Abstract
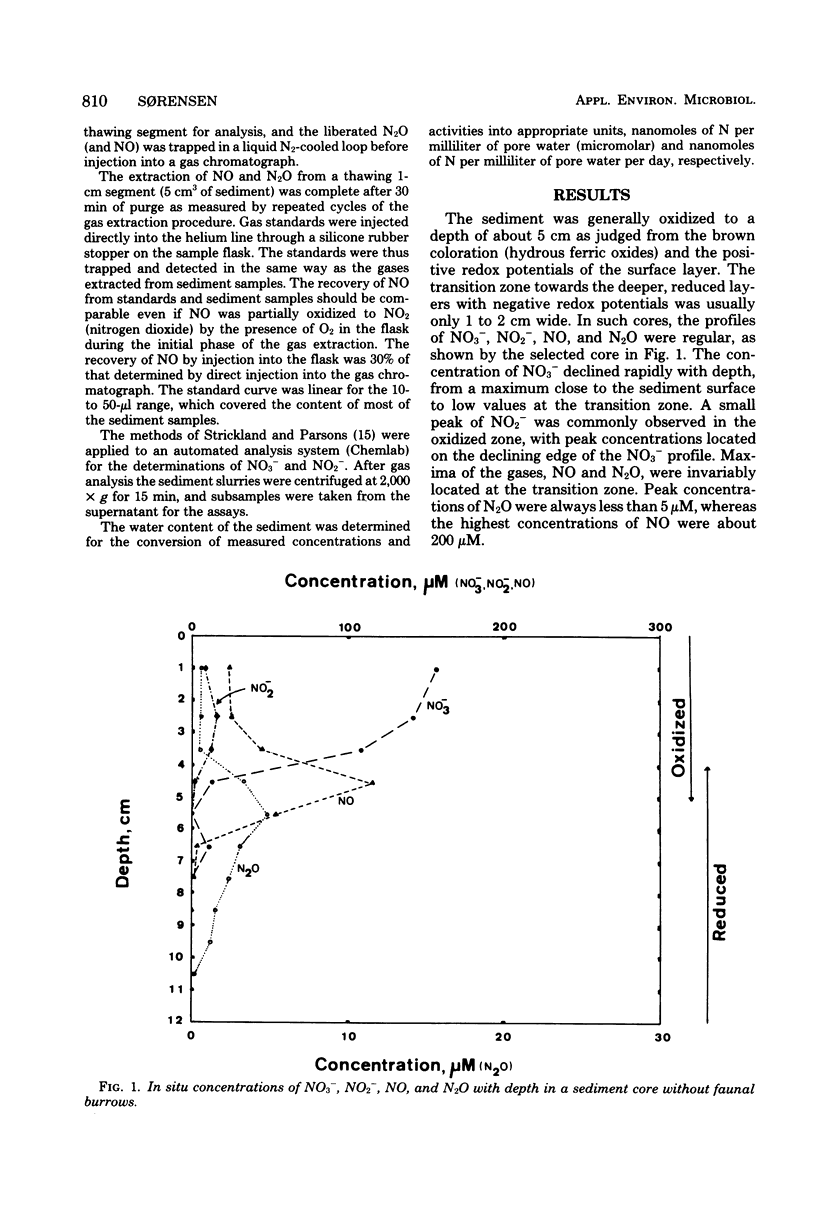
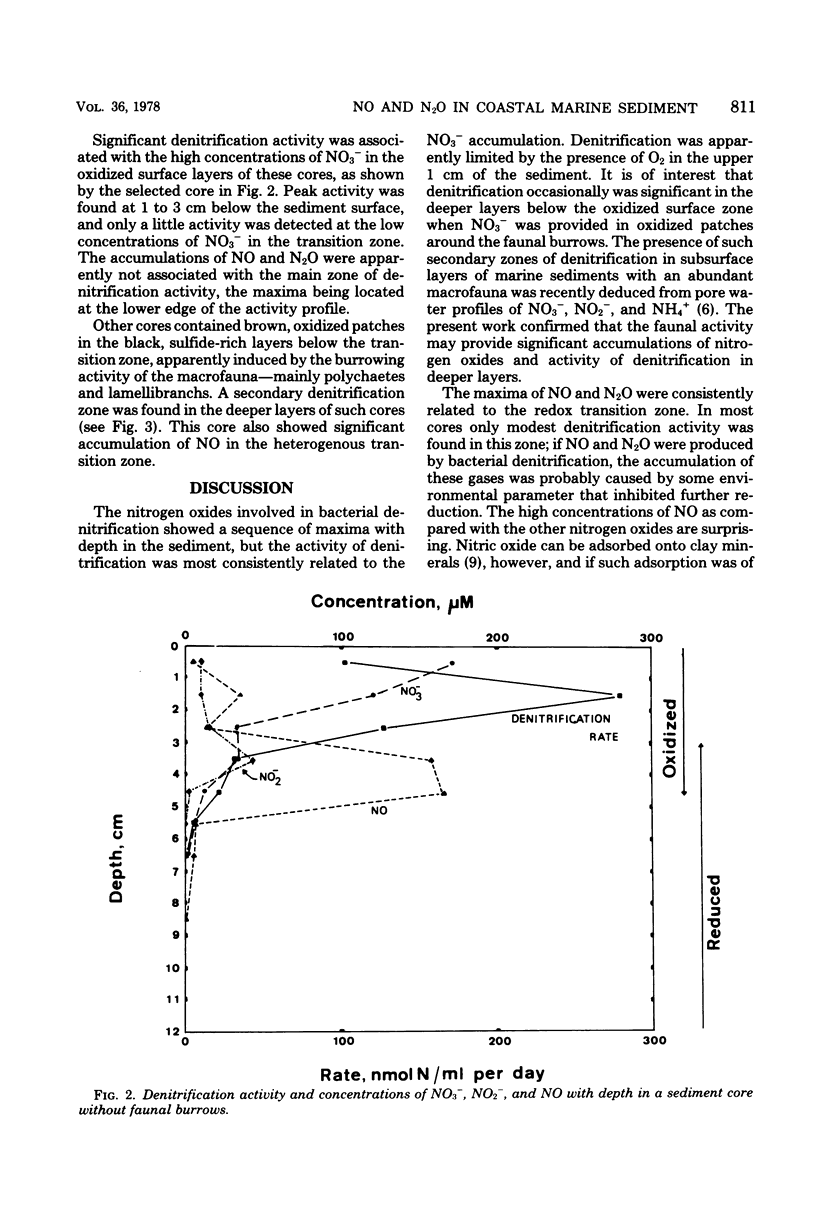
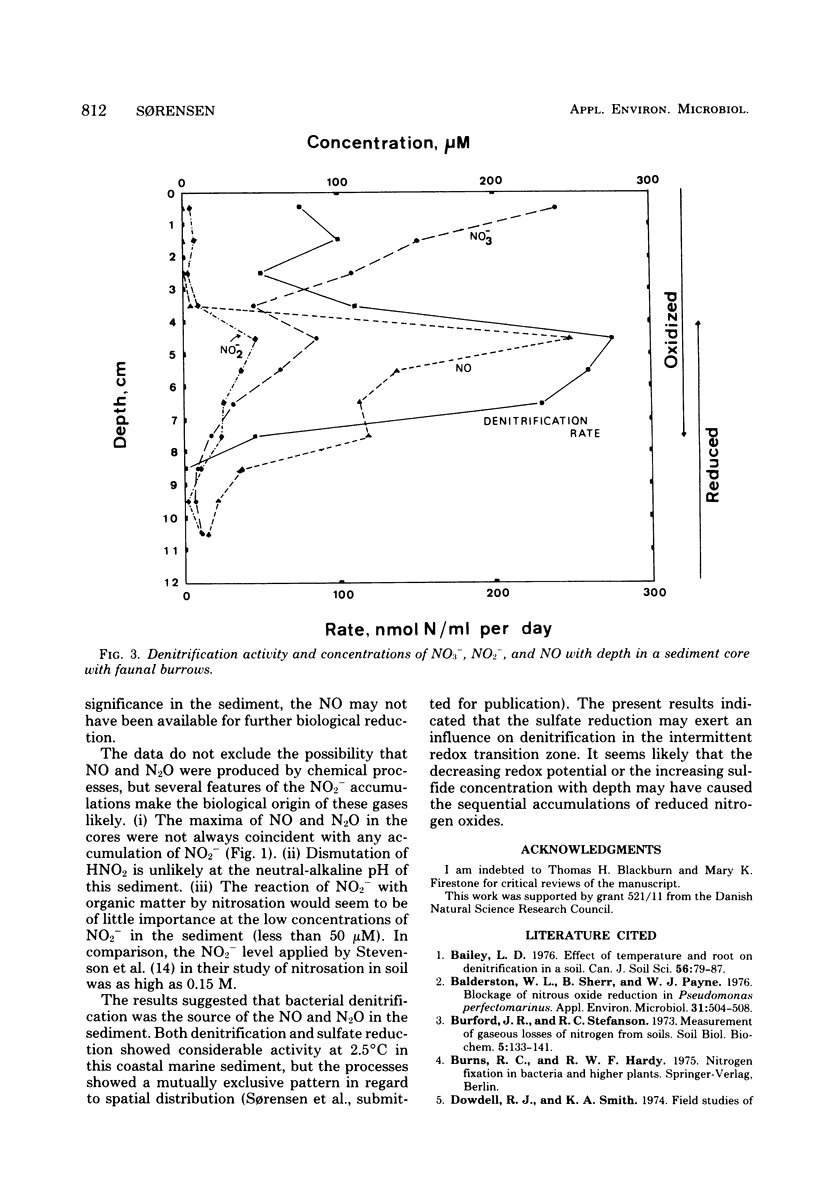
The distribution of denitrification activity in a coastal marine sediment was determined by the acetylene inhibition technique and compared to concentration profiles of NO3-, NO2-, NO, and N2O. The bulk of the denitrification activity was associated with the accumulation of NO3- in the oxidized surface zone of the sediment, but a secondary denitrification zone was occasionally found in the deeper layers where oxidized patches had been introduced by the burrowing activity of the macrofauna. Maxima of NO and N2O were not associated with the peak activity of denitrification in the surface zone but were located at the lower edge of the activity profile. Significant accumulation of NO was found at the redox transition zone towards the deeper, sulfide-rich layers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balderston W. L., Sherr B., Payne W. J. Blockage by acetylene of nitrous oxide reduction in Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):504–508. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.504-508.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):409–452. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.409-452.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John R. T., Hollocher T. C. Nitrogen 15 tracer studies on the pathway of denitrification in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):212–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Denitrification rates in a marine sediment as measured by the acetylene inhibition technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):139–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.139-143.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari T., Knowles R. Acetylene inhibition of nitrous oxide reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):705–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90932-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


