Abstract
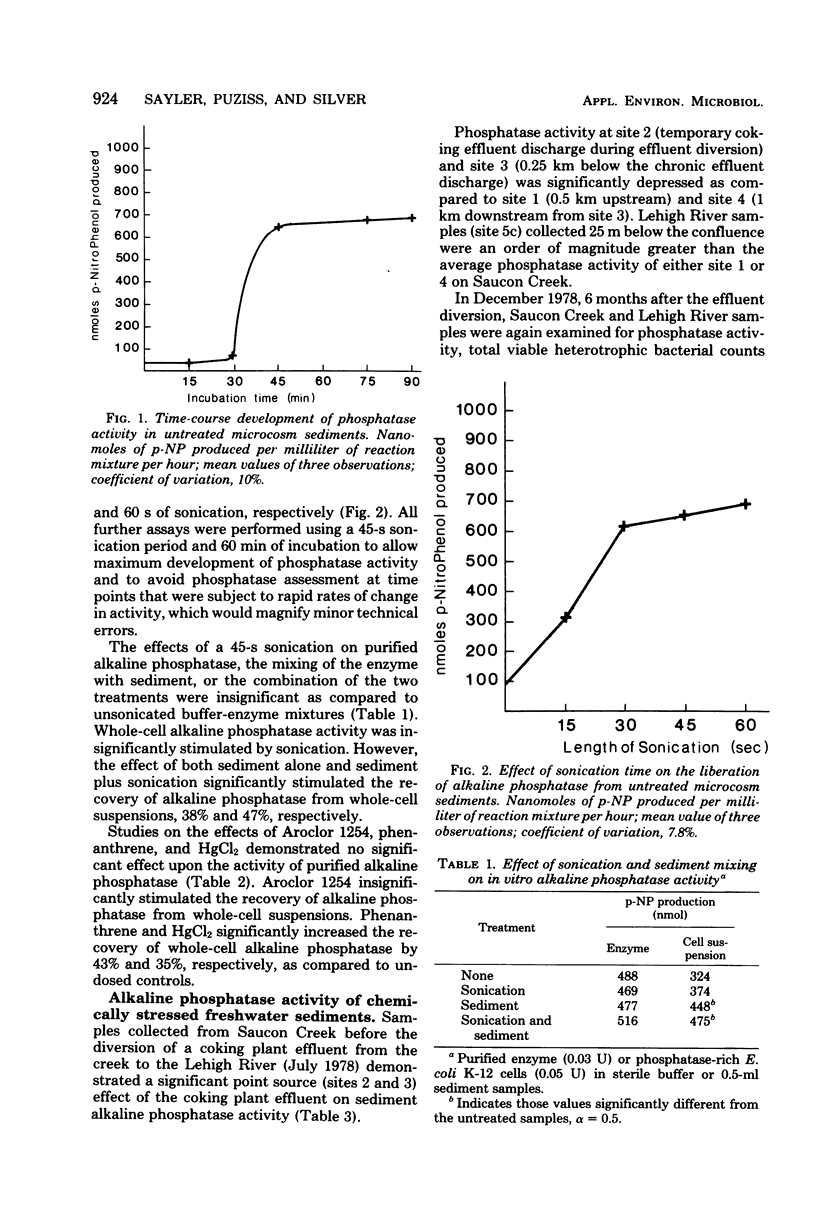
The p-nitrophenyl phosphate hydrolysis-phosphatase assay was modified for use in freshwater sediment. Laboratory studies indicated that the recovery of purified alkaline phosphatase activity was 100% efficient in sterile freshwater sediments when optimized incubation and sonication conditions were used. Field studies of diverse freshwater sediments demonstrated the potential use of this assay for determining stream perturbation. Significant correlations between phosphatase and total viable cell counts, as well as adenosine triphosphate biomass, suggested that alkaline phosphatase activity has utility as an indicator of microbial population density and biomass in freshwater sediments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman T. Phosphatase release of inorganic phosphorus in Lake Kinneret. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1231–1232. doi: 10.1038/2241231b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Interactions of alkaline phosphatase and the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.325-336.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Lund L. C., Shiaris M. P., Sherrill T. W., Perkins R. E. Comparative effects of Aroclor 1254 (polychlorinated biphenyls) and phenanthrene on glucose uptake by freshwater microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):878–885. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.878-885.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


