Abstract
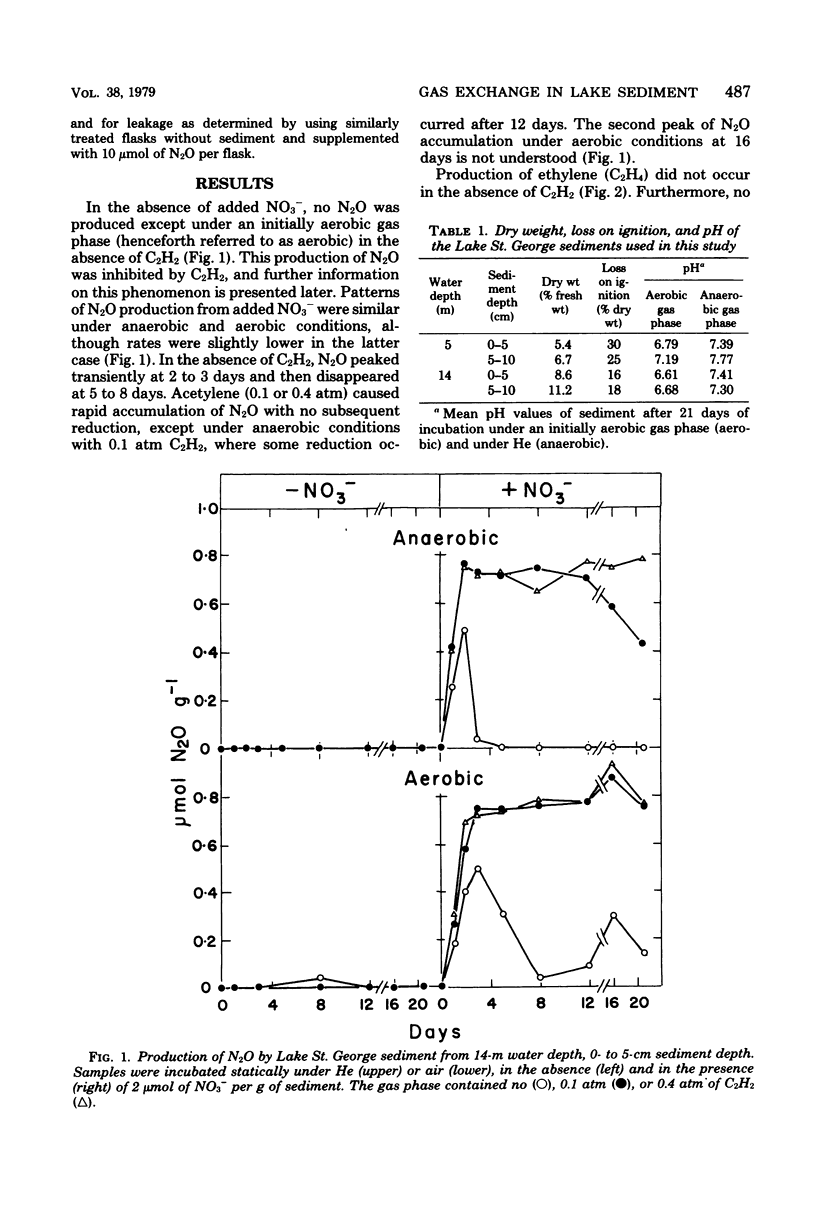
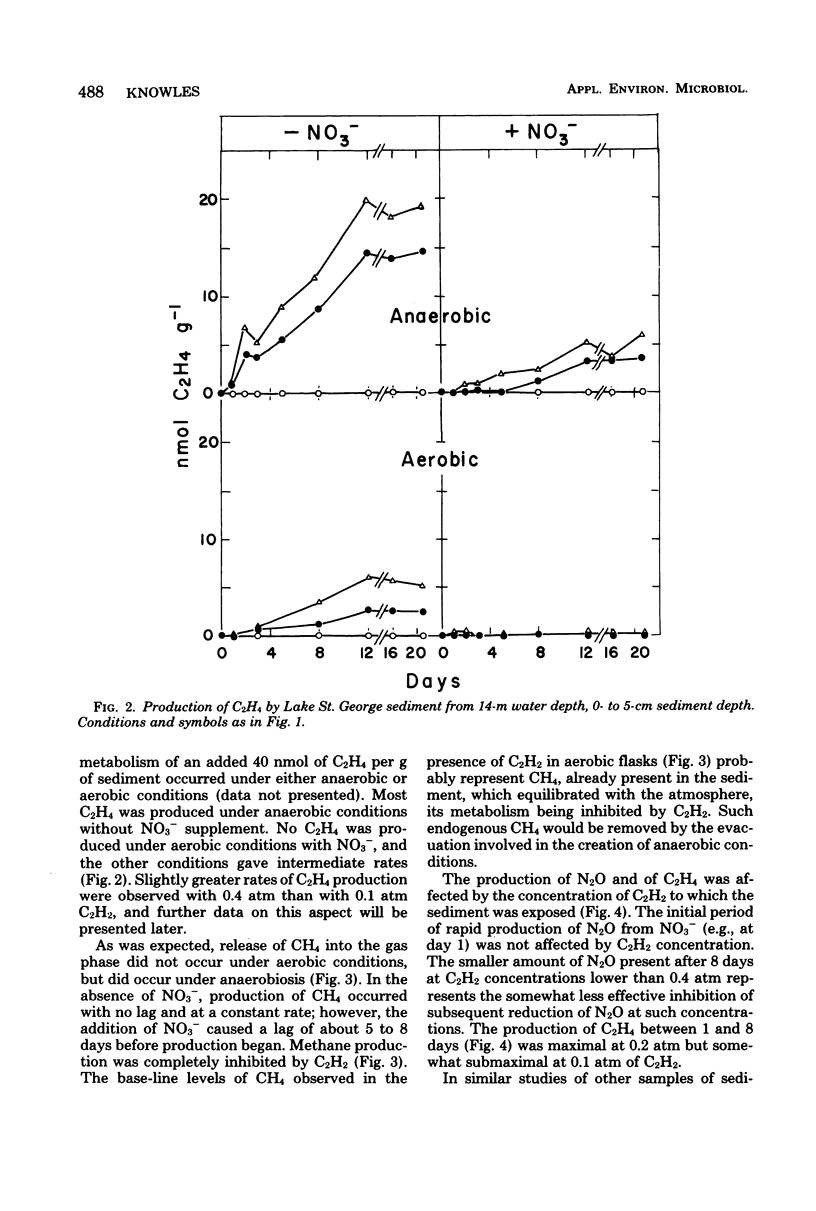
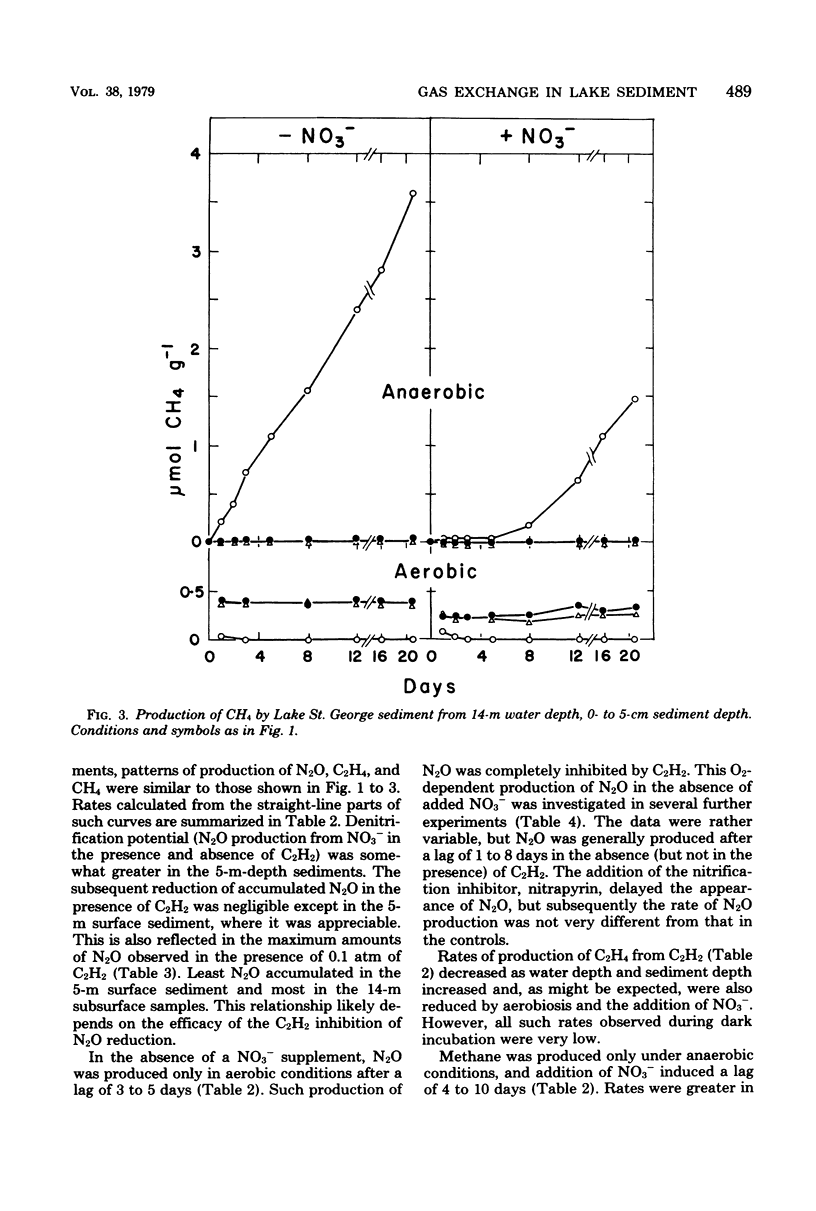
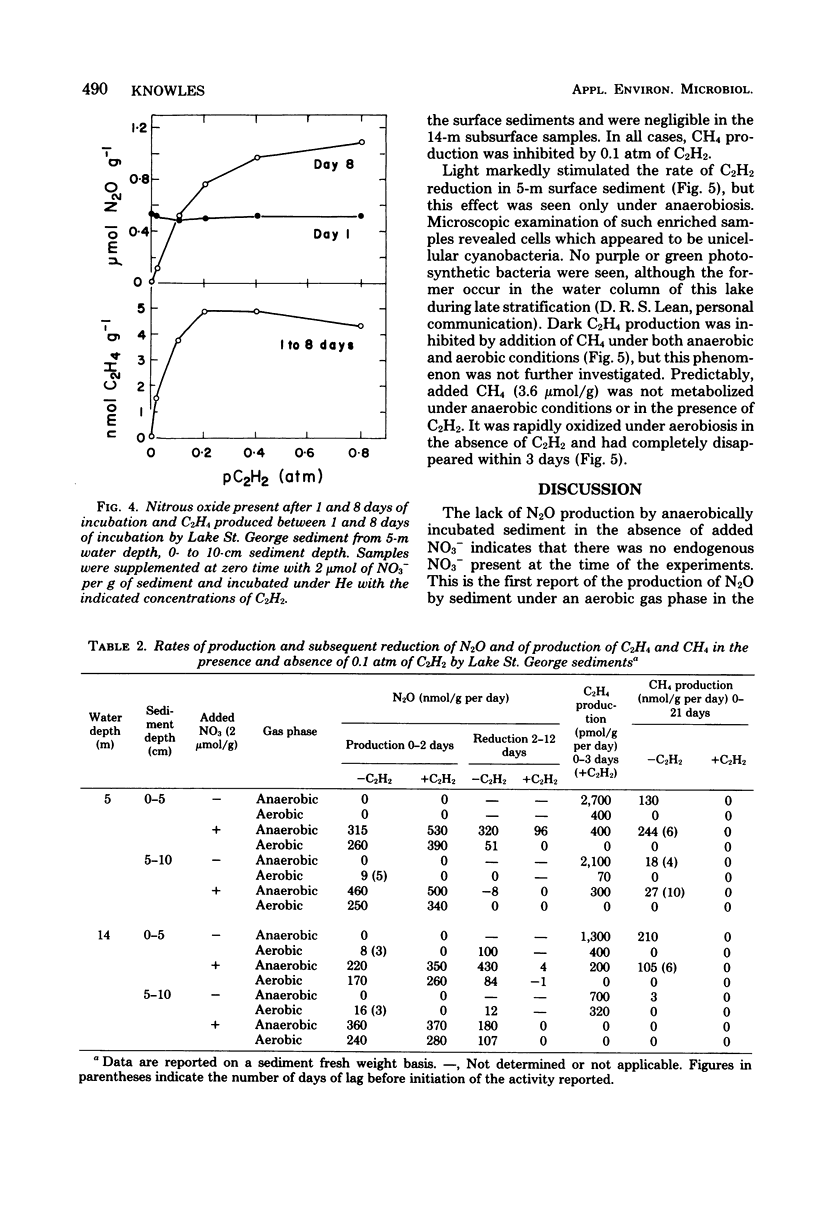
Samples of sediment from Lake St. George, Ontario, Canada, were incubated in the laboratory under an initially aerobic gas phase and under anaerobic conditions. In the absence of added nitrate (NO3−) there was O2-dependent production of nitrous oxide (N2O), which was inhibited by acetylene (C2H2) and by nitrapyrin, suggesting that coupled nitrification-denitrification was responsible. Denitrification of added NO3− was almost as rapid under an aerobic gas phase as under anaerobic conditions. The N2O that accumulated persisted in the presence of 0.4 atm of C2H2, but was gradually reduced by some sediment samples at lower C2H2 concentrations. Low rates of C2H2 reduction were observed in the dark, were maximal at 0.2 atm of C2H2, and were decreased in the presence of O2, NO3−, or both. High rates of light-dependent C2H2 reduction occurred under anaerobic conditions. Predictably, methane (CH4) production, which occurred only under anaerobiosis, was delayed by added NO3− and inhibited by C2H2. Consumption of added CH4 occurred only under aerobic conditions and was inhibited by C2H2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balderston W. L., Payne W. J. Inhibition of methanogenesis in salt marsh sediments and whole-cell suspensions of methanogenic bacteria by nitrogen oxides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):264–269. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.264-269.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balderston W. L., Sherr B., Payne W. J. Blockage by acetylene of nitrous oxide reduction in Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):504–508. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.504-508.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. K., Knowles R. Measurement of denitrification in two freshwater sediments by an in situ acetylene inhibition method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1067-1072.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike I., Hattori A. Denitrification and ammonia formation in anaerobic coastal sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):278–282. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.278-282.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson L. M., Knowles R. Effect of oxygen and nitrate on nitrogen fixation and denitrification by Azospirillum brasilense grown in continuous culture. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Nov;24(11):1395–1403. doi: 10.1139/m78-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimbault M. Etude de l'influence inhibitrice de l'acétylène sur la formation biologique du méthane dans un sol de rizitère. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Feb-Mar;126(2):247–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperl G. T., Hoare D. S. Denitrification with methanol: a selective enrichment for Hyphomicrobium species. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):733–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.733-736.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D. Nitrogen fixation by photosynthetic microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:283–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Capacity for denitrification and reduction of nitrate to ammonia in a coastal marine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):301–305. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.301-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Denitrification rates in a marine sediment as measured by the acetylene inhibition technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):139–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.139-143.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari T., Knowles R. Acetylene inhibition of nitrous oxide reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):705–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90932-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


