Abstract
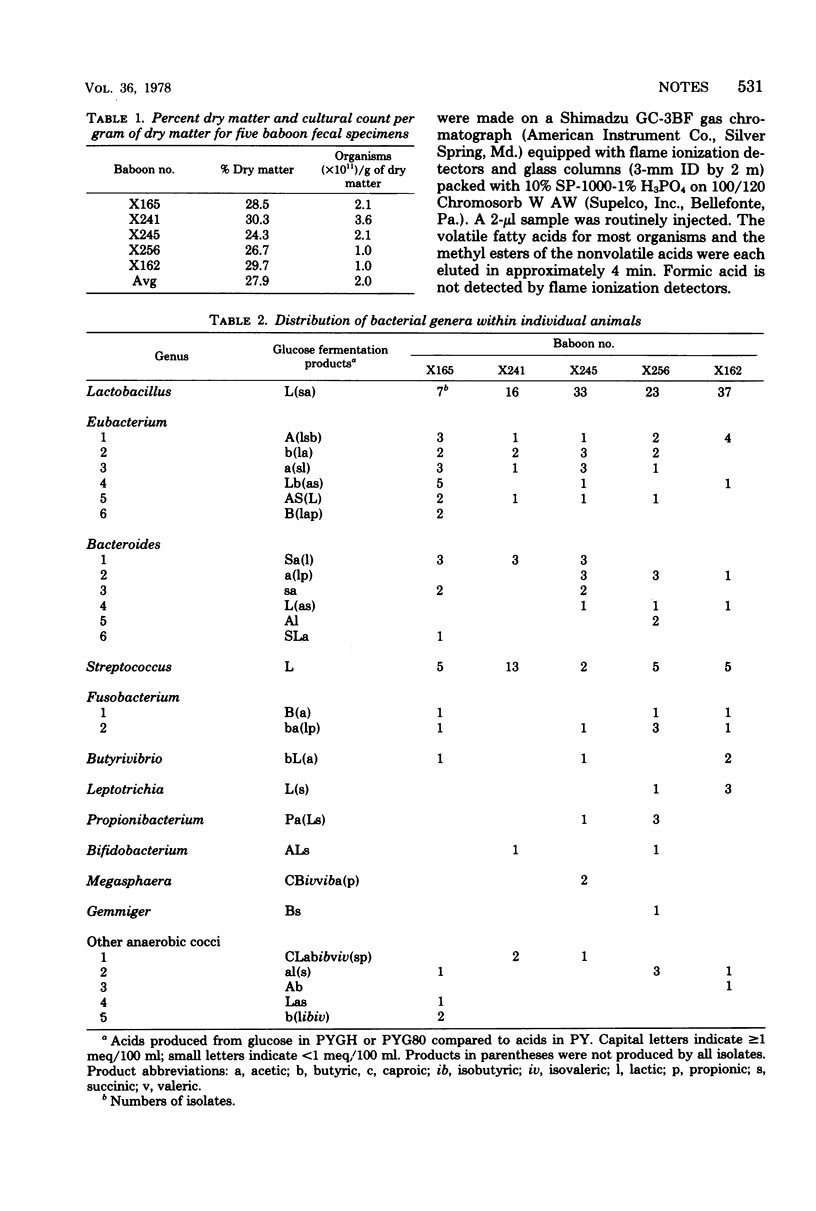
The predominant bacterial genera of baboon feces were enumerated and identified by established procedures. The predominant genera isolated were Lactobacillus, Eubacterium, Streptococcus, and Bacteroides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Effect of a partially chemically defined diet on normal human fecal flora. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1391–1398. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. R., Bryant M. P. Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):794–801. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.794-801.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eller C., Crabill M. R., Bryant M. P. Anaerobic roll tube media for nonselective enumeration and isolation of bacteria in human feces. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):522–529. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.522-529.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L. Effect of diet on human fecal flora: comparison of Japanese and American diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1456–1469. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Blake I. G., Muirhead P. A. Isolation and identification of fecal bacteria from adult swine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):79–84. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.79-84.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uphill P. F. A quantitative comparison of the faecal microflora of baboons fed a natural diet or a synthetic diet complete or deficient in pyridoxine or riboflavin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;36(3):501–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1973.tb04133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uphill P. F., Wilde J. K., Berger J. Repeated examinations, using the laparotomy sampling technique, of the gastro-intestinal microflora of baboons fed a natural or a synthetic diet. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;37(3):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


