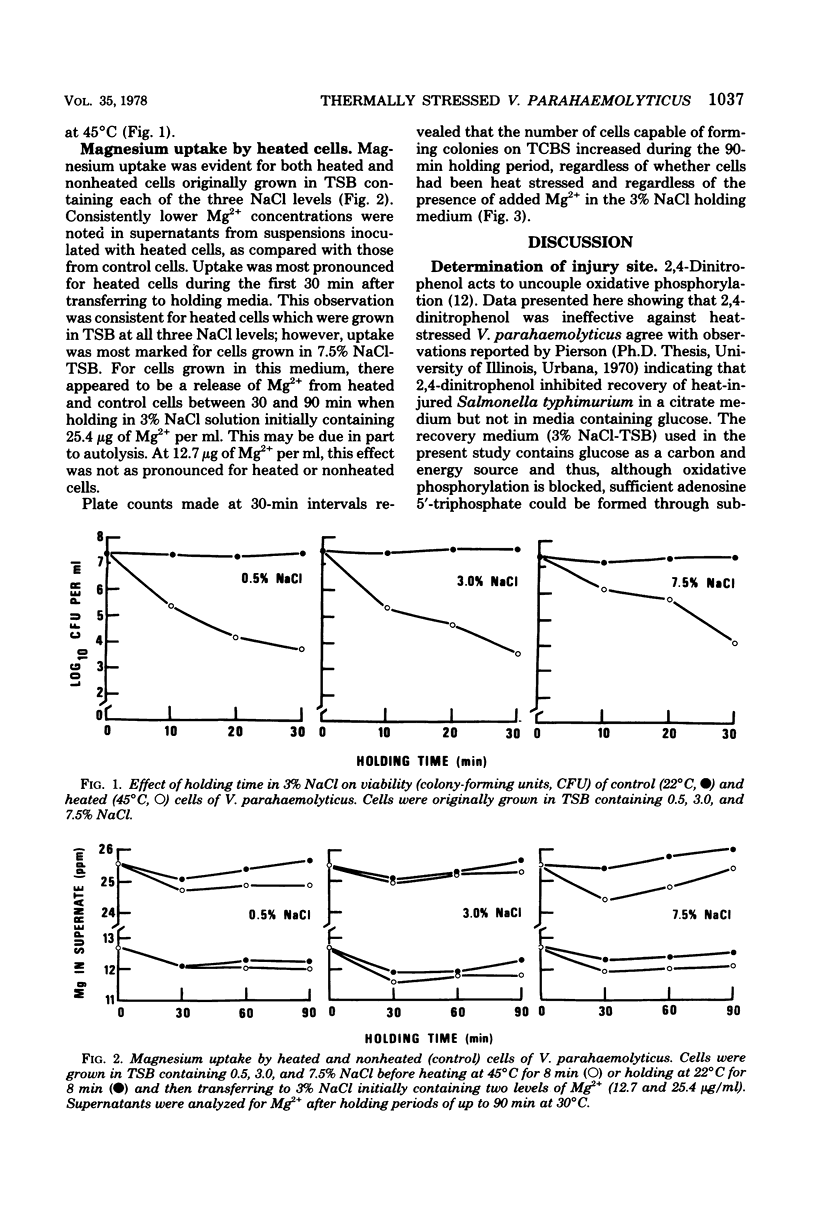
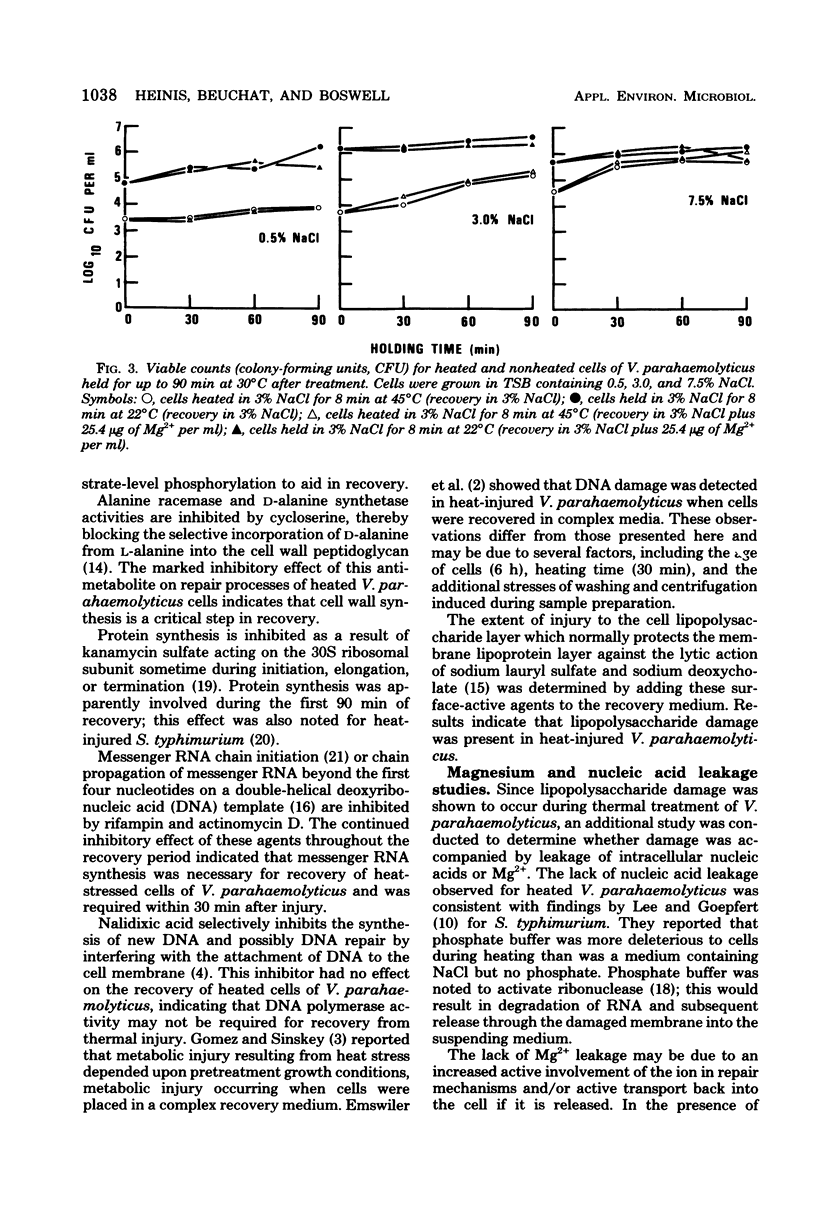
Abstract
Metabolic inhibitors were added to a culture medium inoculated with theramlly stressed Vibrio parahaemolyticus to obtain information pertaining to biosynthetic processes required for recovery from heat damage. Ribonucleic acid and protein syntheses, in addition to membrane repair, were required during recovery of injured cells. Neither nucleic acid nor Mg2+ leakage was noted to occur during the time cells were subjected to heat stress. Studies revealed that Mg2+ was apparently taken up by cells of V. parahaemolyticus during the first 30 min after thermal treatment, indicating a possible increased requirement for Mg2+ for membrane and/or ribosome stability and repair.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allwood M. C., Russell A. D. Influence of ionic and nonionic materials on thermally-induced ribonucleic acid degradation and leakage in Staphylococcus aureus. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Feb;59(2):180–183. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emswiler B. S., Pierson M. D., Shoemaker S. P. Sublethal heat stress of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):792–798. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.792-798.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. F., Sinskey A. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid breaks in heated Salmonella typhimurium LT-2 after exposure to nutritionally complex media. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):522–528. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.522-528.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinis J. J., Beuchat L. R., Jones W. K. Growth of heat-injured Vibrio parahaemolyticus in media supplemented with various cations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1079-1084.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchener B. J., Egan A. F. Outer-membrane damage in sublethally heated Escherichia coli K-12. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Mar;23(3):311–318. doi: 10.1139/m77-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A., Beare-Rogers J. L., Collins-Thompson D. L. Pysiological studies on the recovery of salt tolerance by Staphylococcus aureus after sublethal heating. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):901–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.901-907.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A., Duckworth M., Baddiley J. Loss of D-alanine during sublethal heating of Staphylococcus aureus S6 and magnesium binding during repair. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):277–284. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenis P. R., Morita R. Y. Thermally induced leakage of cellular material and viability in Vibrio marinus, a psychrophilic marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Nov;14(11):1239–1244. doi: 10.1139/m68-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenda J. R., Johnson W. G., Fishbein M., Wentz B., Mehlman I. J., Dadisman T. A., Jr Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis in Maryland: laboratory aspects. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):444–448. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.444-448.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B., Speck M. L., Dobrogosz W. J. Cell wall lipopolysaccharide damage in Escherichia coli due to freezing. Cryobiology. 1976 Apr;13(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(76)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Tolbert G. Purification and properties of a potassium-activated phosphodiesterase (RNAase II) from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1319–1330. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins R. I., Ordal Z. J. Precursor ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosome accumulation in vivo during the recovery of Salmonella typhimurium from thermal injury. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.134-142.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. Actions of the rifamycins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):290–309. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.290-309.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


