Abstract
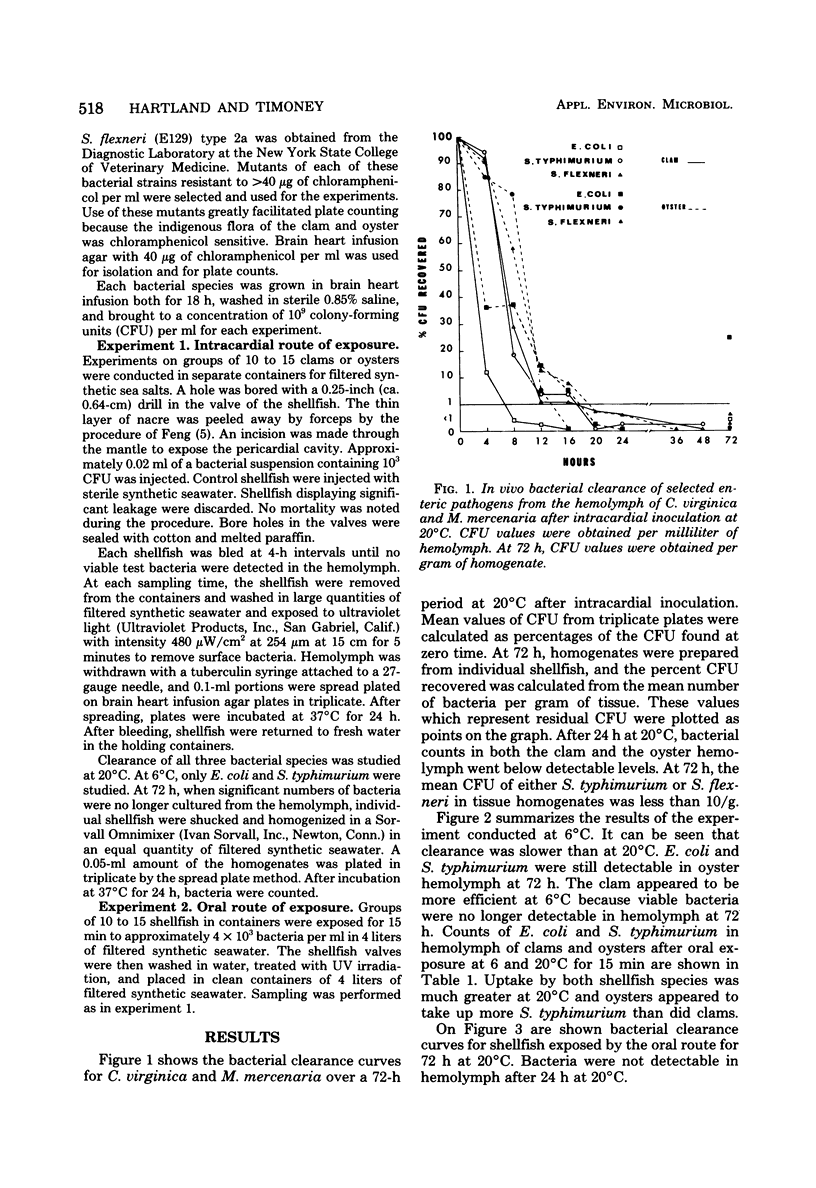
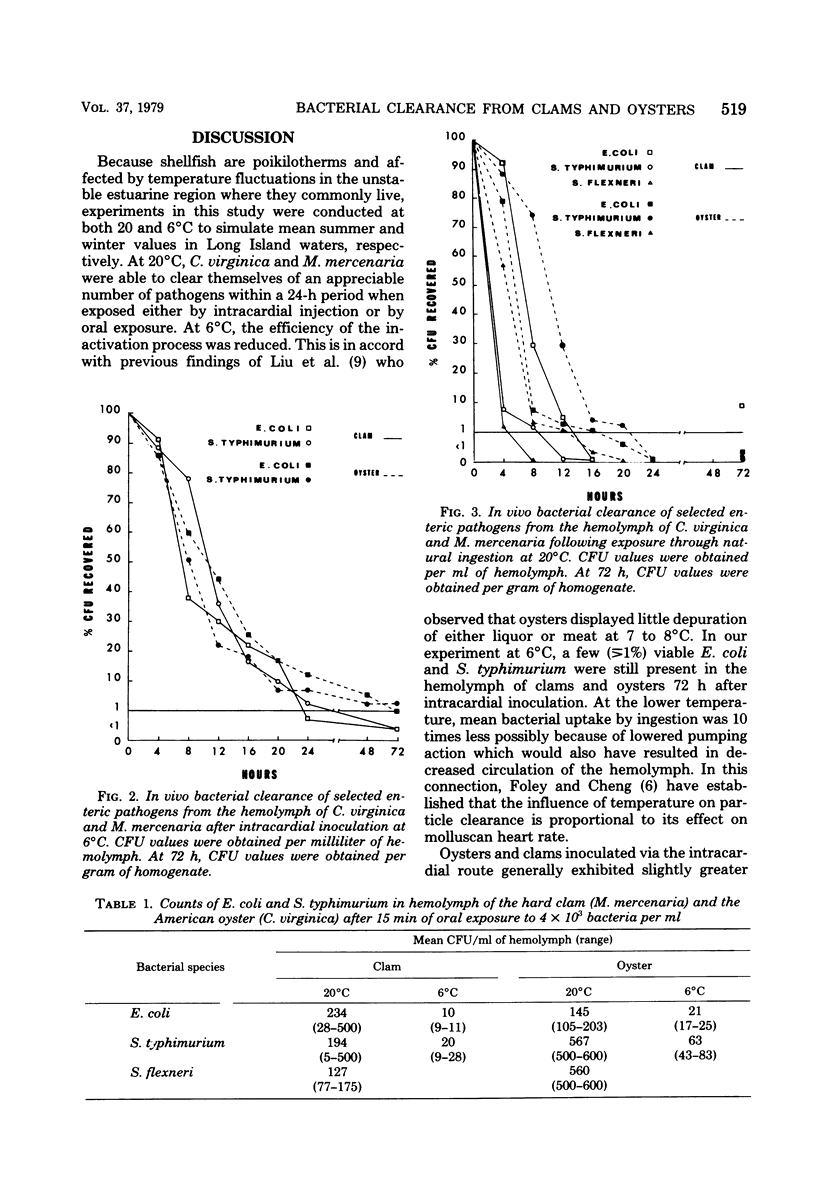
American oysters, Crassostrea virginica, and hard clams, Mercenaria mercenaria, were experimentally contaminated with Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Shigella flexneri either by intracardial injection or via the natural route of ingestion. Bacterial inactivation in the hemolymph was monitored for 72 h after exposure to these enteric pathogens at 20 and 6 degrees C. At 6 degrees C, both mean bacterial uptake by ingestion and subsequent clearance was singificantly lower that at 20 degrees C. However, substantial bacterial clearance from the hemolymph occurred for both shellfish at each temperature. At 20 degrees C, viable bacteria were no longer detectable after 24 h in hemolymph of either clams or oysters after exposure to contaminated water containing 4 x 10(3) bacteria per ml.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bang F. B. Defense reactions in invertebrates. Summary. Fed Proc. 1967 Nov-Dec;26(6):1713–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. C., Rodrick G. E., Foley D. A., Koehler S. A. Release of lysozyme from hemolymph cells of Mercenaria mercenaria during phagocytosis. J Invertebr Pathol. 1975 Mar;25(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(75)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen W. A. Oysters: retention and excretion of three types of human waterborne disease bacteria. Health Lab Sci. 1974 Jan;11(1):20–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu O. C., Seraichekas H. R., Murphy B. L. Viral depuration of the Northern quahaug. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):307–315. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.307-315.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presnell M. W., Miescier J. J. Coliforms and fecal coliforms in an oyster--growing area. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1971 Mar;43(3):407–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slanetz L. W., Bartley C. H., Stanley K. W. Coliforms, fecal streptococci and Salmonella in seawater and shellfish. Health Lab Sci. 1968 Apr;5(2):66–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


