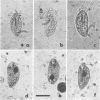
Abstract
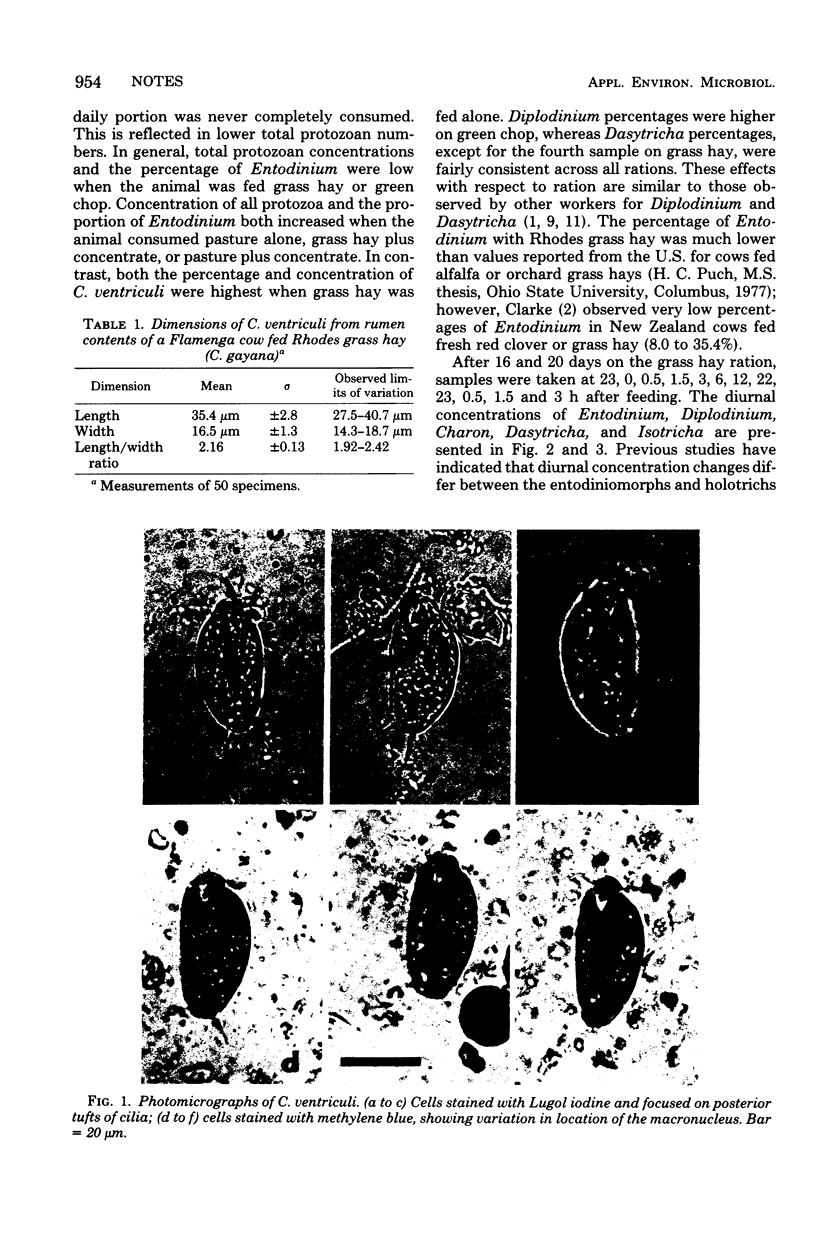
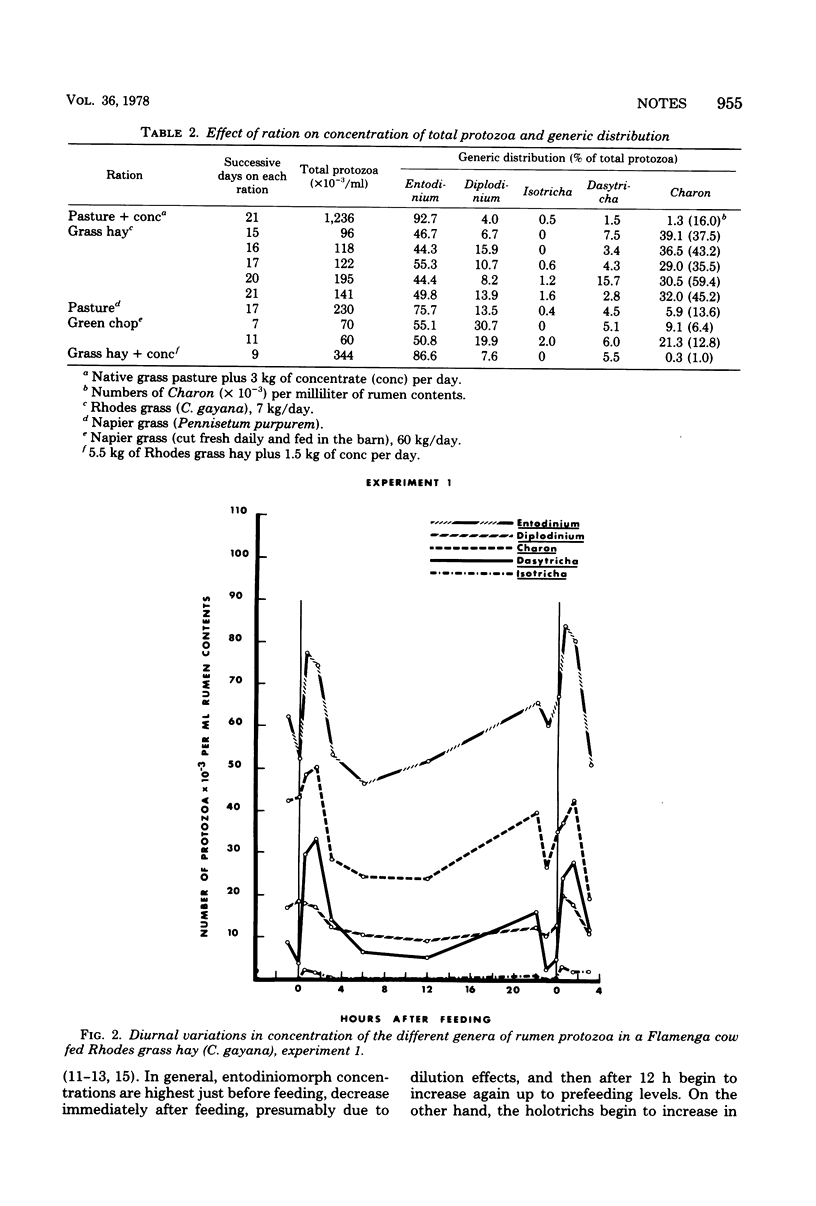
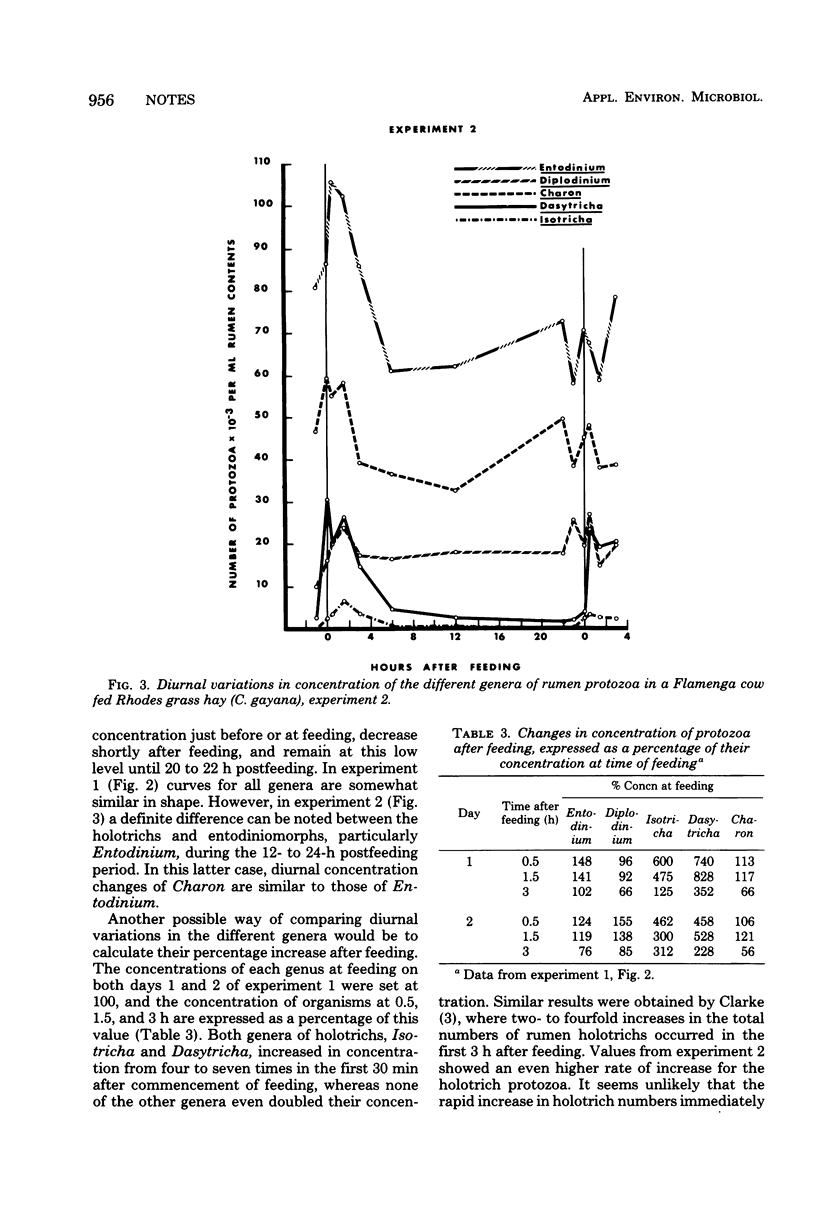
Charon ventriculi comprised over 30% of the total protozoa observed in rumen contents of a Flamenga cow fed Rhodes grass hay (Chloris gayana). Both percentage of composition and concentration decreased markedly when concentrate was added to the ration or the animal was fed in pasture. Although C. ventriculi is classified as a holotrich, concentrations of this species in the rumen appear to follow a diurnal cycle more closely related to be entodiniomorph protozoa.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe M., Shibui H., Iriki T., Kumeno F. Relation between diet and protozoal population in the rumen. Br J Nutr. 1973 Mar;29(2):197–202. doi: 10.1079/bjn19730094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Occurrence of the ciliate protozoa Bütschlia parva Schuberg in the rumen of the ovine. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):179–181. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.179-181.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Potter E. L. Diplodinium flabellum: occurrence and numbers in the rumen of sheep with a description of two new subspecies. J Protozool. 1974 Nov;21(5):686–693. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalowski T. Diurnal changes in concentration of rumen ciliates and in occurrence of dividing forms in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalus) fed once daily. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):802–804. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.802-804.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURSER D. B. A diurnal cycle for Holotrich protozoa of the rumen. Nature. 1961 May 27;190:831–832. doi: 10.1038/190831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. C. Diurnal changes in the concentrations of micro-organisms in the rumens of sheep fed limited diets once daily. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):213–235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R. A., Pilgrim A. F. Passage of protozoa and volatile fatty acids from the rumen of the sheep and from a continuous in vitro fermentation system. Br J Nutr. 1974 Sep;32(2):341–351. doi: 10.1079/bjn19740087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. L., Grainger R. B. Diurnal variation in rumen volume and metabolite concentrations. J Dairy Sci. 1970 Jun;53(6):785–792. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(70)86291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]