Abstract
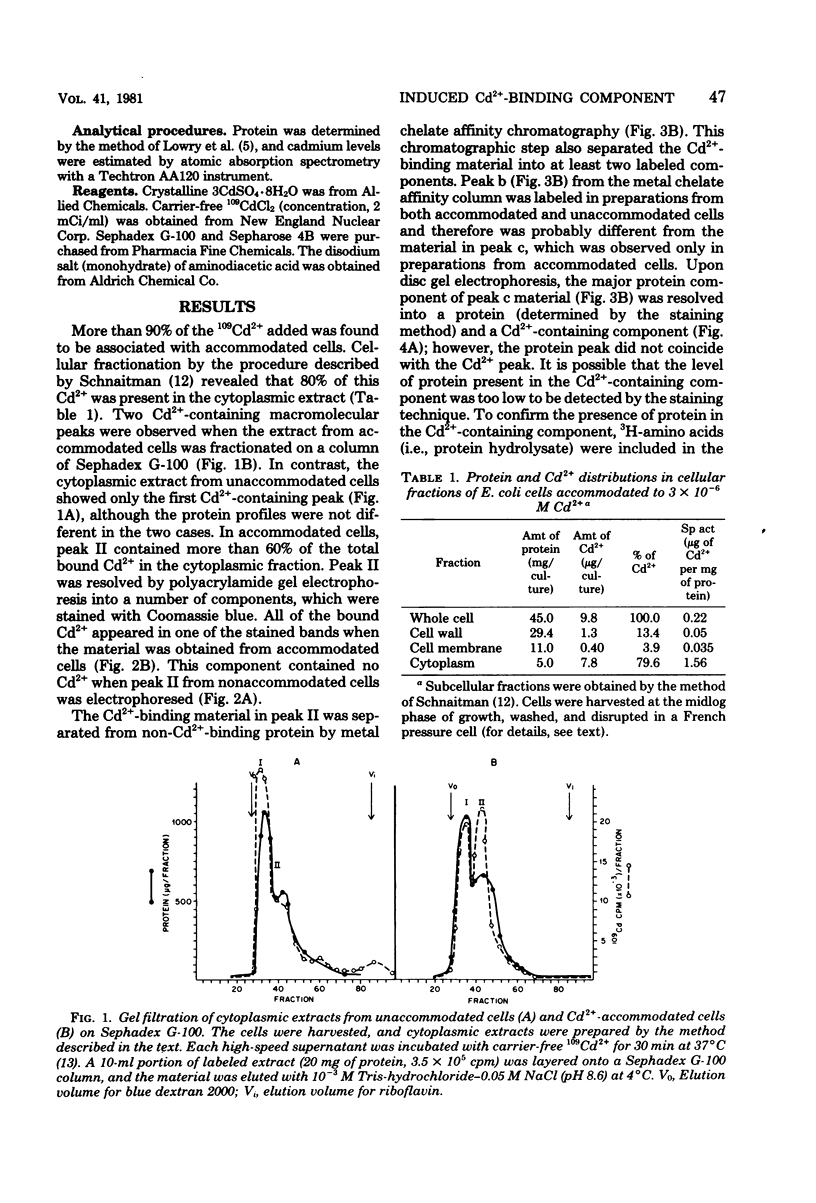
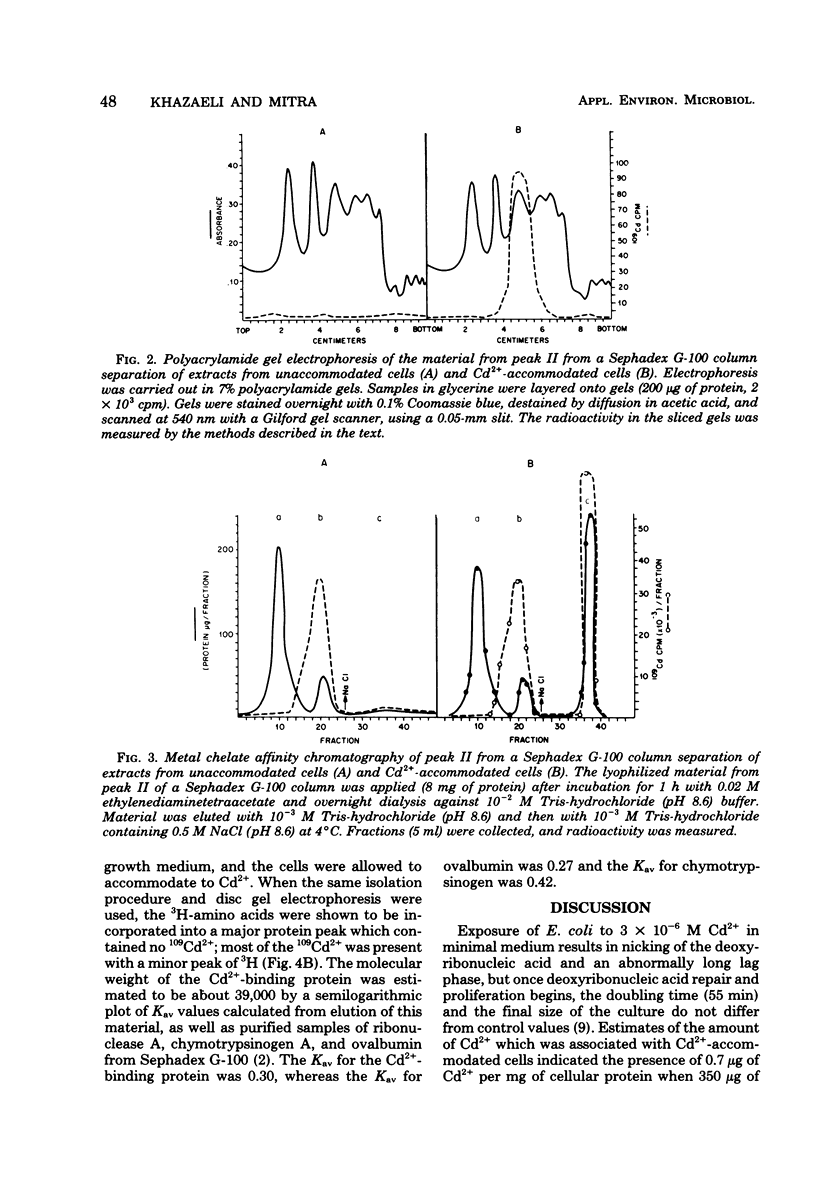
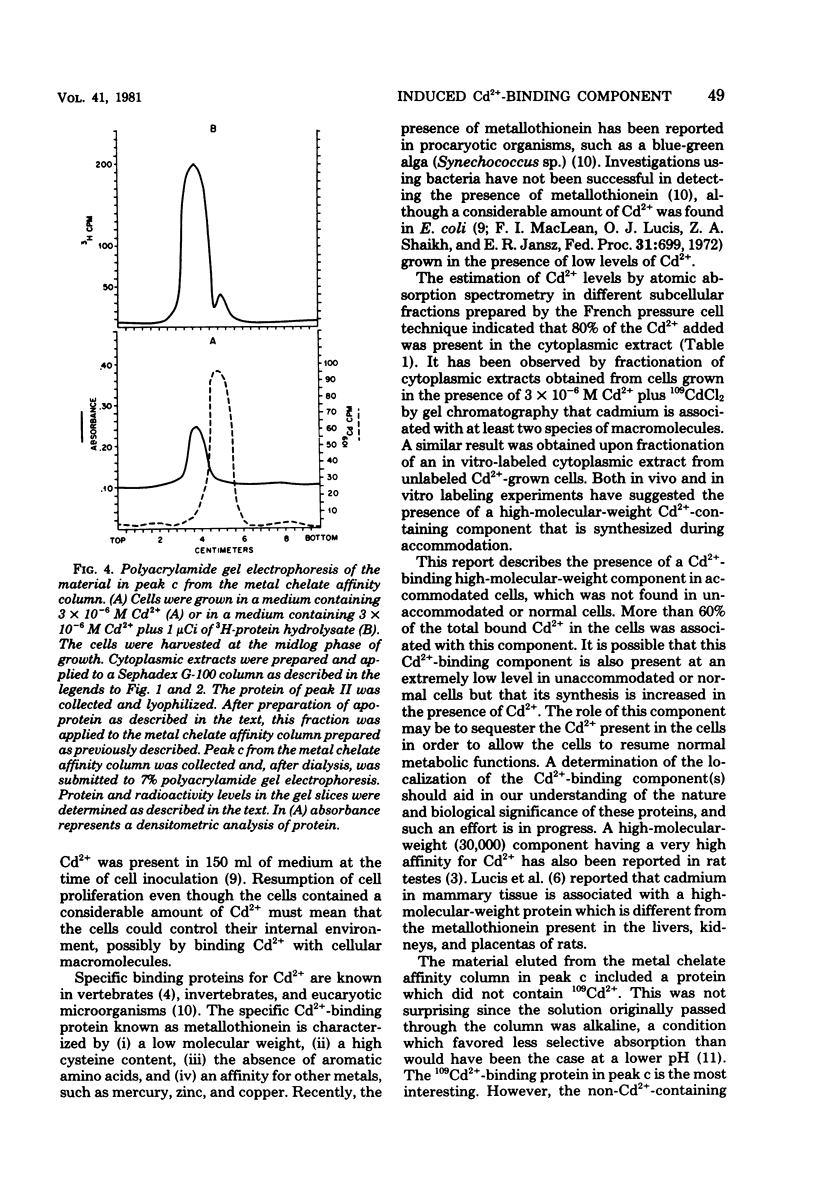
An inducible cadmium-binding protein was isolated from Escherichia coli cells accommodated to 3 X 10(-6) M Cd2+ but not from normal or unaccommodated cells. Sephadex G-100, metal chelate affinity chromatography, and disc gel electrophoresis were used in the purification procedure. The molecular weight of the Cd2+-binding protein was estimated to be about 39,000 by Sephadex G-100 chromatography, making it different from the conventional, much smaller metallothionein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R. D., Winter W. P., Maher J. J., Bernstein I. A. Turnover of metallothioneins in rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):327–338. doi: 10.1042/bj1740327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Ganther H. E. Relative cadmium-binding capacity of metallothionein and other cytosolic fractions in various tissues of the rat. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1975;5(6):378–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Berger C., Vallee B. L., Kägi J. H. Amino-acid sequence of equine renal metallothionein-1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3413–3417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucis O. J., Lucis R., Shaikh Z. A. Cadmium and zinc in pregnancy and lactation. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Jul;25(1):14–22. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R. S., Bernstein I. A. Nature of the repair process associated with the recovery of Escherichia coli after exposure to Cd2+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1450–1455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90604-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R. S., Bernstein I. A. Single-strand breakage in DNA of Escherichia coli exposed to Cd2+. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.75-80.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R. S., Gray R. H., Chin B., Bernstein I. A. Molecular mechanisms of accommodation in Escherichia coli to toxic levels of Cd2+. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1180–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1180-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafson R. W., Abel K., Sim R. G. Prokaryotic metallothionein: preliminary characterization of a blue-green alga heavy metal-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90939-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Carlsson J., Olsson I., Belfrage G. Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):598–599. doi: 10.1038/258598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh Z. A., Lucis O. J. Cadmium and zinc binding in mammalian liver and kidneys. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Jun;24(6):419–425. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


