Abstract
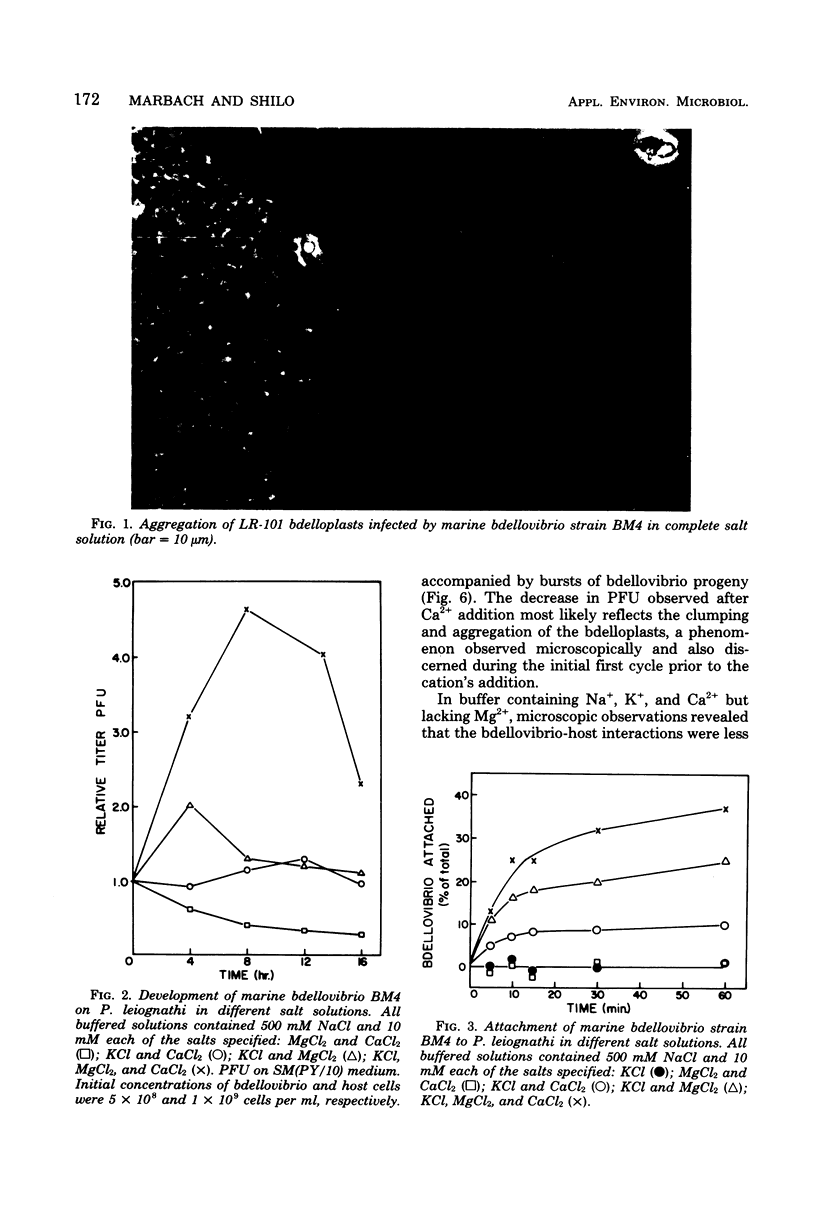
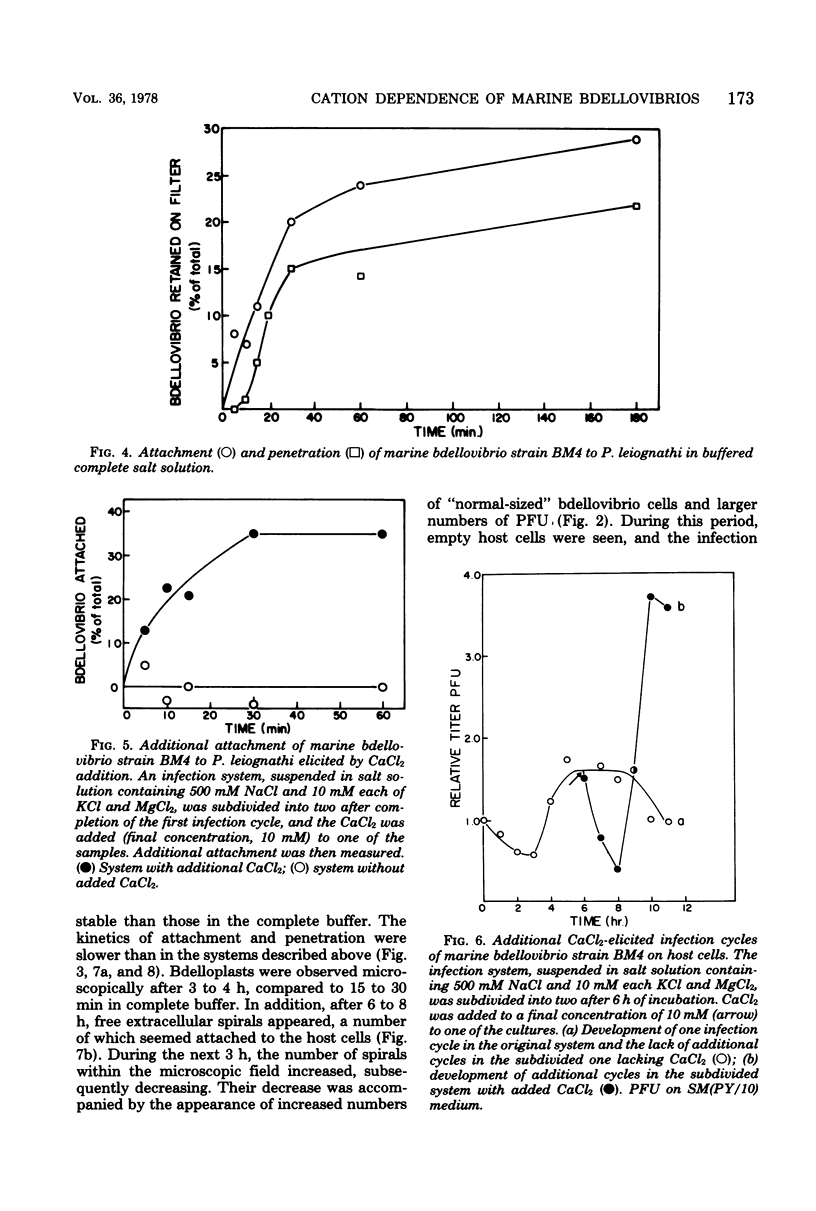
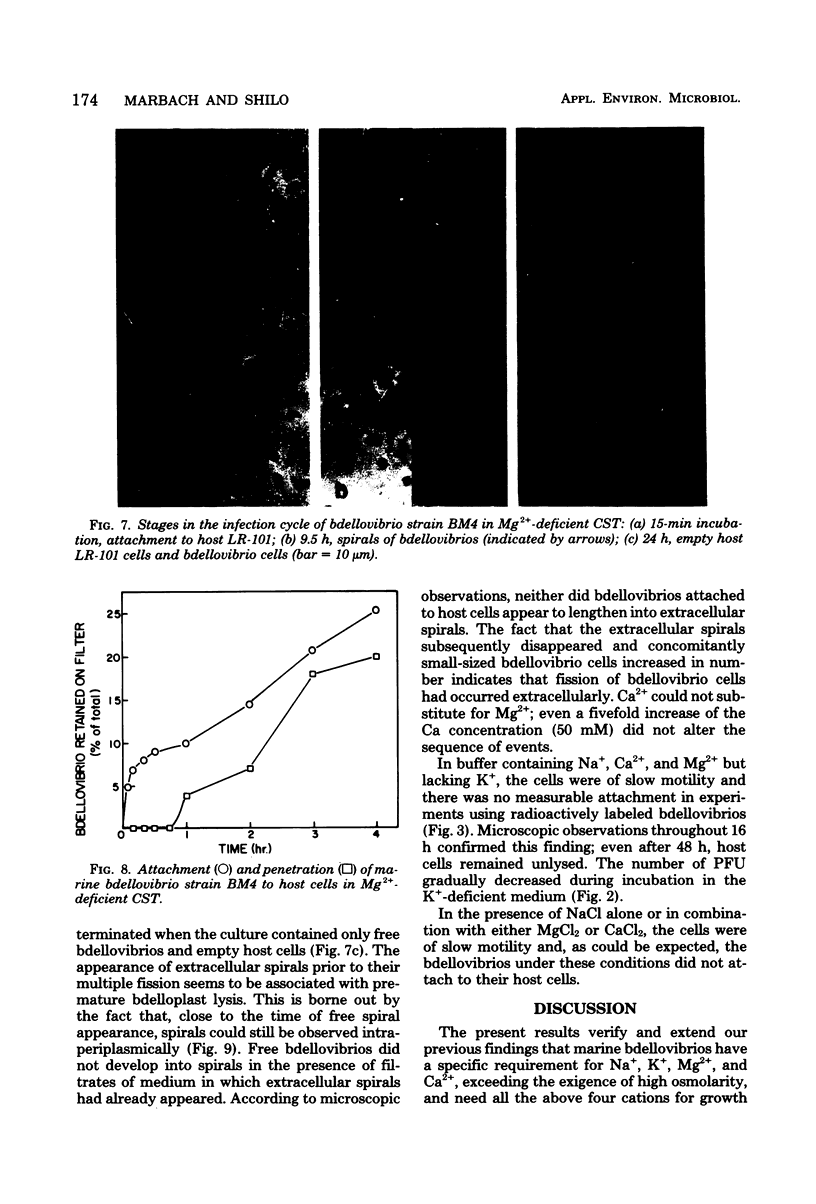
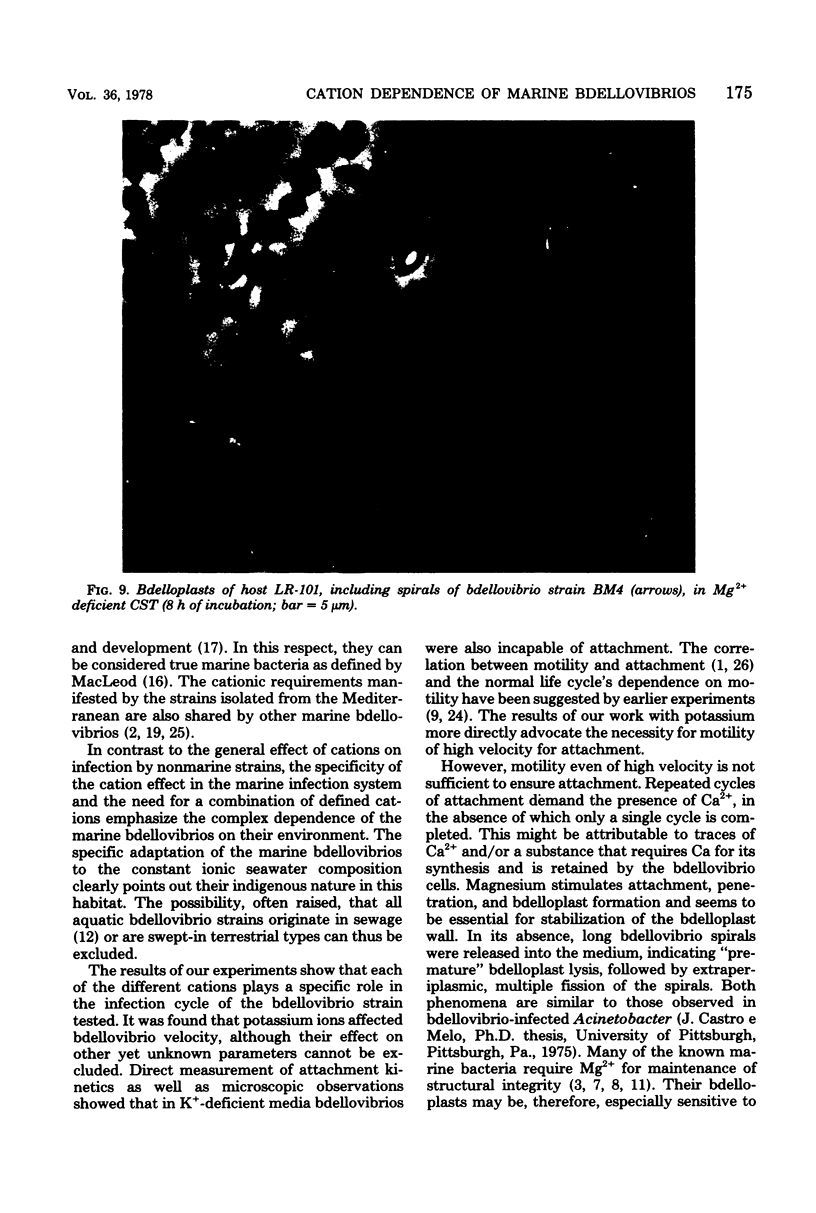
Marine bdellovibrios show a specific requirement for K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+. Potassium is essential for high velocity and seems to be necessary for attachment of the free bdellovibrios. Calcium and magnesium are necessary for attachment and penetration. Magnesium also plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the bdelloplast. The adaptation of these bdellovibrios to the marine environment is manifested by their stringent cation requirements.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Davis B. K. Structural properties and features of parasitic Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):948–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.948-965.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Evidence for the release at low salt concentration of a lipid-protein-carbohydrate complex from isolated envelopes and whole cells of a marine pseudomonad. Can J Microbiol. 1971 May;17(5):713–723. doi: 10.1139/m71-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers S. F., Fackrell H. B., Huang J. C., Robinson J. Relationship between Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 6-5-S and autoclaved host bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Dec;18(12):1941–1948. doi: 10.1139/m72-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers S. F., Robinson J. Changes in the permeability of Escherichia coli during parasitization by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Can J Microbiol. 1971 May;17(5):689–697. doi: 10.1139/m71-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Antagonistic effect of monovalent cations in maintenance of cellular integrity of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1355–1367. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1355-1367.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Cation interactions and biochemical composition of the cell envelope of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1368–1377. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1368-1377.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich D. L., Denny C. F., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Facultatively parasitic strain of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):989–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.989-996.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzinger R. M., Cooper R. C. Role of bacteria and protozoa in the removal of Escherichia coli from estuarine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):758–763. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.758-763.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Separation and localization of cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1338–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1338-1353.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. C., Staples D. G. Distribution of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus in sewage works, river water, and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):469–474. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.469-474.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guélin A., Lépine P., Lamblin D. Pouvoir bactéricide des eaux polluées et role de Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Oct;113(4):660–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Starr M. P. Effects of calcium and magnesium ions and host viability on growth of bdellovibrios. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(1):151–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02578850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R., Yankfsky S., Jannasch H. W. Lysis of Escherichia coli by marine micro-organisms. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):891–893. doi: 10.1038/215891a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Kuroda K. Lethal effect of fresh sea water on Vibrio parahaemolyticus and isolation of Bdellovibrio parasitic against the organism. Jpn J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;19(4):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1975.tb00884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLP H., STARR M. P. BDELLOVIBRIO BACTERIOVORUS GEN. ET SP. N., A PREDATORY, ECTOPARASITIC, AND BACTERIOLYTIC MICROORGANISM. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:217–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02046064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Starr M. P. Factors affecting the intracellular parasitic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus developing within Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):912–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.912-923.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M. Morphological and physiological aspects of the interaction of Bdellovibrio with host bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;50:174–204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46169-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor V. I., Baumann P., Reichelt J. L., Allen R. D. Isolation, enumeration, and host range of marine Bdellovibrios. Arch Microbiol. 1974 Jul 4;98(2):101–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00425273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shil M. Interacton of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. I. Kinetic studies of attachment and invasion of Escherichia coli B by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.744-753.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]