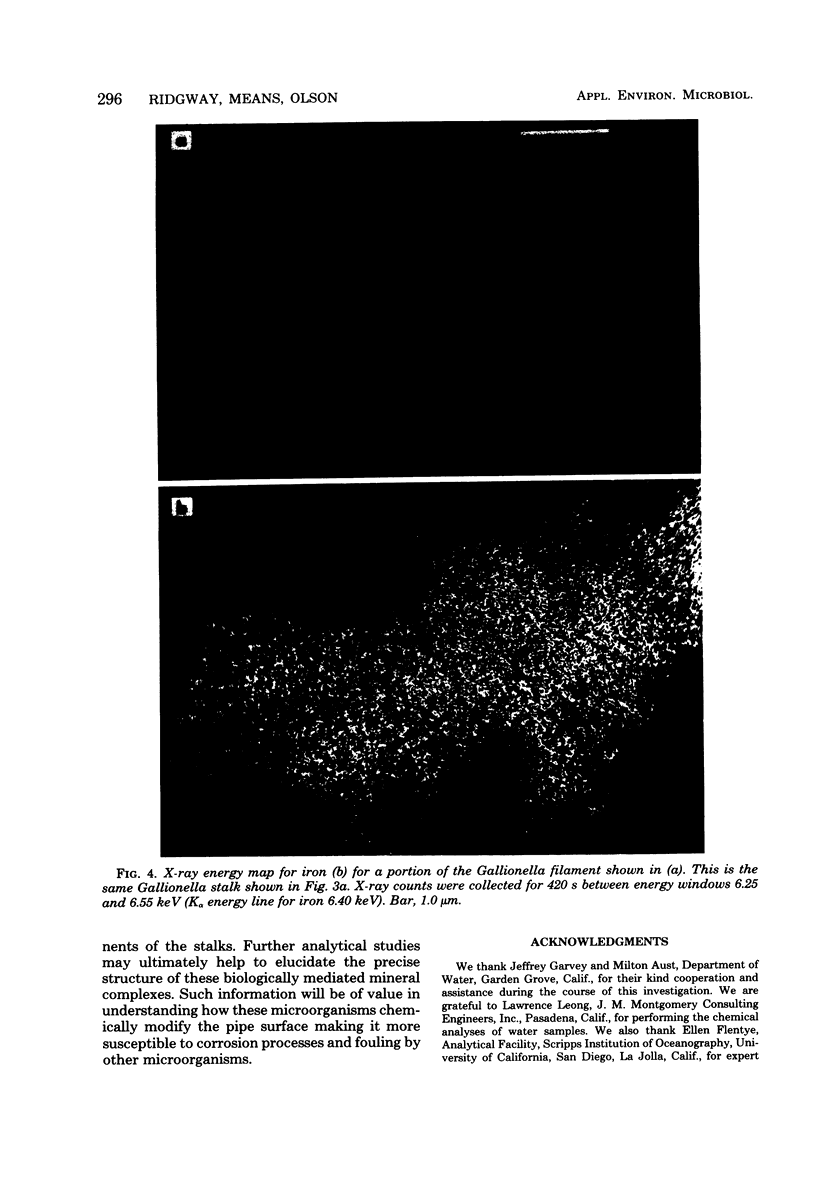
Abstract
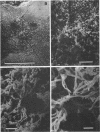
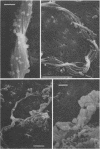
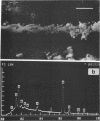
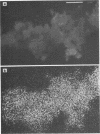
“Iron” bacteria belonging to the genus Gallionella were observed by scanning electron microscopy in water samples and attached to pipe surfaces in a Southern California drinking-water distribution system. The cells were recognized by their characteristic elongated helical stalks composed of numerous intertwined microfibrils. Many of the stalks were partially coated with insoluble ferric salt deposits. Stalks recovered directly from water samples were analyzed for their elemental composition by using X-ray energy-dispersive microanalysis. Silicon, aluminum, calcium, and iron were the predominant elements present in the stalks. Smaller quantities of the elements phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, copper, and zinc were also detected. Manganese, though present in measurable quantities in the water supply, was not detected in the stalks, suggesting that this organism is unable to utilize this element as an electron donor. This represents the first such analysis of Gallionella stalks recovered from environmental samples without prior subculturing in artificial laboratory media.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balashova V. V., Cherni N. E. Ul'trastruktura Gallionella filamenta. Mikrobiologiia. 1970 Mar-Apr;39(2):348–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balashova V. V. K taksonomii roda Gallionella. Mikrobiologiia. 1968 Jul-Aug;37(4):715–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmer A. R., Hinkle M. E. The Role of Microorganisms in Acid Mine Drainage: A Preliminary Report. Science. 1947 Sep 19;106(2751):253–256. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2751.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUCERA S., WOLFE R. S. A selective enrichment method for Gallionella ferruginea. J Bacteriol. 1957 Sep;74(3):344–349. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.3.344-349.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardanian S. S., Balashova V. V. O sostoianii zheleza na voloknakh Gallionella. Mikrobiologiia. 1971 Jan-Feb;40(1):121–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMPLE K. L., COLMER A. R. The autotrophic oxidation of iron by a new bacterium, thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1951 Nov;62(5):605–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.5.605-611.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Veen W. L., Mulder E. G., Deinema M. H. The Sphaerotilus-Leptothrix group of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):329–356. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.329-356.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]