achieved at 4 X 10(10) reovirus particles per oyster, implying that an oyster possesses a large but finite number of sites for virus adsorption. When the rates of uptake of two viruses of similar size but differing surface properties were compared, the rate of accumulation of the lipoprotein-enveloped Semliki Forest virus was found to be less than that for the protein-enclosed reovirus. This observation, together with the finding that the oyster shell has a strong affinity for virus, suggests that surface properties, rather than size, are the principal factors governing the accumulation of viruses by filter-feeding marine bivalves.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELBERG E. A., BURNS S. N. Genetic variation in the sex factor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1960 Mar;79:321–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.3.321-330.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badman D. G. Filtration of neutral red by fresh water clams in aerobic and hypoxic conditions. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1975 Aug 1;51(4):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(75)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Shapiro L., August J. T., Joklik W. K. Studies on reovirus RNA. I. Characterization of reovirus genome RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli V. J., Heffernan W. P. Accumulation of Escherichia coli by the Northern quahaug. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Feb;19(2):239–244. doi: 10.1128/am.19.2.239-244.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canzonier W. J. Accumulation and elimination of coliphage S-13 by the hard clam, Mercenaria mercenaria. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jun;21(6):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/am.21.6.1024-1031.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo R., Liston J., Matches J. Ionic bonding, the mechanism of viral uptake by shellfish mucus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.19-25.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J. A., Harvey J. D., Bellamy A. R. Biophysical studies of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Joklik W. K. Isolation and preliminary genetic and biochemical characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Sharp D. G. Aggregation of poliovirus and reovirus by dilution in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.159-167.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I., Burke D. C. Studies on the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jan;14(1):87–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METCALF T. G., STILES W. C. THE ACCUMULATION OF ENTERIC VIRUSES BY THE OYSTER, CRASSOSTREA VIRGINICA. J Infect Dis. 1965 Feb;115:68–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. The arrangement of proteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon C. P. Studies on the instantaneous death of airborne Escherichia coli. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jul;84(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


