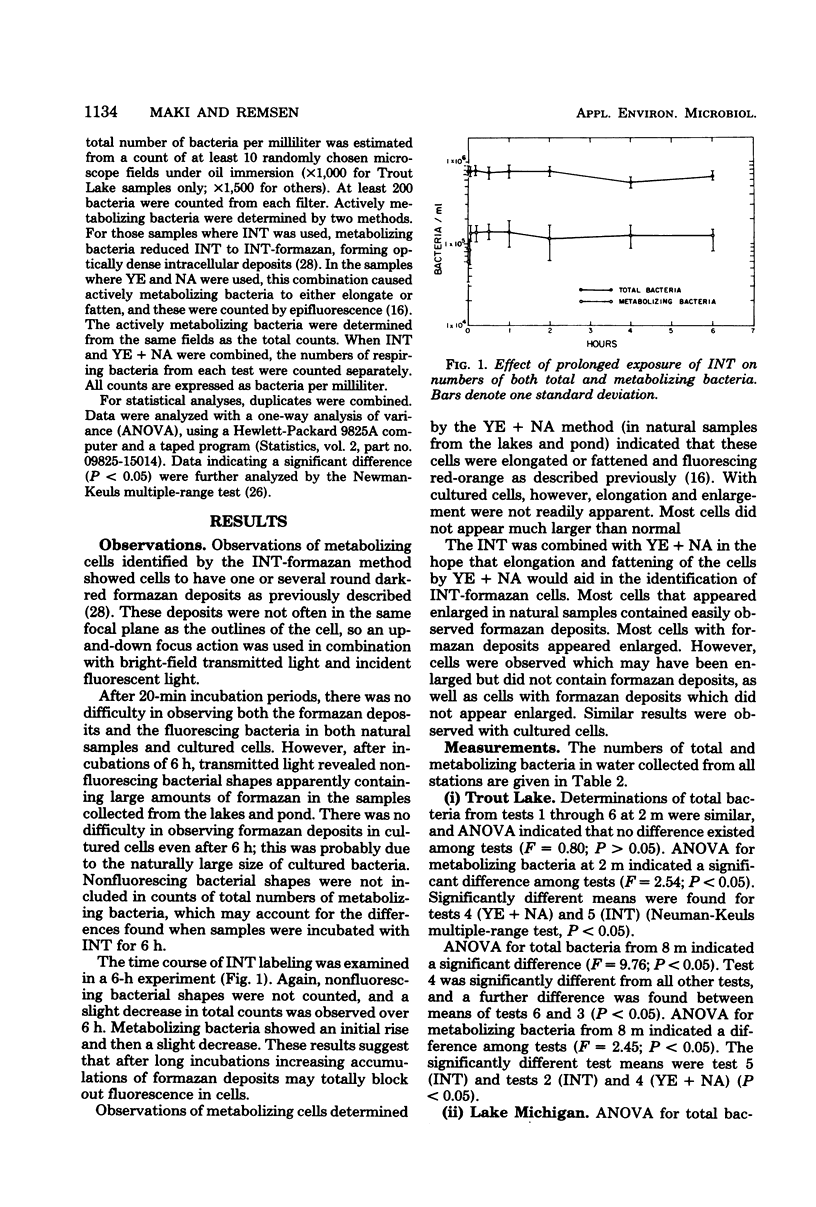
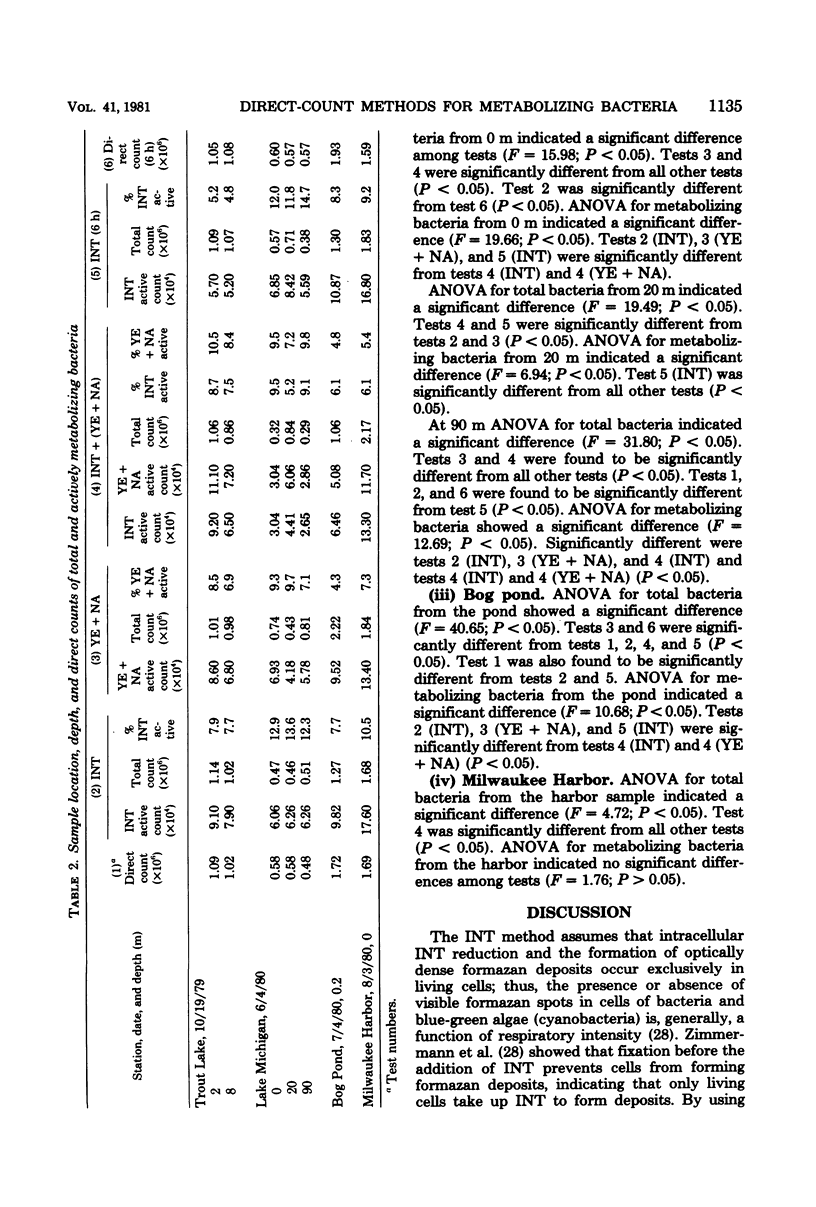
Abstract
Planktonic bacteria collected from several freshwater environments and cultured bacteria were used to compare two methods for determining the numbers of metabolizing bacteria. The methods used were (i) reduction of 2-(ρ-iodophenyl)-3-(ρ-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyl tetrazolium chloride 2-(ρ-iodophenyl)-3-(ρ-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyl to tetrazolium chloride-formazan and (ii) elongation of cells by using yeast extract and nalidixic acid. No statistically significant difference was found between methods in determining metabolizing bacteria, although significant differences (P < 0.05) were found when comparing numbers of total bacteria. A combination of the two methods yielded significant changes, both positive and negative, in the numbers of metabolizing bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowden W. B. Comparison of two direct-count techniques for enumerating aquatic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1229–1232. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1229-1232.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francisco D. E., Mah R. A., Rabin A. C. Acridine orange-epifluorescence technique for counting bacteria in natural waters. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 1973 Jul;92(3):416–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI.II. INHIBITION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1068-1074.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. G., Simon B. M. An investigation of errors in direct counts of aquatic bacteria by epifluorescence microscopy, with reference to a new method for dyeing membrane filters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;39(3):317–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Simidu U., Taga N. A tentative direct microscopic method for counting living marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):415–420. doi: 10.1139/m79-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Simidu U., Taga N. Distribution of viable marine bacteria in neritic seawater around Japan. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Mar;26(3):318–323. doi: 10.1139/m80-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson K., Weibull C., Cronberg G. Comparison of light and electron microscopic determinations of the number of bacteria and algae in lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):397–404. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.397-404.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky J. A., Morita R. Y. Survival of a psychrophilic marine Vibrio under long-term nutrient starvation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):635–641. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.635-641.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. W., Novitsky T. J., Quinby H. L., Valois F. W. Determination of bacterial number and biomass in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):940–946. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.940-946.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. T. Measurement and significance of specific activity in the heterotrophic bacteria of natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):297–305. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.297-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Iturriaga R., Becker-Birck J. Simultaneous determination of the total number of aquatic bacteria and the number thereof involved in respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):926–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.926-935.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


