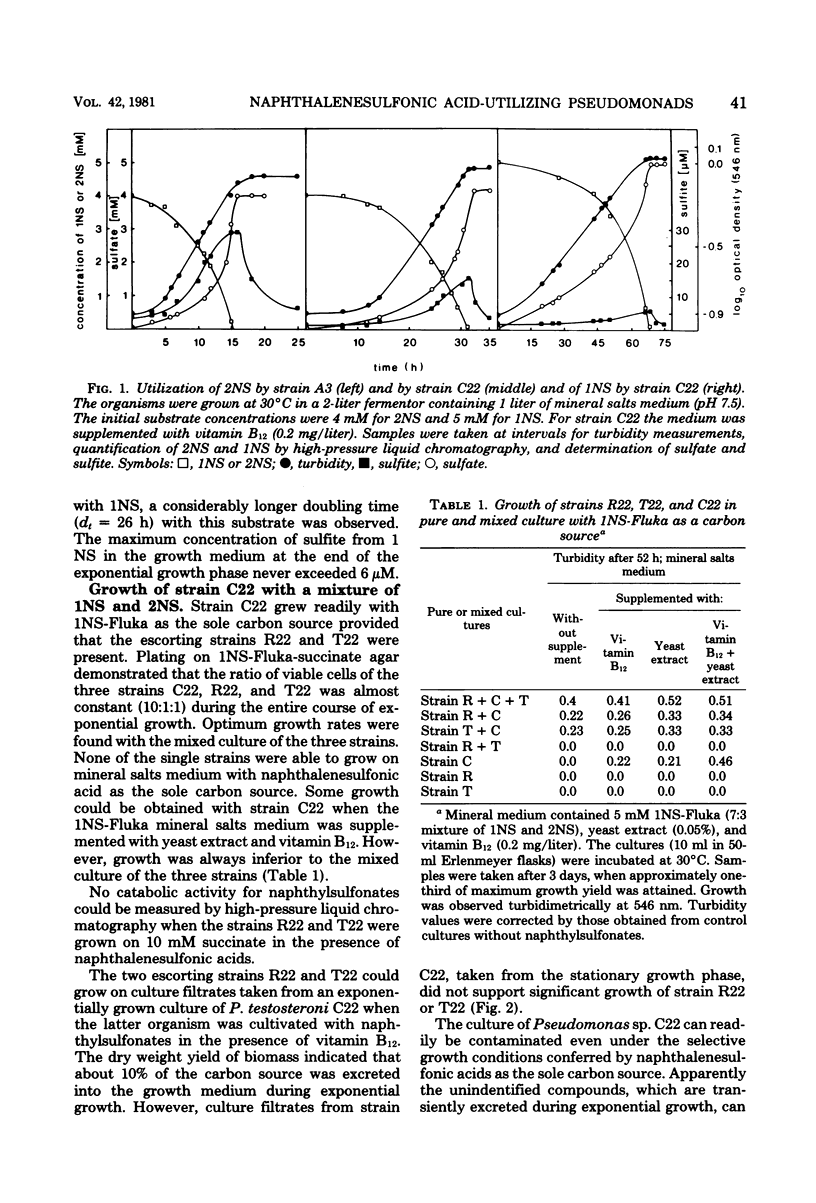
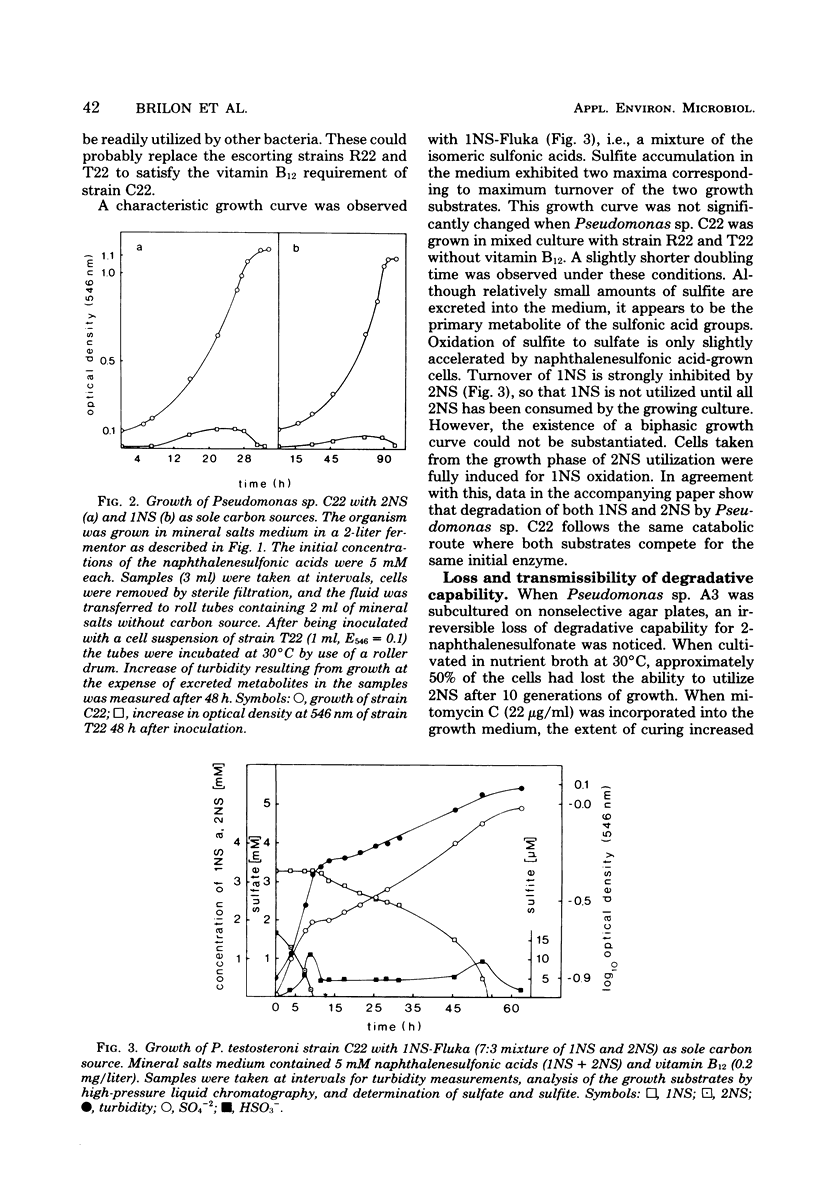
Abstract
Naphthalenesulfonate-degrading bacteria were obtained by continuous enrichment from a naphthalene-degrading population from sewage. In addition to naphthalene, Pseudomonas sp. A3 can utilize 2-naphthalenesulfonate (2NS) and Pseudomonas sp. C22 can utilize both 1-naphthalenesulfonate (1NS) and 2NS as sole carbon sources. In a mixture of 1NS and 2NS, the former substrate is utilized by strain C22 only after complete consumption of 2NS. During exponential growth, approximately 10% of the organic carbon of naphthalenesulfonates is temporarily excreted. These unidentified metabolites can readily be used by other bacteria, which, by supplying strain C22 with vitamins, allow optimal growth in stable mixed cultures. The degradative capability of Pseudomonas sp. A3 for 2NS was irreversibly lost under nonselective growth conditions and could be transferred from the wild type to a distinguishable cured strain of the wild type.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Knackmuss H. J. Catabolism of Naphthalenesulfonic Acids by Pseudomonas sp. A3 and Pseudomonas sp. C22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.44-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo K., Kondo H., Ishimoto M. Degradation of benzenesulfonate to sulfite in bacterial extract. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1397–1402. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. B., Murray K., Cain R. B. Microbial metabolism of aryl sulphonates a re-assessment of colorimetric methods for the determination of sulphite and their use in measuring desulphonation of aryl and alkylbenzene sulphonates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(4):493–511. doi: 10.1007/BF02565092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


