Abstract
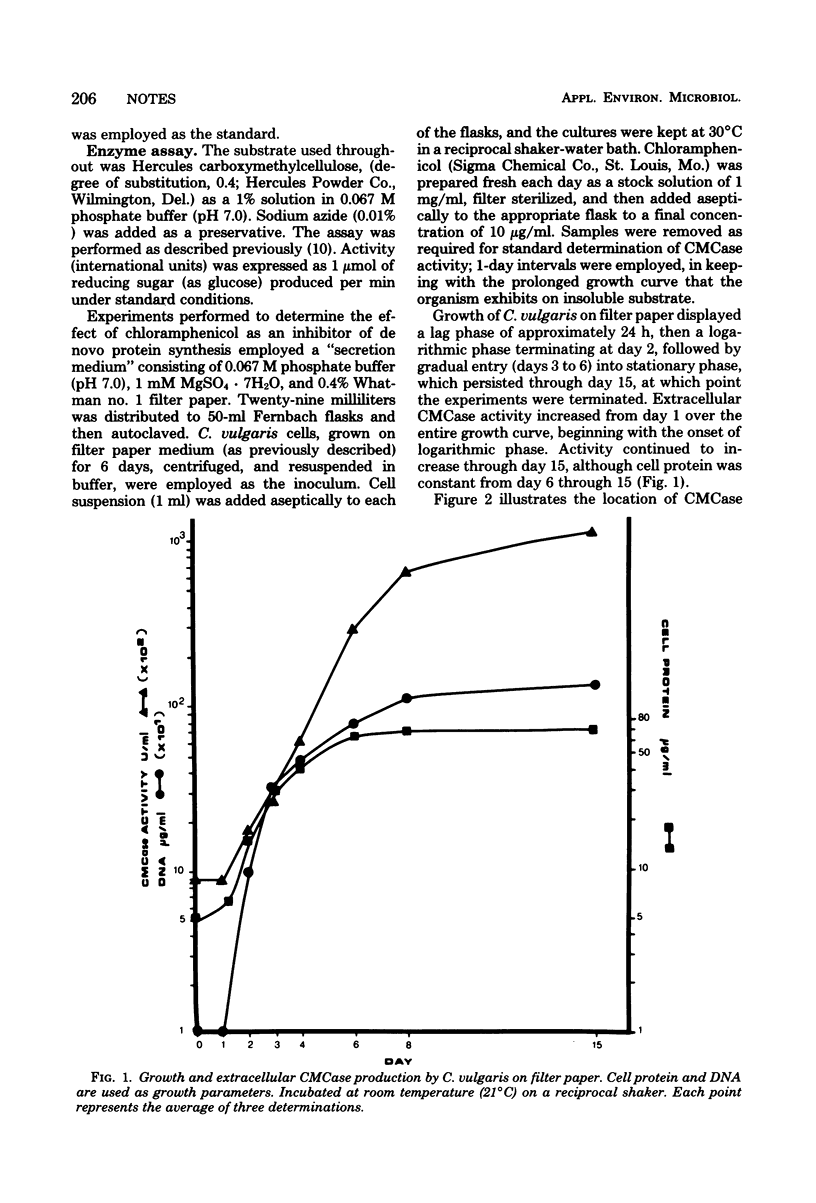
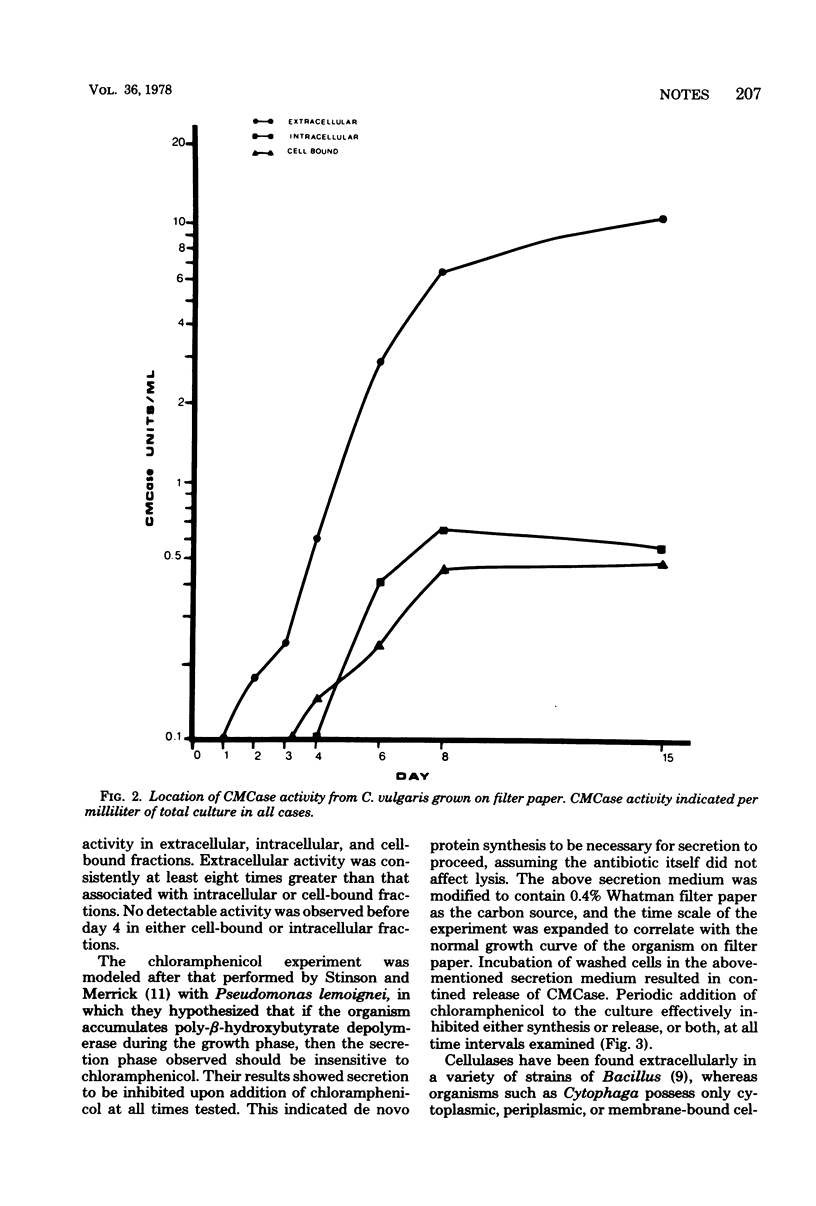
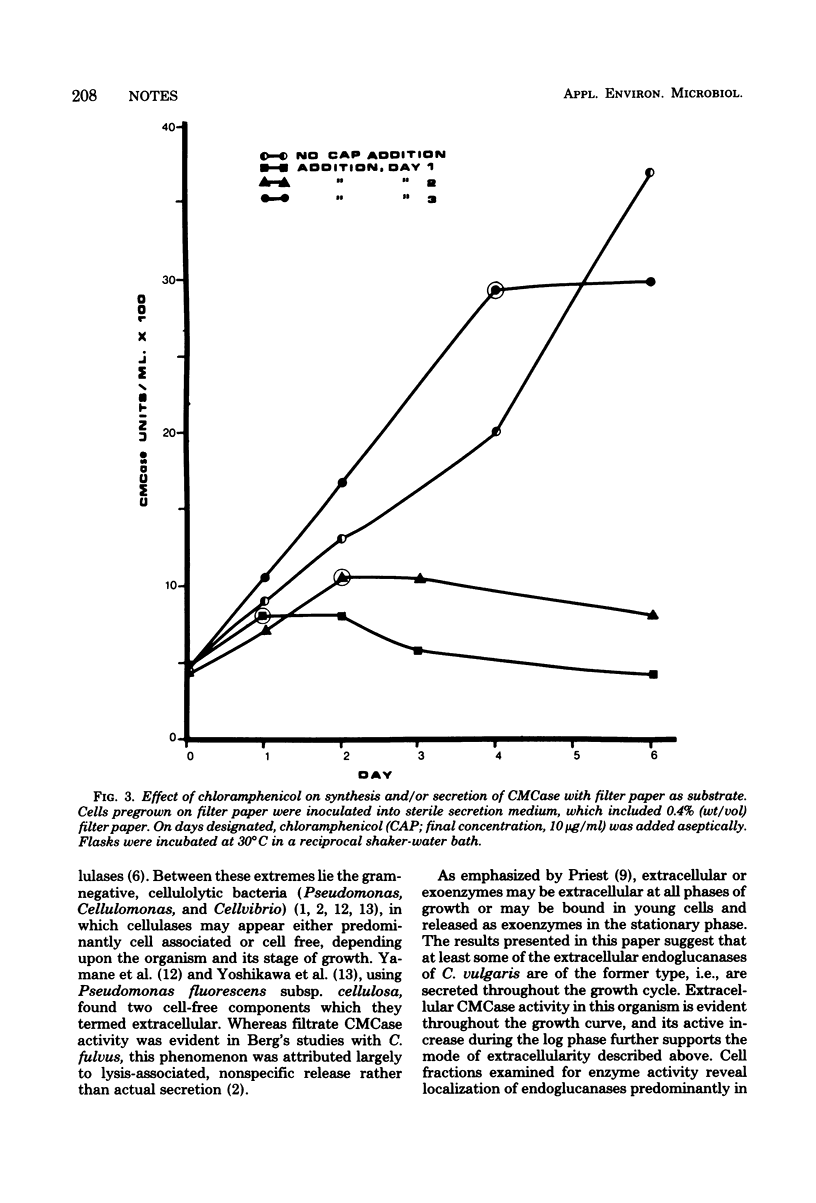
Endo-beta-1,4-glucanase of the cellulolytic bacterium Cellvibrio vulgaris is an actively secreted, truly extracellular enzyme, as supported by growth and secretion studies using filter paper as the sole carbon source.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. Cellulase location in Cellvibrio fulvus. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):51–57. doi: 10.1139/m75-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B., von Hofsten B., Pettersson G. Growth and cellulase formation by Cellvibrio fulvus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;35(2):201–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., McInnes J. L., Hanlon J. E., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Evidence for an accumulation of messenger RNA specific for extracellular protease and its relevance to the mechanism of enzyme secretion in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 20;67(2):199–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuil C., Kushner D. J. Cellulase induction and the use of cellulose as a preferred growth substrate by Cellvibrio gilvus. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Dec;22(12):1776–1781. doi: 10.1139/m76-264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. T., Thayer D. W. The cellulase system of a Cytophaga species. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1285–1292. doi: 10.1139/m77-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Merrick J. M. Extracellular enzyme secretion by Pseudomonas lemoignei. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.152-161.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Suzuki H., Hirotani M., Ozawa H., Nisizawa K. Effect of nature and supply of carbon sources on cellulase formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens var. cellulosa. J Biochem. 1970 Jan;67(1):9–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa T., Suzuki H., Nisizawa K. Biogenesis of multiple cellulase components of Pseudomonas fluorescens var. cellulosa. I. Effects of culture conditions on the multiplicity of cellulase. J Biochem. 1974 Mar;75(3):531–540. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


