Abstract
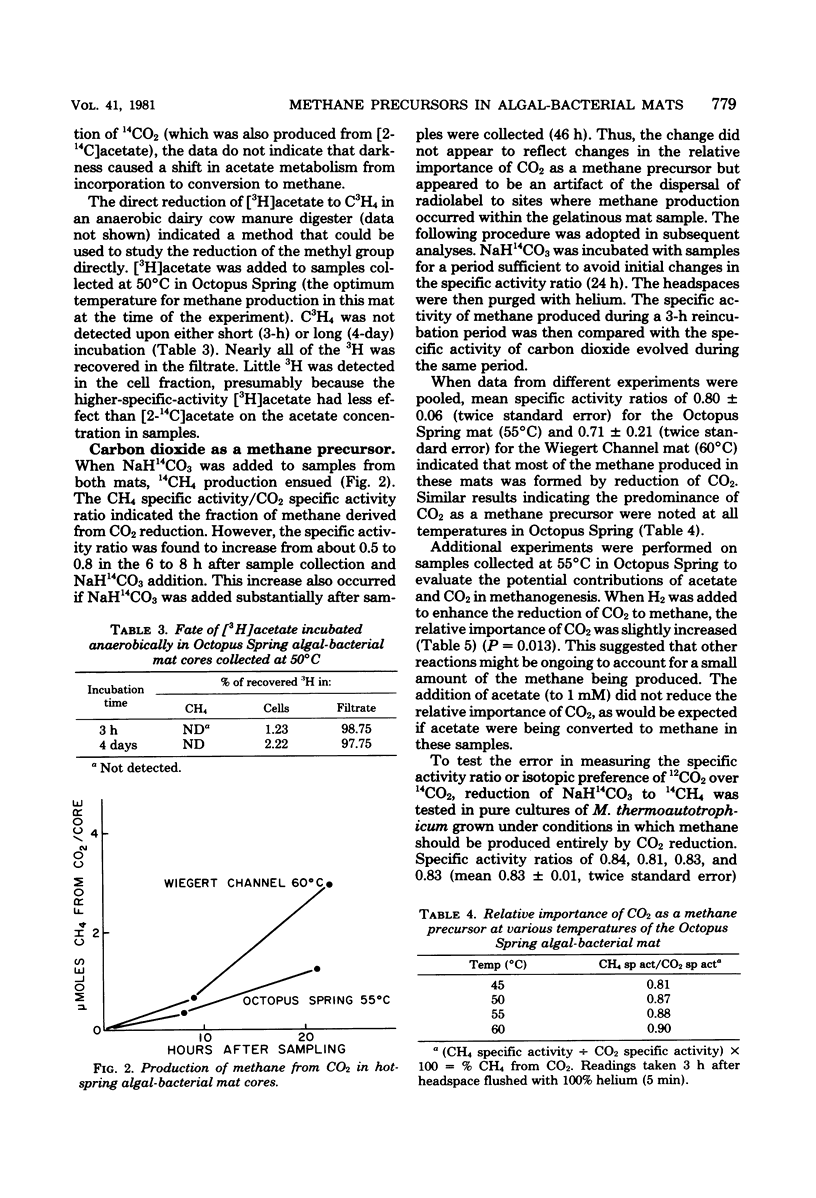
The fates of acetate and carbon dioxide were examined in several experiments designed to indicate their relative contributions to methane production at various temperatures in two low-sulfate, hot-spring algal-bacterial mats. [2-14C]acetate was predominantly incorporated into cell material, although some 14CH4 and 14CO2 was produced. Acetate incorporation was reduced by dark incubation in short-term experiments and severely depressed by a 2-day preincubation in darkness. Autoradiograms showed that acetate was incorporated by long filaments resembling phototrophic microorganisms of the mat communities. [3H]acetate was not converted to C3H4 in samples from Octopus Spring collected at the optimum temperature for methanogenesis. NaH14CO3 was readily converted to 14CH4 at temperatures at which methanogenesis was active in both mats. Comparisons of the specific activities of methane and carbon dioxide suggested that of the methane produced, 80 ± 6% in Octopus Spring and 71 ± 21% in Wiegert Channel were derived from carbon dioxide. Addition of acetate to 1 mM did not reduce the relative importance of carbon dioxide as a methane precursor in samples from Octopus Spring. Experiments with pure cultures of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum suggested that the measured ratio of specific activities might underestimate the true contribution of carbon dioxide in methanogenesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castenholz R. W. Thermophilic blue-green algae and the thermal environment. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):476–504. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.476-504.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doemel W. N., Brock T. D. Structure, growth, and decomposition of laminated algal-bacterial mats in alkaline hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):433–452. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.433-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe H., Caspari D., Fiebig K., Gottschalk G. Utilization of trimethylamine and other N-methyl compounds for growth and methane formation by Methanosarcina barkeri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):494–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Hydrogen as an intermediate in the rumen fermentation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):158–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00406327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah R. A., Ward D. M., Baresi L., Glass T. L. Biogenesis of methane. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:309–341. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mink R. W., Dugan P. R. Tentative identification of methanogenic bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):713–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.713-717.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Asher R. A. Changes in proportions of acetate and carbon dioxide used as methane precursors during the anaerobic digestion of bovine waste. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):648–654. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.648-654.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPERMANN R. A., NELSON W. O., BROWN R. E. In vivo studies of methanogenesis in the bovine rumen: dissimilation of acetate. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:103–111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson B. K., Castenholz R. W. A phototrophic gliding filamentous bacterium of hot springs, Chloroflexus aurantiacus, gen. and sp. nov. Arch Microbiol. 1974;100(1):5–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00446302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Mah R. A. Acetate as sole carbon and energy source for growth of methanosarcina strain 227. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):993–999. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.993-999.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Mah R. A. Growth and methanogenesis by Methanosarcina strain 227 on acetate and methanol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):870–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.870-879.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Olson G. J. Terminal processes in the anaerobic degradation of an algal-bacterial mat in a high-sulfate hot spring. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):67–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.67-74.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M. Thermophilic methanogenesis in a hot-spring algal-bacterial mat (71 to 30 degrees C). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1019-1026.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Acetate metabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Nov 13;119(2):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00964270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. One carbon metabolism in methanogenic bacteria. Cellular characterization and growth of Methanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00407927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdel F., Pfennig N. A new anaerobic, sporing, acetate-oxidizing, sulfate-reducing bacterium, Desulfotomaculum (emend.) acetoxidans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):119–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00446665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Anaerobic metabolism of immediate methane precursors in Lake Mendota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):244–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.244-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Huser B. A., Brock T. D., Wuhrmann K. Characterization of an acetate-decarboxylating, non-hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jan;124(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00407022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder S. H., Doemel W. N., Brock T. D. Production of volatile sulfur compounds during the decomposition of algal mats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):859–860. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.859-860.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder S. H., Mah R. A. Isolation and Characterization of a Thermophilic Strain of Methanosarcina Unable to Use H(2)-CO(2) for Methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):996–1008. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.996-1008.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



