Abstract
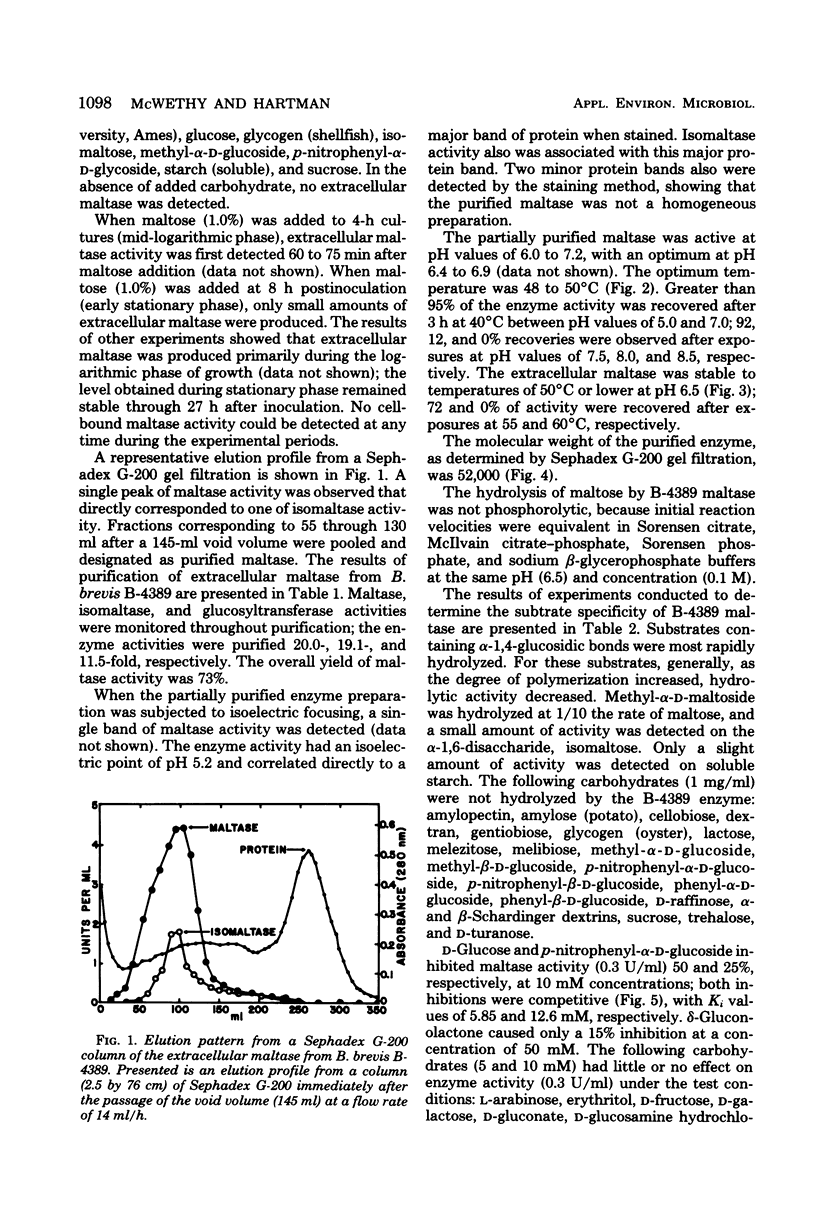
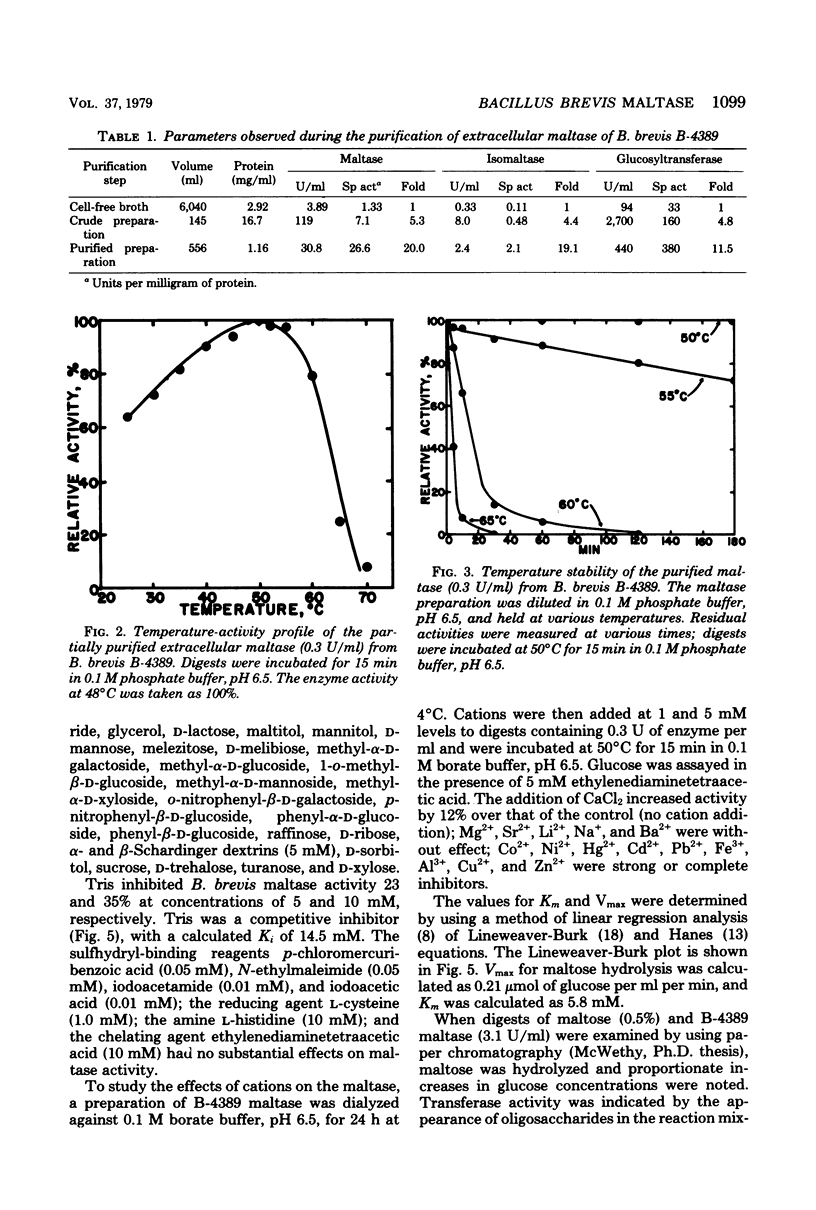
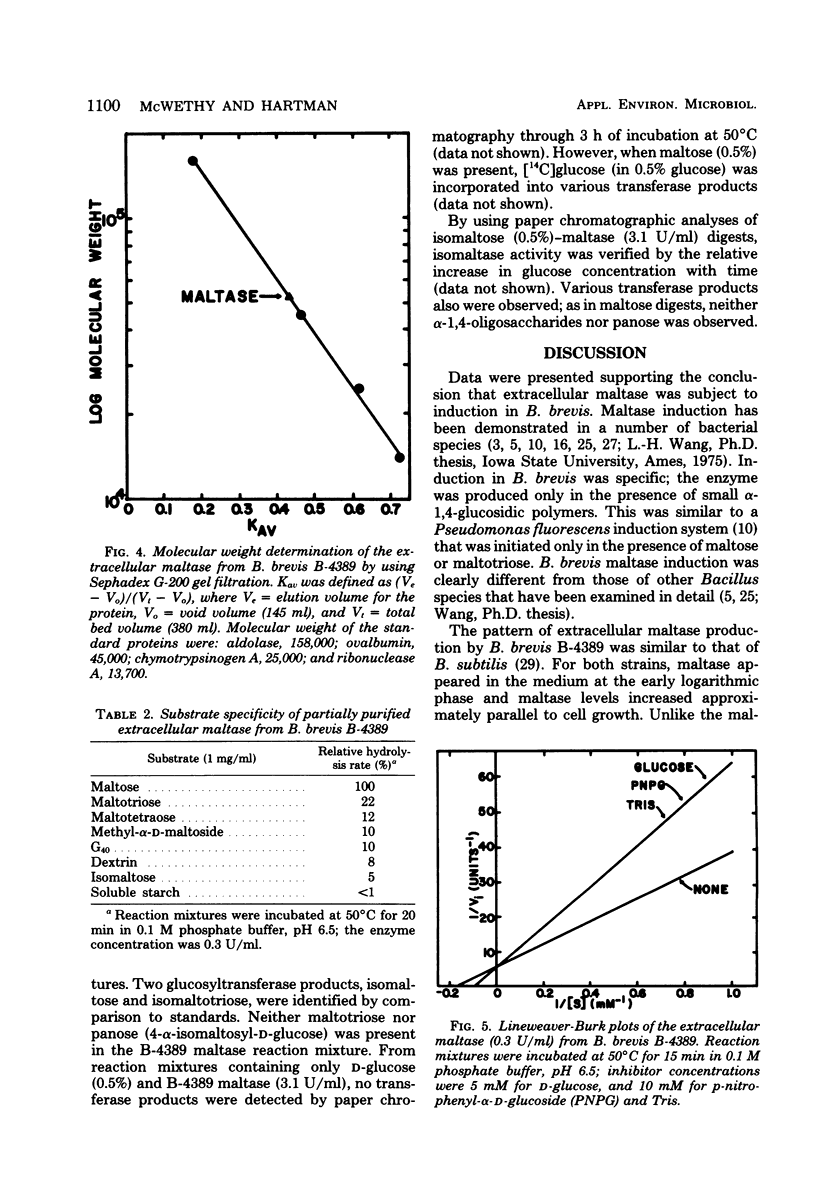
Bacillus brevis NRRL B-4389 produced extracellular maltase (α-glucosidase; EC 3.2.1.20) only in the presence of short α-1,4-glucosidic polymers, such as maltose and maltotriose. An optimum medium was developed; it contained 2.5% maltose, 0.5% nonfat dry milk, 0.4% yeast extract, and 0.01% CaCl2. The enzyme was produced extracellularly during the logarithmic phase of growth; no cell-bound activity was detected at any time. Partial purification of the maltase was accomplished by using diethylaminoethyl cellulose batch adsorption, ammonium sulfate precipitation, and Sephadex G-200 gel filtration. Maltase, isomaltase (oligo-1,6-glucosidase), and glucosyltransferase activities were purified 20.0-, 19.1-, and 11.5-fold, respectively. Some properties of the partially purified maltase were determined: optimum pH, 6.5; optimum temperature, 48 to 50°C; pH stability range, 5.0 to 7.0; temperature stability range, 0 to 50°C; isoelectric point, pH 5.2; and molecular weight, 52,000. The relative rates of hydrolysis of maltose (G2), maltotriose (G3), G4, methyl-α-d-maltoside, G40, dextrin, and isomaltose were 100, 22, 12, 10, 10, 8, and 5%, respectively; the Km on maltose was 5.8 mM; d-glucose, p-nitrophenyl-α-d-glucoside, and tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane were competitive inhibitors; transglucosylase activity of the enzyme on maltose resulted in the synthesis of isomaltose, isomaltotroise, and larger oligosaccharides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhumiratana A., Costilow R. N. Utilization of -methyl-D-mannoside by Bacillus popilliae. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Feb;19(2):169–176. doi: 10.1139/m73-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH D., KNAPP D. W. The maltase of Clostridium acetobutylicum; its specificity range and mode of action. J Biol Chem. 1950 Dec;187(2):463–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Corpe W. A. Maltose metabolism of Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):262–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.262-268.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Corpe W. A. Partial purification and characterization of alpha-glucosidase from Pseudomonas fluorescens W. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Apr 1;107(3):269–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00425338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H., ELLIAS L. The purification and properties of an alpha-glucosidase of Saccharomyces italicus Y1225. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Oct;30(1):28–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes C. S. Studies on plant amylases: The effect of starch concentration upon the velocity of hydrolysis by the amylase of germinated barley. Biochem J. 1932;26(5):1406–1421. doi: 10.1042/bj0261406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. L., Brown D. H., Brown B. I. Studies of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase. I. Purification and properties of the rat liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1403–1415. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATAGIRI H., YAMADA H., IMAI K. On the transglycosidation relating to riboflavin by Escherichia coli. I. Formation of riboflavinyl glucoside. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1957 Dec 10;3(4):264–273. doi: 10.5925/jnsv1954.3.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWethy S. J., Hartman P. A. Purification and some properties of an extracellular alpha-amylase from Bacteroides amylophilus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1537–1544. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1537-1544.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Tani Y., Uchida Y., Ochikura T. Studies on transglycosidation to vitamin B6 by microorganisms. I. Formation of a new vitamin B6 derivative, pyridoxine glucoside, by Sarcina lutea. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1969 Jun 10;15(2):142–150. doi: 10.5925/jnsv1954.15.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAN S. C., NICHOLSON L. W., KOLACHOV P. Enzymic synthesis of oligosaccharides a transglycosidation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):406–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., FRENCH D. The action of transglucosidase of Aspergillus oryzae on maltose. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBYT J., FRENCH D. Action pattern and specificity of an amylase from Bacillus subtilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Mar;100:451–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Thalenfeld B., Grossowicz N. Methyl-alpha-D-glucoside uptake and splitting by a thermophilic bacillus. Nature. 1976 Apr 1;260(5550):433–435. doi: 10.1038/260433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Amemura A., Harada T. Formations of extracellular isoamylase and intracellular alpha-glucosidase and amylase(s) by Pseudomonas SB15 and a mutant strain. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):336–339. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.336-339.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Tsuji T., Abe S. Production of an extracellular maltase by thermophilic Bacillus sp. KP 1035. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):747–752. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.747-752.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESMEYER H., COHN M. The characterization of the pathway of maltose utilization by Escherichia coli. II. General properties and mechanism of action of amylomaltase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:427–439. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Hartman P. A. Purification and some properties of an extracellular maltase from Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.108-118.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., McWethy S. J., Hartman P. A. Detection of microorganisms that produce extracellular maltases. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):380–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


