Abstract
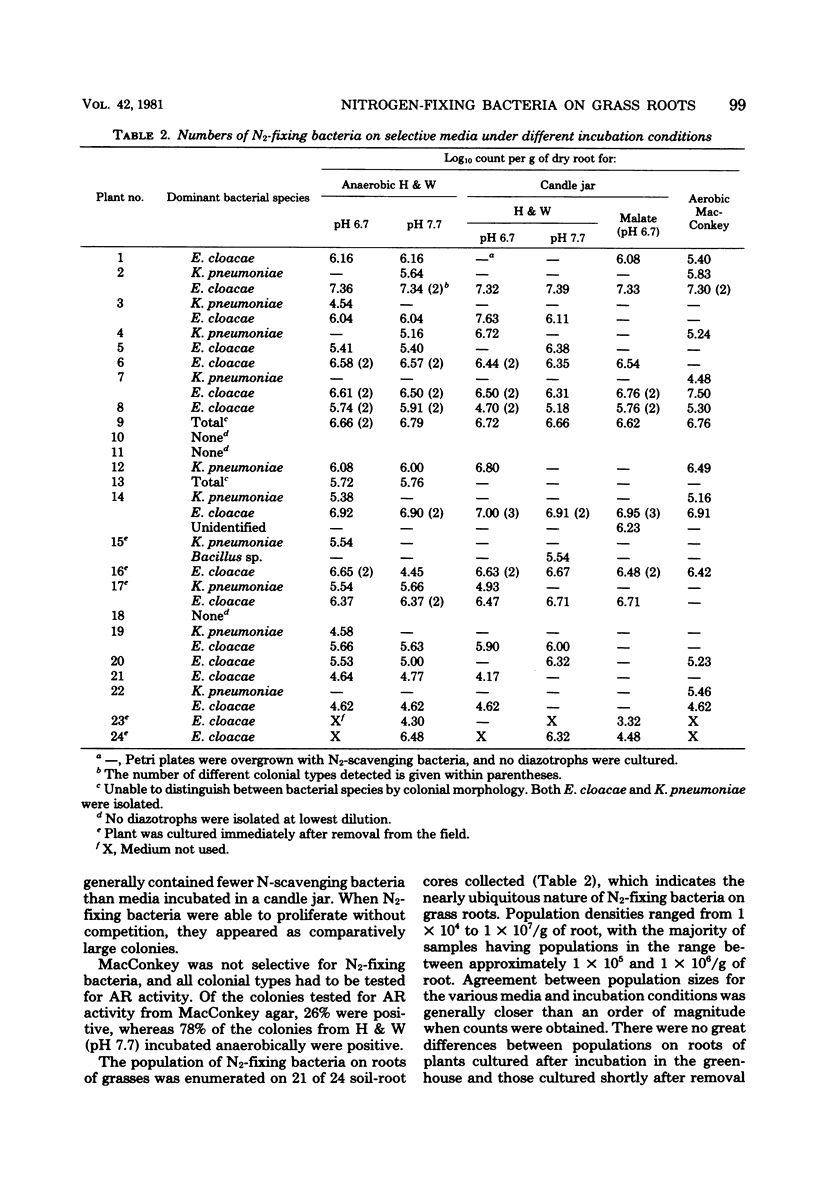
Root-soil cores were collected from forage grasses growing in a subtropical region of Texas and tested for acetylene reduction activity. The population density of nitrogen-fixing bacteria was measured, using various media and incubation conditions. Bacteria were confirmed as nitrogen fixing, using the acetylene reduction assay, and were classified according to standard biochemical and cultural methods. The majority of the nitrogen-fixing bacteria isolated from roots were Enterobacter cloacae or Klebsiella pneumoniae. Root-associated, nitrogen-fixing bacteria were isolated from 21 of 24 root-soil cores. The population densities of nitrogen-fixing bacteria ranged from approximately 104 to 3 × 107 per g of root. Population density on roots was significantly correlated with the rate of acetylene reduction but the relationship was not linear.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attebery H. R., Finegold S. M. A miniature anaerobic jar for tissue transport or for cultivation of anaerobes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;53(3):383–388. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber L. E., Tjepkema J. D., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Acetylene reduction (nitrogen fixation) associated with corn inoculated with Spirillum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.108-113.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINO S., WILSON P. W. Nitrogen fixation by a facultative bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):403–408. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.403-408.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson A. D., Barber L. E., Tjepkema J., Russell S. A., Powelson R., Evans H. J. Nitrogen fixation associated with grasses in Oregon. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):523–530. doi: 10.1139/m76-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okon Y., Albrecht S. L., Burris R. H. Methods for Growing Spirillum lipoferum and for Counting It in Pure Culture and in Association with Plants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):85–88. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.85-88.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen W. L., Chakrabarty K., Klucas R. V., Vidaver A. K. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) associated with roots of winter wheat and sorghum in Nebraska. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.129-135.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilsucki R. W., Clayton N. W., Cabelli V. J., Cohen P. S. Limitations of the Moeller lysine and ornithine decarboxylase tests. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):254–260. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.254-260.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju P. N., Evans H. J., Seidler R. J. An asymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacterium from the root environment of corn. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3474–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler M. E., Milam J. R., Smith R. L., Schank S. C., Zuberer D. A. Isolation of Azospirullum from diverse geographic regions. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):693–697. doi: 10.1139/m79-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe I., Barraquio W. L., De Guzman M. R., Cabrera D. A. Nitrogen-fixing (acetylene redution) activity and population of aerobic heterotrophic nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with wetland rice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):813–819. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.813-819.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. W., Kullmann E. D. A Statistical Inquiry into Methods for Estimating Numbers of Rhizobia. J Bacteriol. 1931 Jul;22(1):71–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.22.1.71-90.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


