Abstract
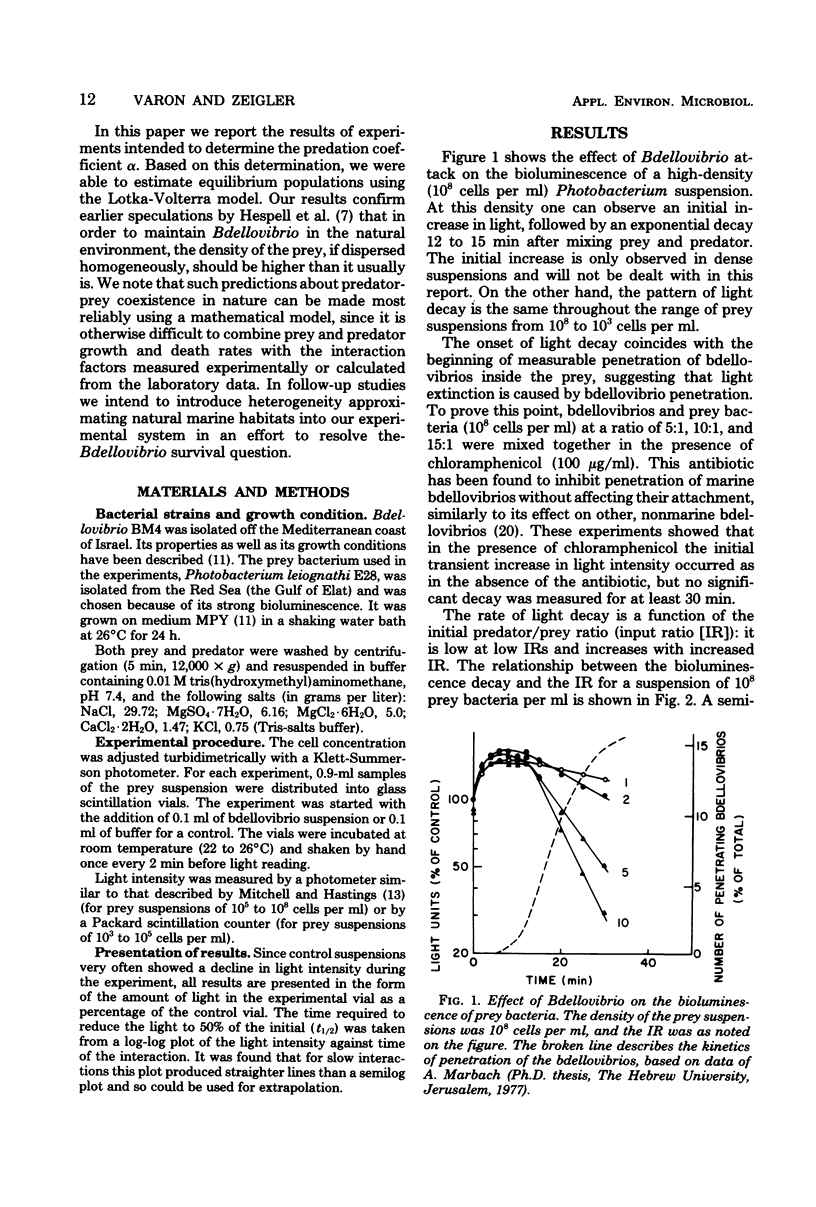
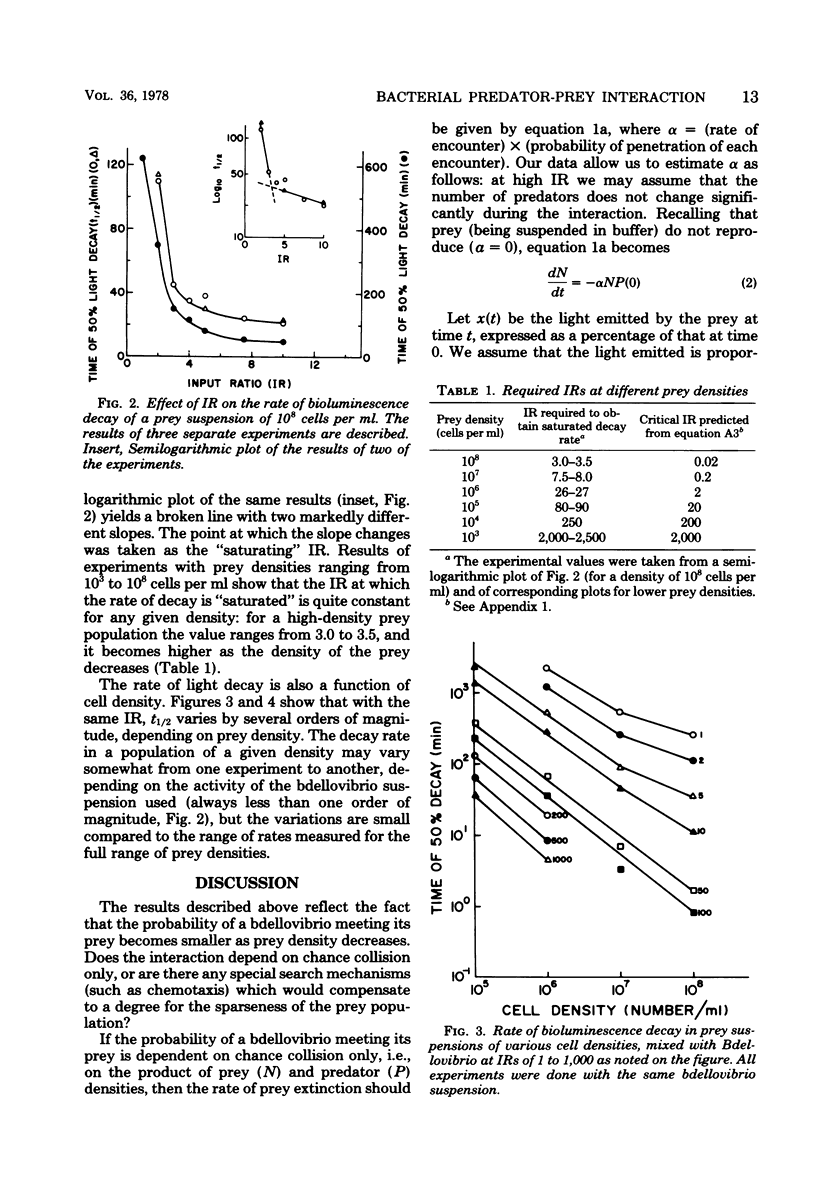
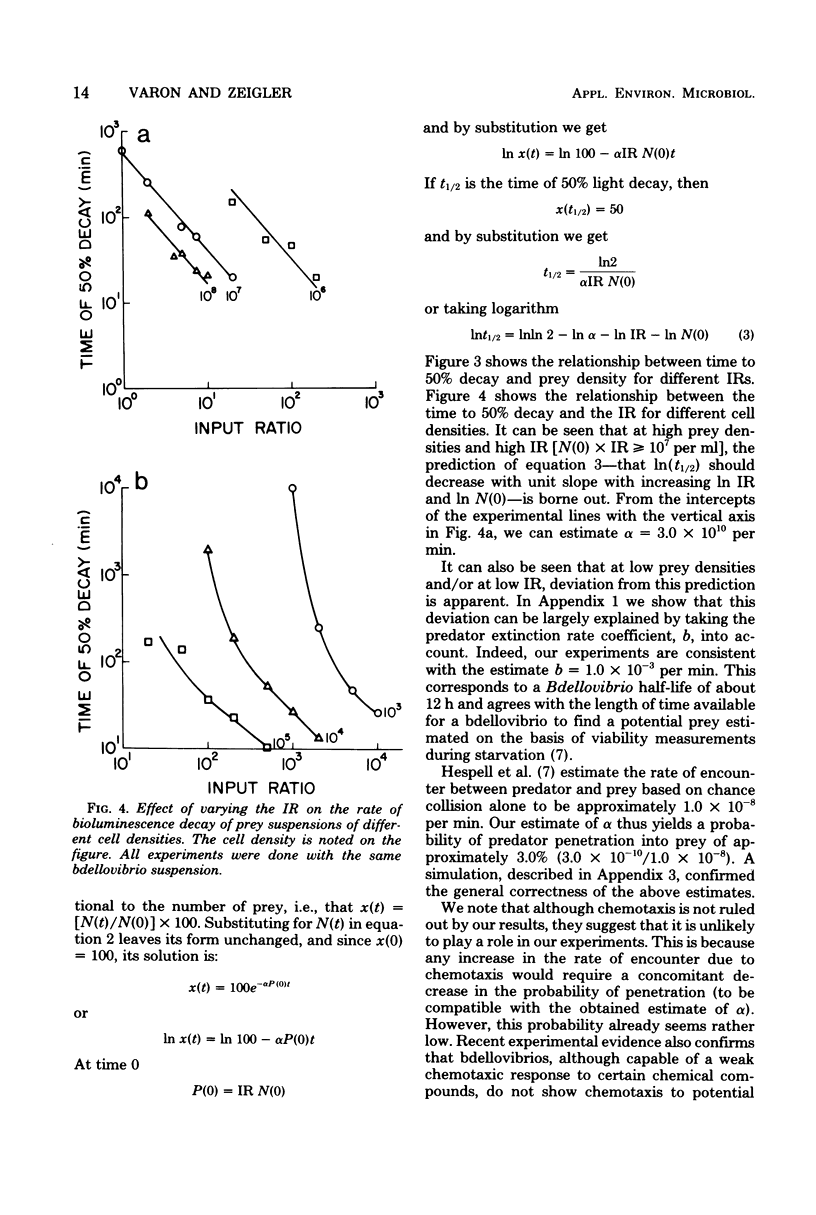
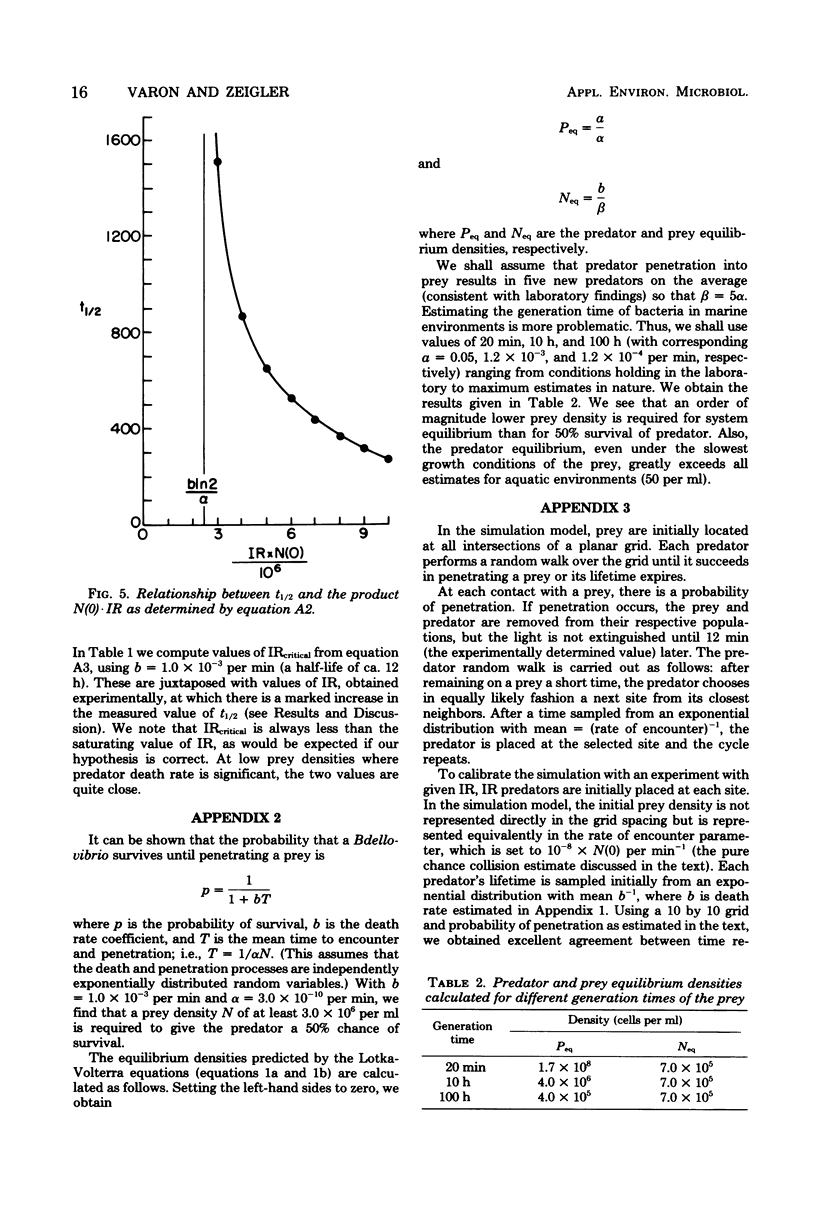
A bacterial predator-prey interaction was studied using Bdellovibrio and bioluminescent prey bacteria. The attacking bdellovibrio causes decay of bioluminescence, which is correlated with bdellovibrio penetration into the prey. The behavior of the prey and predator populations over time was found to be well described by a Lotka-Volterra model. By using this model, the probability of bdellovibrio penetration after encountering a prey cell was found to be approximately 3.0%. The prey density required to give the bdellovibrios a 50% chance of survival was calculated to be at least 3.0 × 106 cells per ml, and the density required for population equilibria was calculated to be about 7 × 105 prey bacteria per ml. These values, not generally characteristic of natural habitats, suggest that the existence of Bdellovibrio in nature is limited to special ecological niches.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell D. E., Overbeck J. The planktonic microflora of lakes. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977 Jul;5(3):305–370. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Changes in cell composition and viability of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus during starvation. Arch Microbiol. 1974 May 20;97(4):313–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00403070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. W., Hastings J. W. A stable, inexpensive, solid-state photomultiplier photometer. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieburth J. M., Willis P. J., Johnson K. M., Burney C. M., Lavoie D. M., Hinga K. R., Caron D. A., French F. W., 3rd, Johnson P. W., Davis P. G. Dissolved organic matter and heterotrophic microneuston in the surface microlayers of the north atlantic. Science. 1976 Dec 24;194(4272):1415–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.194.4272.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Conti S. F. Chemotaxis by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus toward prey. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):628–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.628-640.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor V. I., Baumann P., Reichelt J. L., Allen R. D. Isolation, enumeration, and host range of marine Bdellovibrios. Arch Microbiol. 1974 Jul 4;98(2):101–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00425273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudor J. J., Conti S. F. Characterization of bdellocysts of Bdellovibrio sp. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):314–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.314-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shil M. Interacton of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. I. Kinetic studies of attachment and invasion of Escherichia coli B by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.744-753.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigler B. P. Persistence and patchiness of predator-prey systems induced by discrete event population exchange mechanisms. J Theor Biol. 1977 Aug 22;67(4):687–713. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(77)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


