Abstract
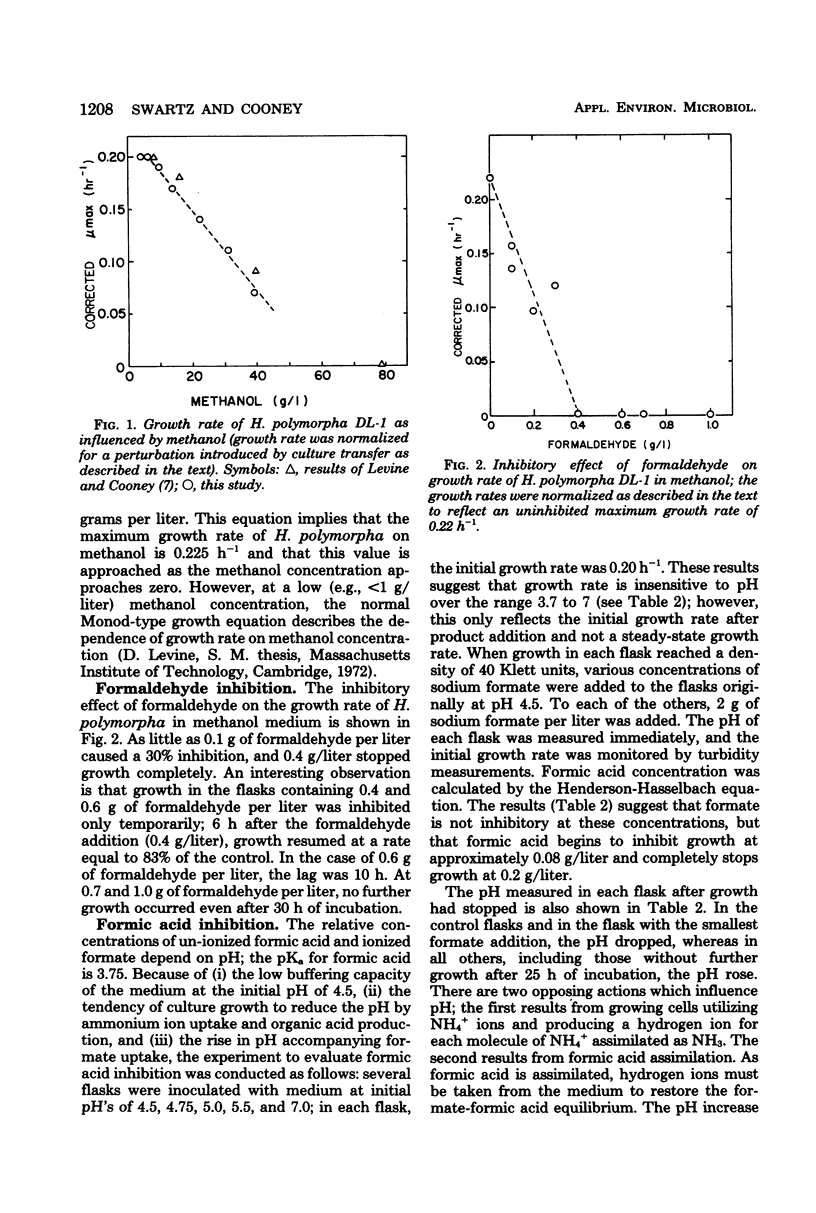
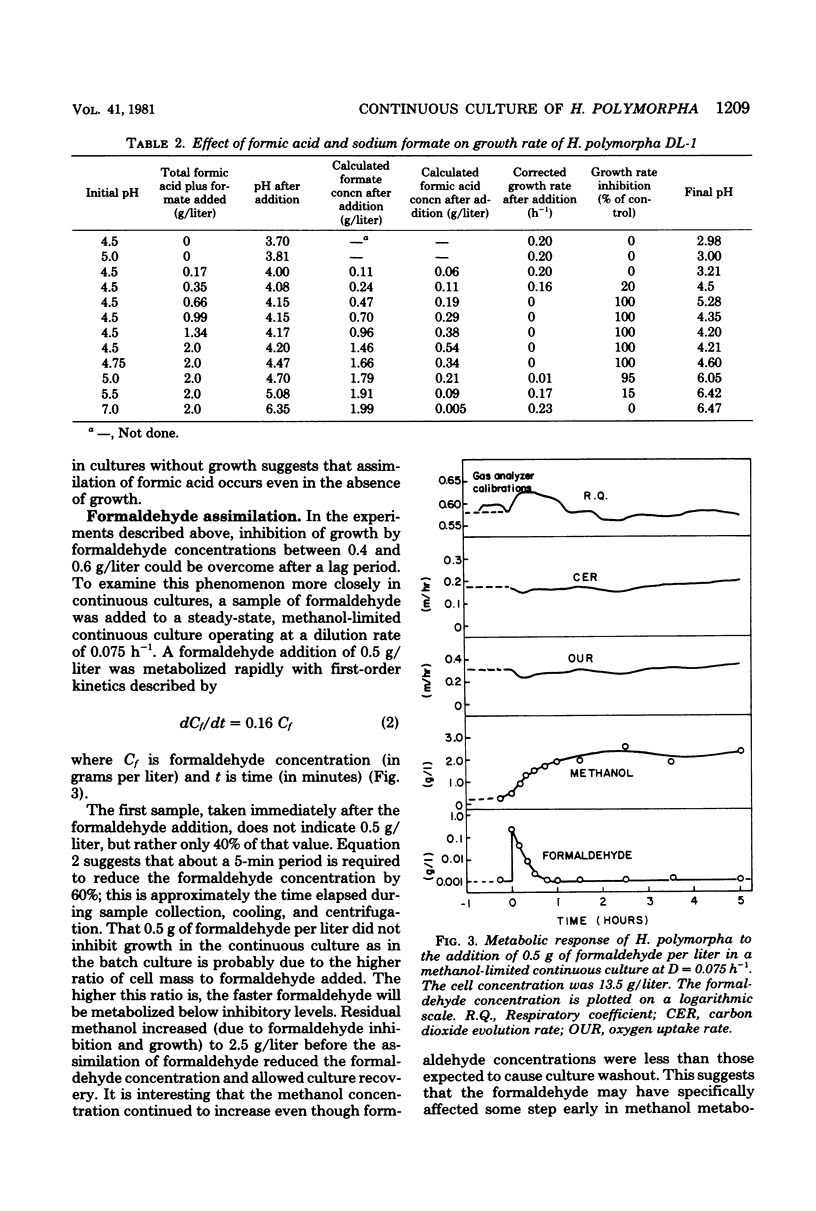
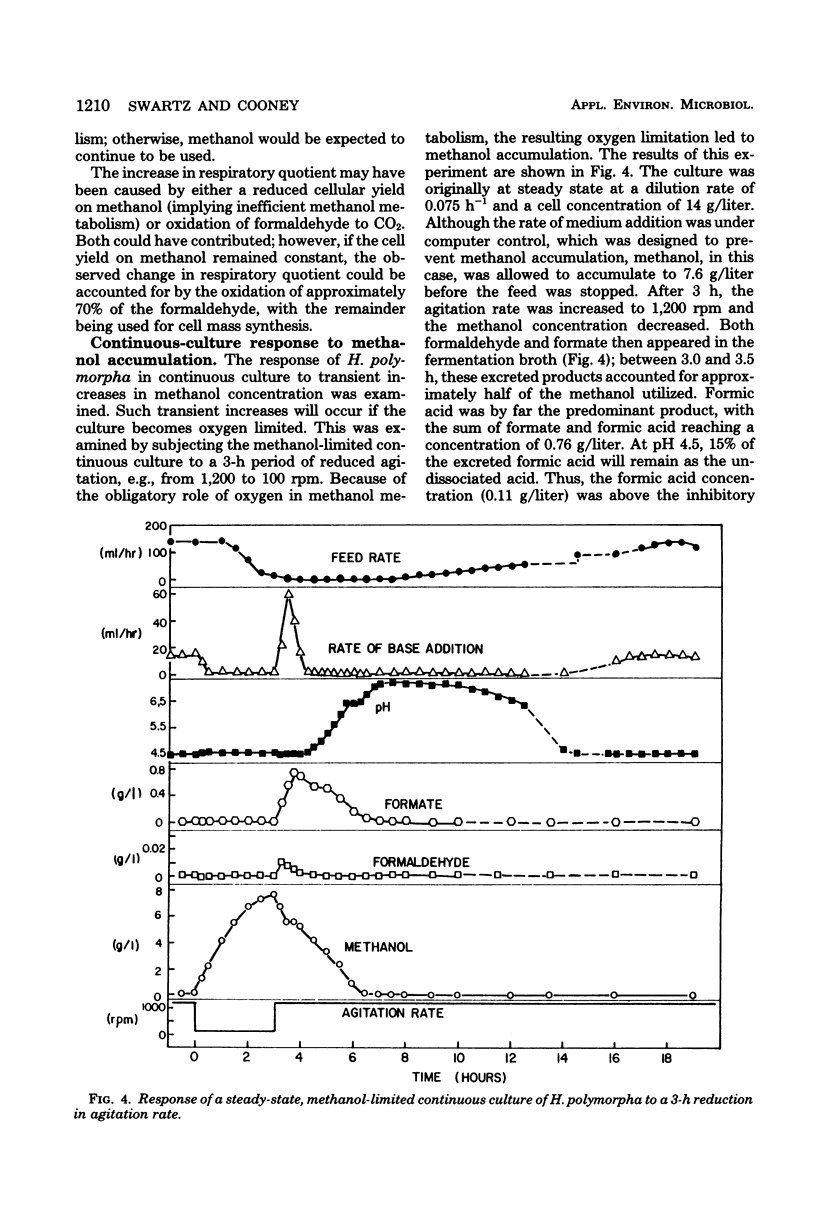
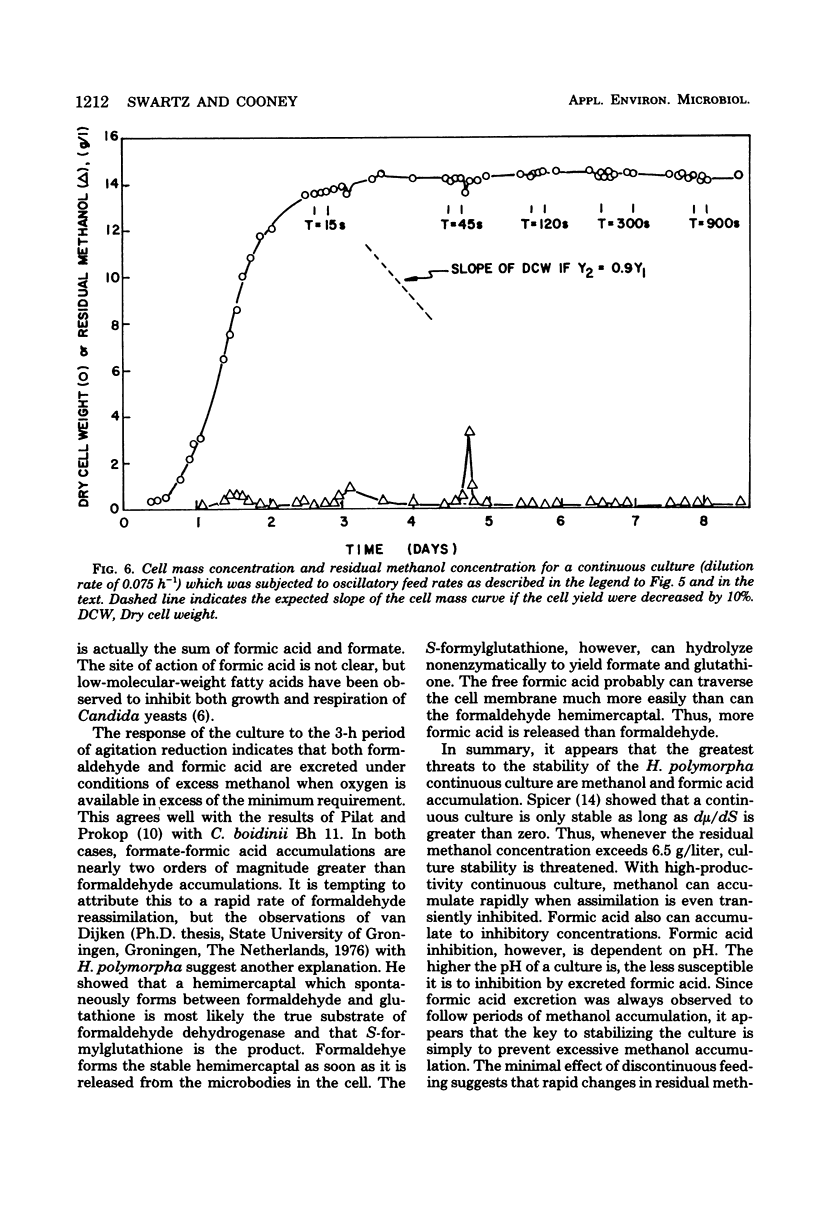
Growth inhibition of Hansenula polymorpha DL-1 by methanol, formaldehyde, formate, and formic acid was examined to determine the causes of unstable behavior observed during continuous cultures on methanol. The much greater inhibition of growth by formic acid than by formate and the effect of formic acid excretion and assimilation on pH helped to explain culture dynamics observed after transitory oxygen limitations. Oxygen limitation caused by temporary reduction of agitation in a continuous fermentation caused methanol to accumulate to inhibitory concentrations. Immediately after resumption of agitation, formic acid was produced and caused culture inhibition. To ensure the stability of H. polymorpha in continuous culture, it was therefore necessary to prevent transient methanol accumulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edwards V. H. The influence of high substrate concentrations on microbial kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Sep;12(5):679–712. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. S. Yeast production. Prog Ind Microbiol. 1971;10:129–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. W., Cooney C. L. Isolation and characterization of a thermotolerant methanol-utilizing yeast. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):982–990. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.982-990.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilát P., Prokop A. Oxidation of methanol, formaldehyde and formic acid by methanol-utilizing yeast. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1976;21(4):306–314. doi: 10.1007/BF02876908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilát P., Prokop A. The effect of methanol, formaldehyde, and formic acid on growth of Candida boidinii 11 Bh. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1975 Dec;17(12):1717–1728. doi: 10.1002/bit.260171203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


