Abstract
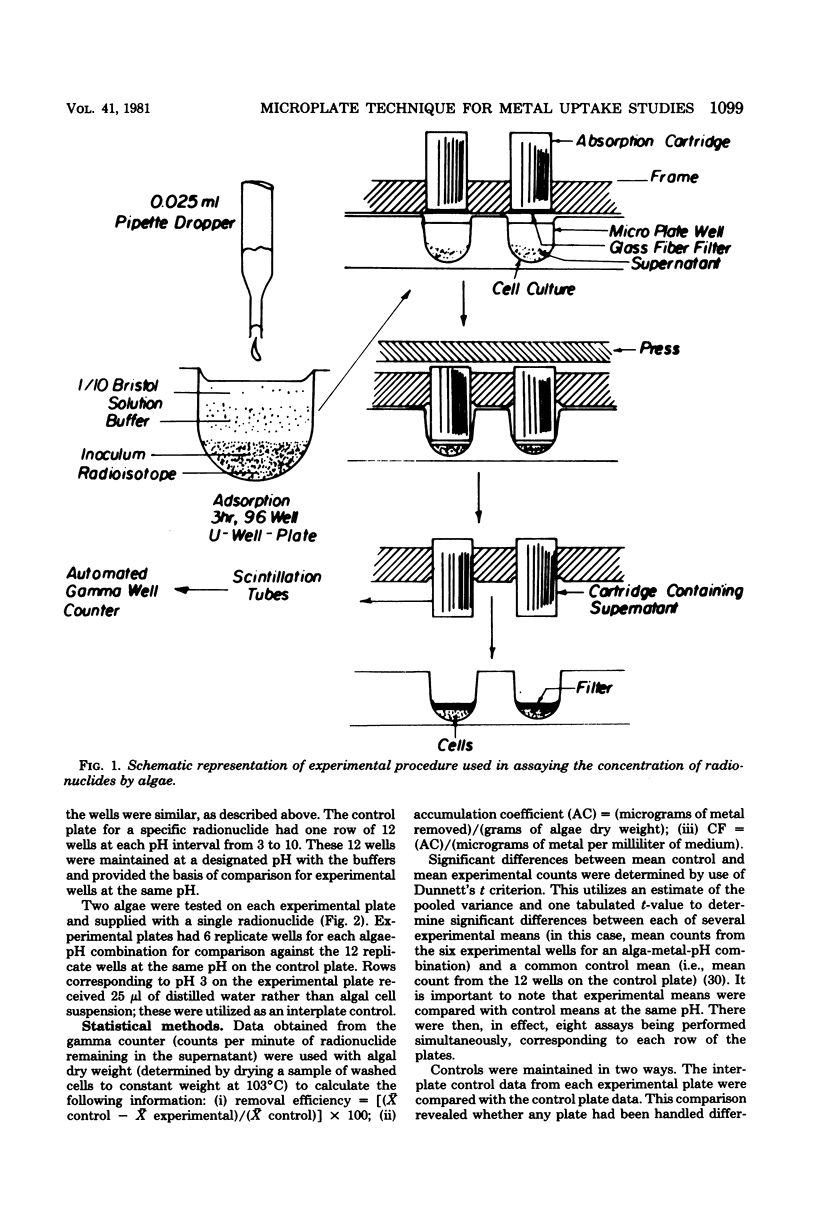
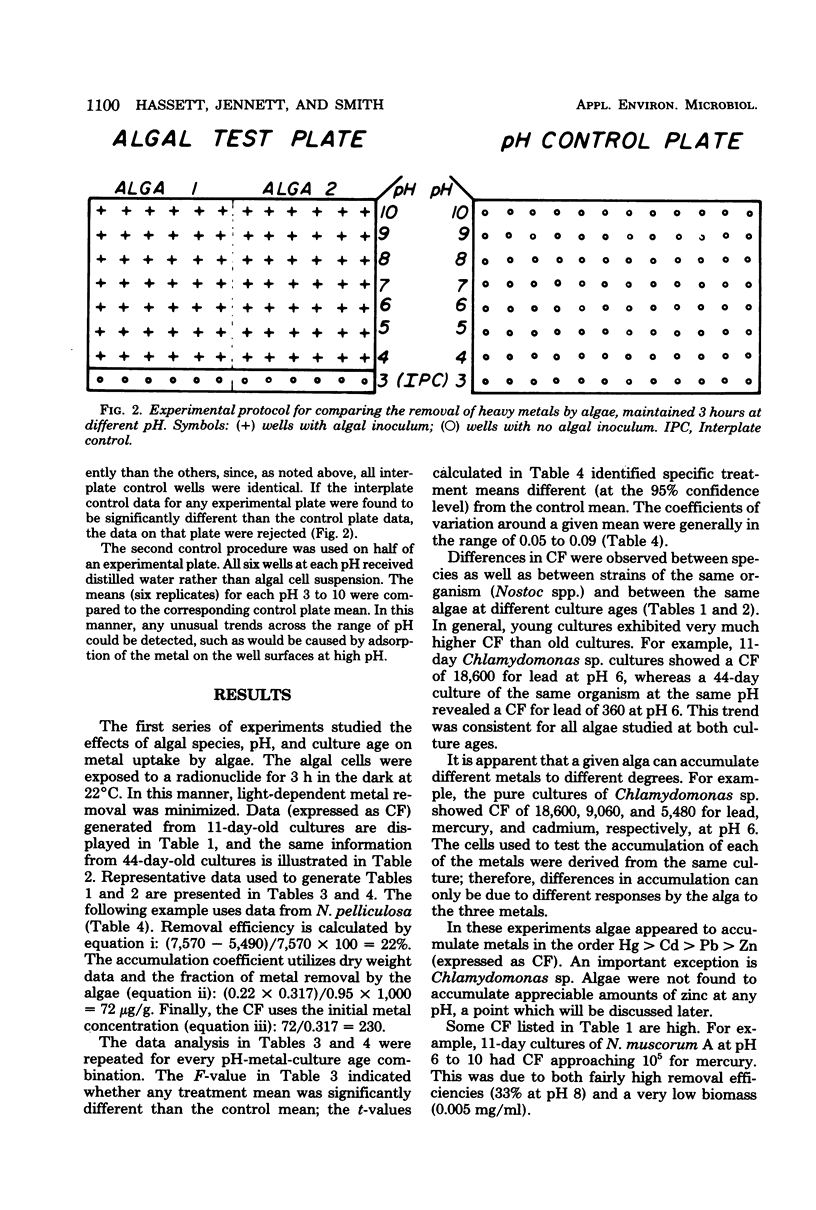
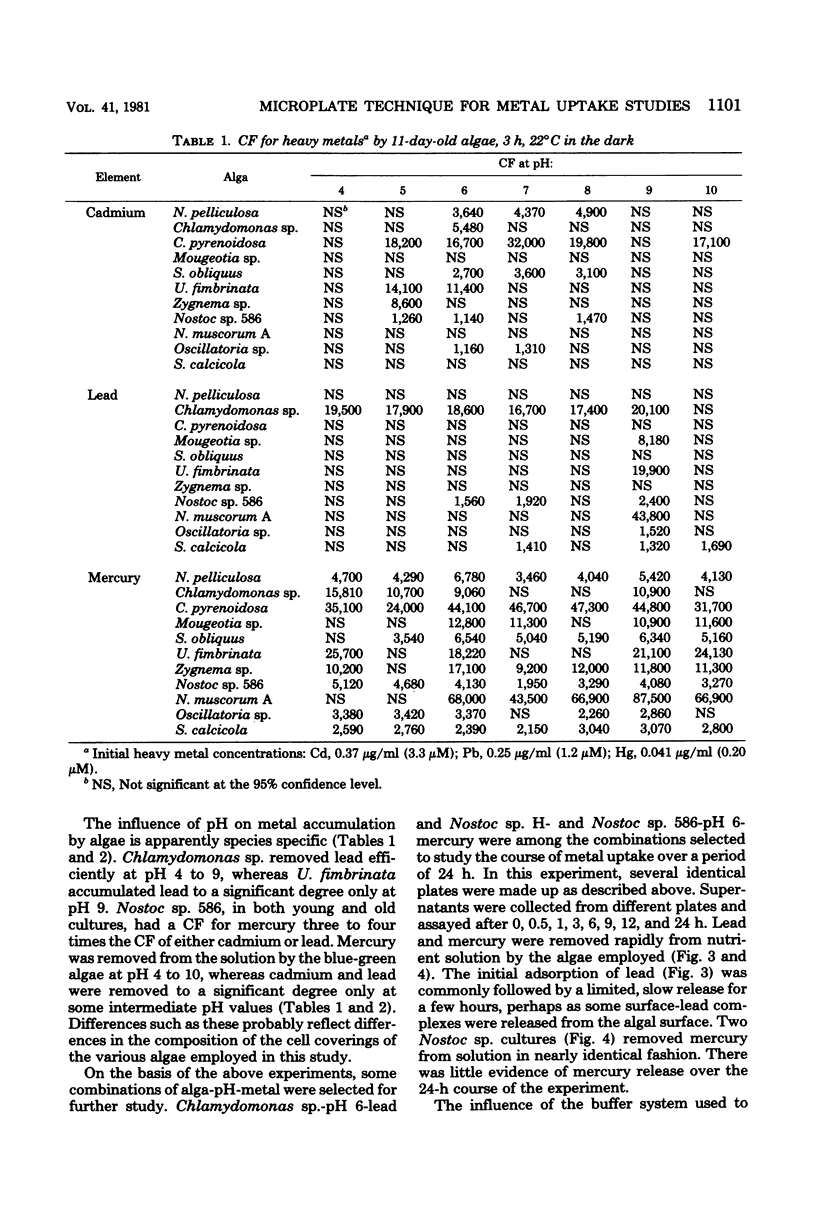
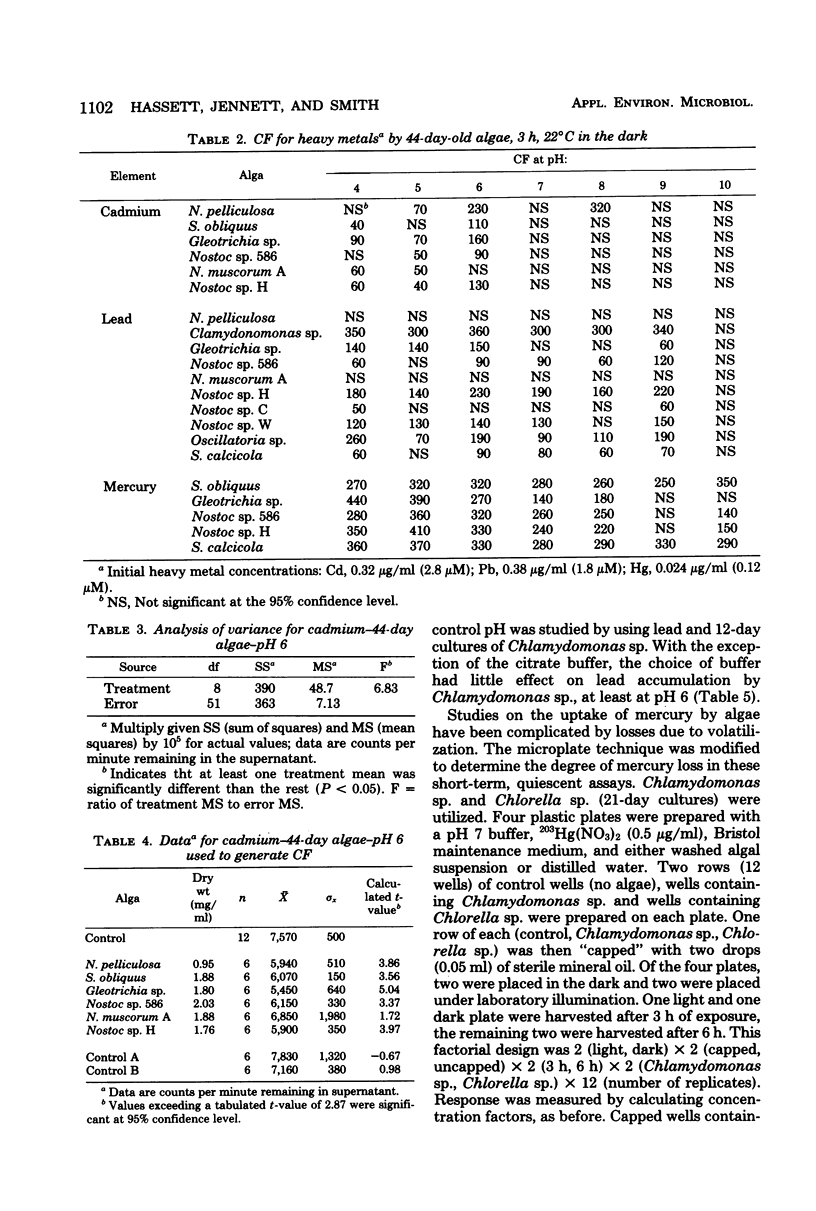
A microplate technique was developed to determine the conditions under which pure cultures of algae removed heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Variables investigated included algal species and strain, culture age (11 and 44 days), metal (mercury, lead, cadmium, and zinc), pH, effects of different buffer solutions, and time of exposure. Plastic, U-bottomed microtiter plates were used in conjunction with heavy metal radionuclides to determine concentration factors for metal-alga combinations. The technique developed was rapid, statistically reliable, and economical of materials and cells. Results (expressed as concentration factors) were in reasonably good agreement with literature values. All species of algae studied removed mercury from solution. Green algae proved better at accumulating cadmium than did blue-green algae. No alga studied removed zinc, perhaps because cells were maintained in the dark during the labeling period. Chlamydomonas sp. proved superior in ability to remove lead from solution.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama I., Inomo K., Inoue Y. Uptake and release of some radionuclides by fresh water phytoplankton in batch culture. J Radiat Res. 1976 Jun;17(2):69–81. doi: 10.1269/jrr.17.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Skare H., Thorsby E. Cell mediated lympholysis: CML. a microplate technique requiring few target cells and employing a new method of supernatant collection. J Immunol Methods. 1977;16(2):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkade M. L., Erdman H. E. The influence of hardness components (Ca2+ and Mg2+) in water on the uptake and concentration of cadmium in a simulated freshwater ecosystem. Environ Res. 1975 Oct;10(2):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(75)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. W. Trace metal variations in sea water of the Menai Straits caused by a bloom of Phaeocystis. Nature. 1971 Oct 8;233(5319):427–428. doi: 10.1038/233427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafson R. W., Abel K., Sim R. G. Prokaryotic metallothionein: preliminary characterization of a blue-green alga heavy metal-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90939-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


